|
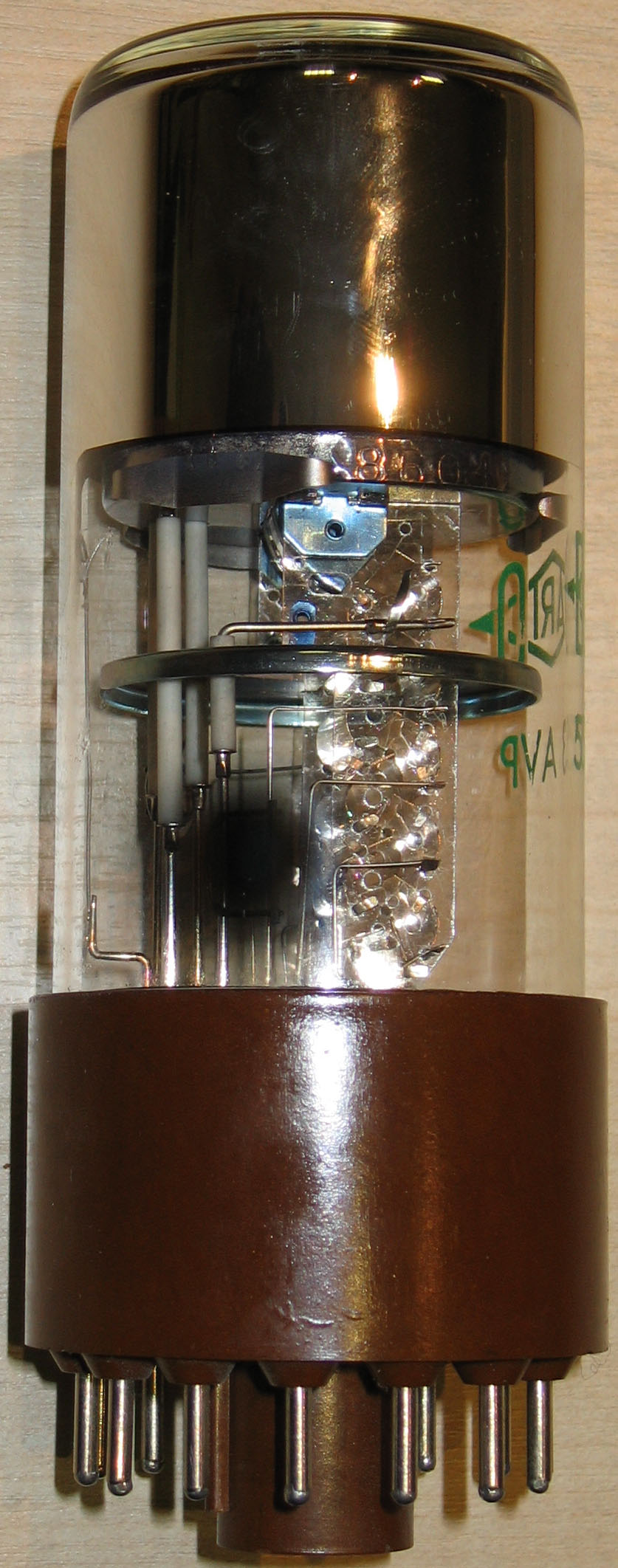
Electron Multiplier
An electron multiplier is a vacuum-tube structure that multiplies incident charges. In a process called secondary emission, a single electron can, when bombarded on secondary-emissive material, induce emission of roughly 1 to 3 electrons. If an electric potential is applied between this metal plate and yet another, the emitted electrons will accelerate to the next metal plate and induce secondary emission of still more electrons. This can be repeated a number of times, resulting in a large shower of electrons all collected by a metal anode, all having been triggered by just one. History In 1930, Russian physicist Leonid Aleksandrovitch Kubetsky proposed a device which used photocathodes combined with dynodes, or secondary electron emitters, in a single tube to remove secondary electrons by increasing the electric potential through the device. The electron multiplier can use any number of dynodes in total, which use a coefficient, σ, and created a gain of σn where n is the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
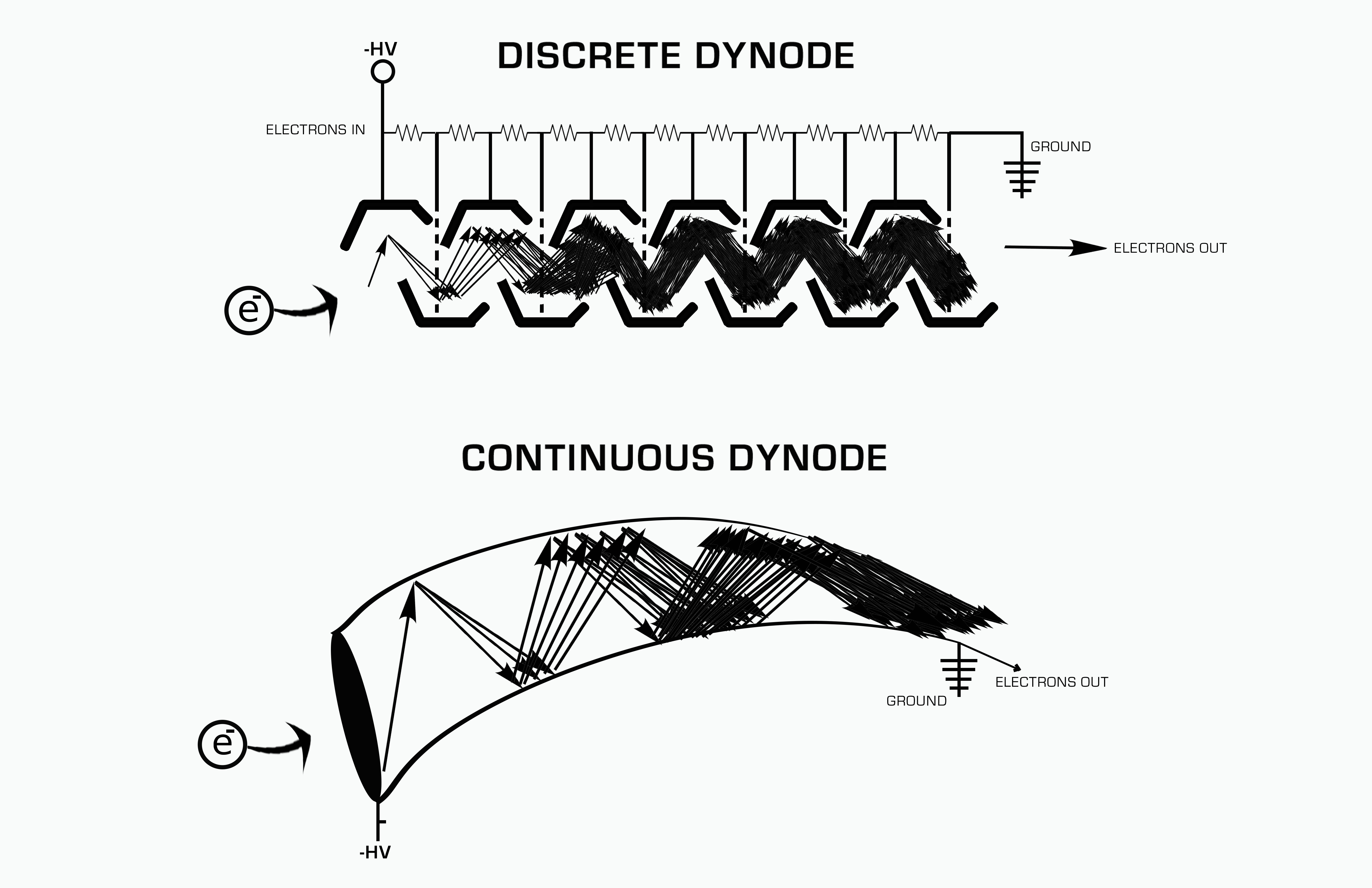
Discrete And Continuous Dynode Systems
Discrete may refer to: *Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory *Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit *Discrete group, a group with the discrete topology *Discrete category, category whose only arrows are identity arrows *Discrete mathematics, the study of structures without continuity *Discrete optimization, a branch of optimization in applied mathematics and computer science *Discrete probability distribution, a random variable that can be counted *Discrete space, a simple example of a topological space *Discrete spline interpolation, the discrete analog of ordinary spline interpolation *Discrete time, non-continuous time, which results in discrete-time samples *Discrete variable In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete if they are typically obtained by ''measuring'' or ''counting'', respectively. If it c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Cup
A Faraday cup is a metal (conductive) cup designed to catch charged particles in vacuum. The resulting current can be measured and used to determine the number of ions or electrons hitting the cup. The Faraday cup was named after Michael Faraday who first theorized ions around 1830. Examples of devices which use Faraday cups include space probes (Voyager 1, & 2, Parker Solar Probe, etc.) and mass spectrometers. Principle of operation When a beam or packet of ions hits the metallic body of the cup, the apparatus gains a small net charge while the ions are neutralized as the charge is transferred to the metal walls. The metal part can then be discharged to measure a small current proportional to the number of impinging ions. The Faraday cup is essentially part of a circuit where ions are the charge carriers in vacuum and it is the interface to the solid metal where electrons act as the charge carriers (as in most circuits). By measuring the electric current (the number of elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, per the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Electronics
