|
Egon Mayer
Egon Mayer (19 August 1917 – 2 March 1944) was a Luftwaffe wing commander and fighter ace of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was credited with 102 enemy aircraft shot down in over 353 combat missions. His victories were all claimed over the Western Front and included 26 four-engine bombers, 51 Supermarine Spitfires and 12 P-47 Thunderbolts. Mayer was the first fighter pilot to score 100 victories entirely on the Western Front. Born in Konstanz, Mayer, volunteered for military service in the Luftwaffe of Nazi Germany in 1937. Following flight training he was posted to ''Jagdgeschwader'' 2 "Richthofen" (JG 2—2nd Fighter Wing) in 1939. He fought in the Battle of France and claimed his first aerial victory in that campaign on 13 June 1940. Mayer was appointed squadron leader of the 7. '' Staffel'' (7th squadron) of JG 2 in June 1941. Two months later, following his 21st aerial victory, he received the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 1 August 1941. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
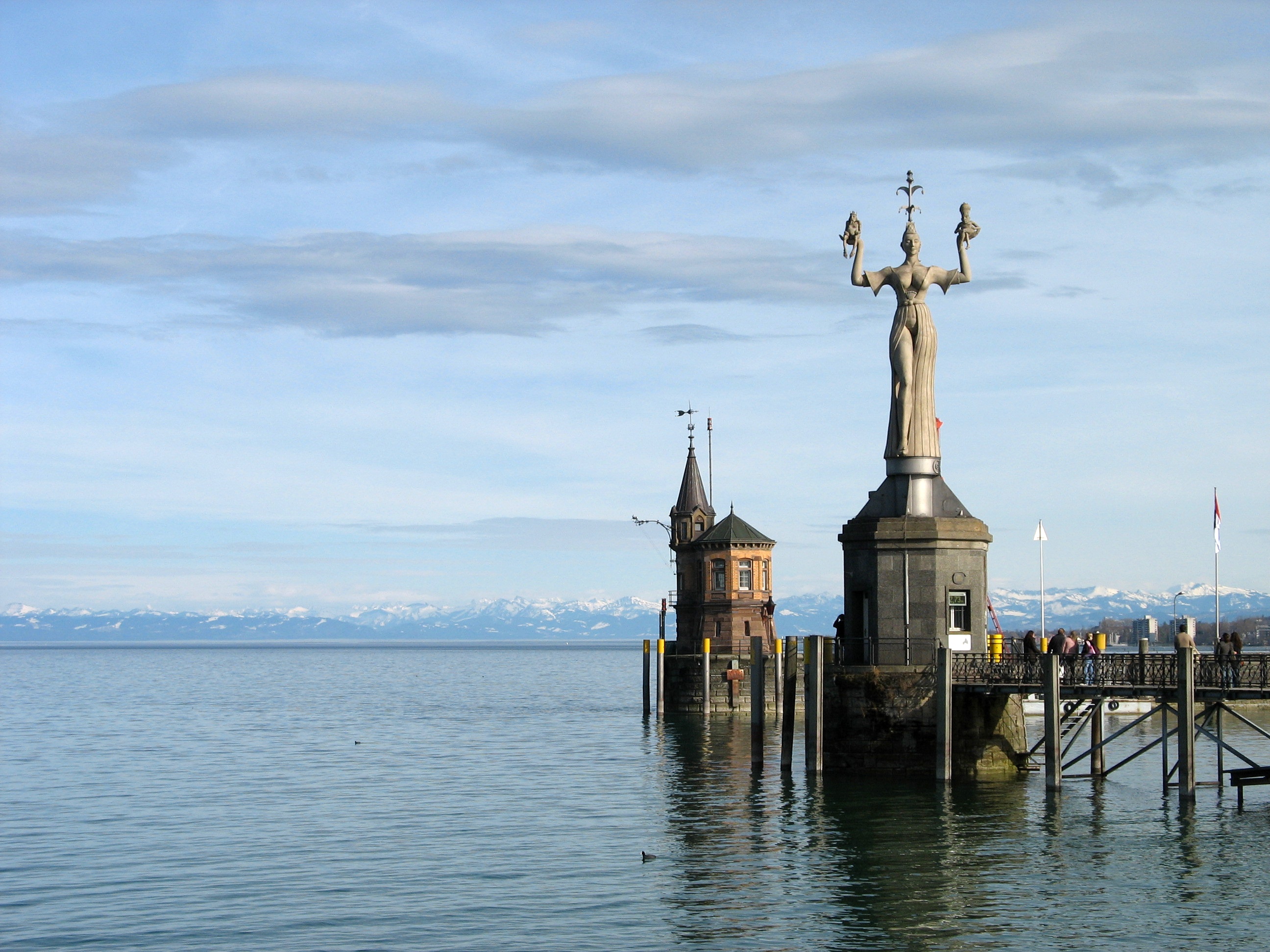
Konstanz
Konstanz (, , locally: ; also written as Constance in English) is a university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the south of Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was the residence of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Konstanz for more than 1,200 years. Location The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the Swiss Alps, passes through Lake Constance and leaves it, considerably larger, by flowing under a bridge connecting the two parts of the city. North of the river lies the larger part of the city with residential areas, industrial estates, and the University of Konstanz; while south of the river is the old town, which houses the administrative centre and shopping facilities in addition to the ''Hochschule'' or the ''University of Applied Sciences''. Car ferries provide access across Lake Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviator credited with shooting down five or more enemy aircraft during aerial combat. The exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ace is varied, but is usually considered to be five or more. The concept of the "ace" emerged in 1915 during World War I, at the same time as aerial dogfighting. It was a propaganda term intended to provide the home front with a cult of the hero in what was otherwise a war of attrition. The individual actions of aces were widely reported and the image was disseminated of the ace as a chivalrous knight reminiscent of a bygone era. For a brief early period when air-to-air combat was just being invented, the exceptionally skilled pilot could shape the battle in the skies. For most of the war, however, the image of the ace had little to do with the reality of air warfare, in which fighters fought in formation and air superiority depended heavily on the relative availabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Cross Of The Iron Cross With Oak Leaves
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The Knight's Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of military valour. Presentations were made to members of the three military branches of the : the (army), the (navy) and the (air force), as well as the , the Reich Labour Service and the (German People storm militia), along with personnel from other Axis powers. The award was instituted on 1 September 1939, at the onset of the German invasion of Poland. The award was created to replace the many older merit and bravery neck awards of the German Empire. A higher grade, the Oak Leaves to the Knight's Cross, was instituted in 1940. In 1941, two higher grades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
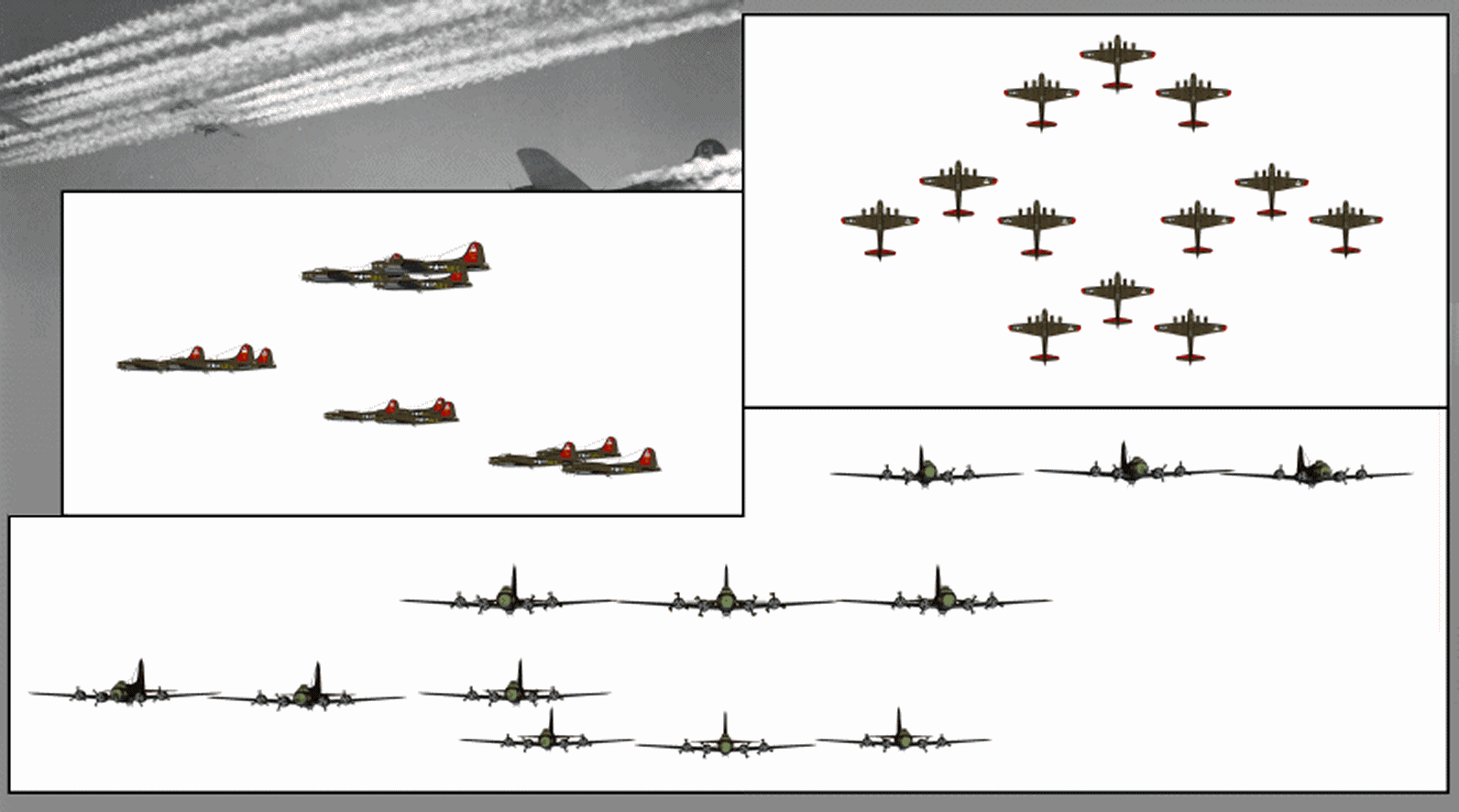