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instruments
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments. Time In the past, a common time measuring instrument was the sundial. Today, the usual measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoltán Lajos Bay
Zoltán Lajos Bay (July 24, 1900 in Gyulavári – October 4, 1992 in Washington, D.C.)"Fizikai Szemle 1999/5 - Zsolt Bor: OPTICS BY HUNGARIANS" (with Zoltán Bay), József Attila University, Szeged, Hungary, 199KFKI-Hungary-Bor/ref> was a Hungarian physicist, professor, and engineer who developed technologies, including tungsten lamps and microwave devices. He was the leader of the second group to observe radar echoes from the Moon ( Moonbounce). From 1930, he worked at the University of Szeged as a professor of theoretical physics. In 1923 at Tungsram Ltd., a research laboratory was established for improving light sources, mainly electric bulbs. The head of that laboratory was Ignác Pfeifer, whose research staff included Zoltán Bay, along with Tivadar Millner, Imre Bródy, György Szigeti, Ernő Winter, and many others. György Szigeti worked together with Zoltán Bay on metal-vapor lamps and fluorescent light sources. They received a U.S. patent on "Electroluminesce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucas Cell
A Lucas cell is a type of scintillation counter. It is used to acquire a gas sample, filter out the radioactive particulates through a special filter and then count the radioactive decay. The inside of the gas chamber is coated with ZnS( Ag) - a chemical that emits light when struck by alpha particles. A photomultiplier tube at the top of the chamber counts the photons and sends the count to a data logger. Radon measurement A Lucas cell can be used to measure radon gas concentrations. Radon itself is an inert gas. Its danger lies in the fact that it undergoes radioactive decay. The radon decay products may lodge in the lungs and bombard them with alpha and beta particles, thus increasing the risk of lung cancer Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign .... See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillation Counter
A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the excitation effect of incident radiation on a scintillating material, and detecting the resultant light pulses. It consists of a scintillator which generates photons in response to incident radiation, a sensitive photodetector (usually a photomultiplier tube (PMT), a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera, or a photodiode), which converts the light to an electrical signal and electronics to process this signal. Scintillation counters are widely used in radiation protection, assay of radioactive materials and physics research because they can be made inexpensively yet with good quantum efficiency, and can measure both the intensity and the energy of incident radiation. History The first electronic scintillation counter was invented in 1944 by Sir Samuel Curran whilst he was working on the Manhattan Project at the University of California at Berkeley. There was a requirement to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo-multiplier Tube
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 108 (i.e., 160 dB),Decibels are power ratios. Power is proportional to I2 (current squared). Thus a current gain of 108 produces a power gain of 1016, or 160 dB in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. The combination of high gain, low noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in low light level spectroscopy, confocal microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, nuclear and particle physics, astronomy, medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototube
A phototube or photoelectric cell is a type of gas-filled or vacuum tube that is sensitive to light. Such a tube is more correctly called a 'photoemissive cell' to distinguish it from photovoltaic or photoconductive cells. Phototubes were previously more widely used but are now replaced in many applications by solid state photodetectors. The photomultiplier tube is one of the most sensitive light detectors, and is still widely used in physics research. Operating principles Phototubes operate according to the photoelectric effect: Incoming photons strike a photocathode, knocking electrons out of its surface, which are attracted to an anode. Thus current is dependent on the frequency and intensity of incoming photons. Unlike photomultiplier tubes, no amplification takes place, so the current through the device is typically of the order of a few microamperes. The light wavelength range over which the device is sensitive depends on the material used for the photoemissive cathod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daly Detector
A Daly detector is a gas-phase ion detector that consists of a metal "doorknob", a scintillator (phosphor screen) and a photomultiplier.N. R. DalyScintillation Type Mass Spectrometer ion Detector. ''Rev. Sci. Instrum.'' 31(3), 264–267 (1960). It was named after its inventor Norman Richard Daly. Daly detectors are typically used in mass spectrometers. Principle of operation Ions that hit the doorknob release secondary electrons. A high voltage (about ) between the doorknob and the scintillator accelerates the electrons onto the phosphor screen, where they are converted to photons. These photons are detected by the photomultiplier. The advantage of the Daly detector is that the photomultiplier can be separated by a window, which lets the photons through from the high vacuum of the mass spectrometer, thus preventing an otherwise possible contamination and extending life span of the detector. The Daly detector also allows a higher acceleration after the field-free region of a time- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




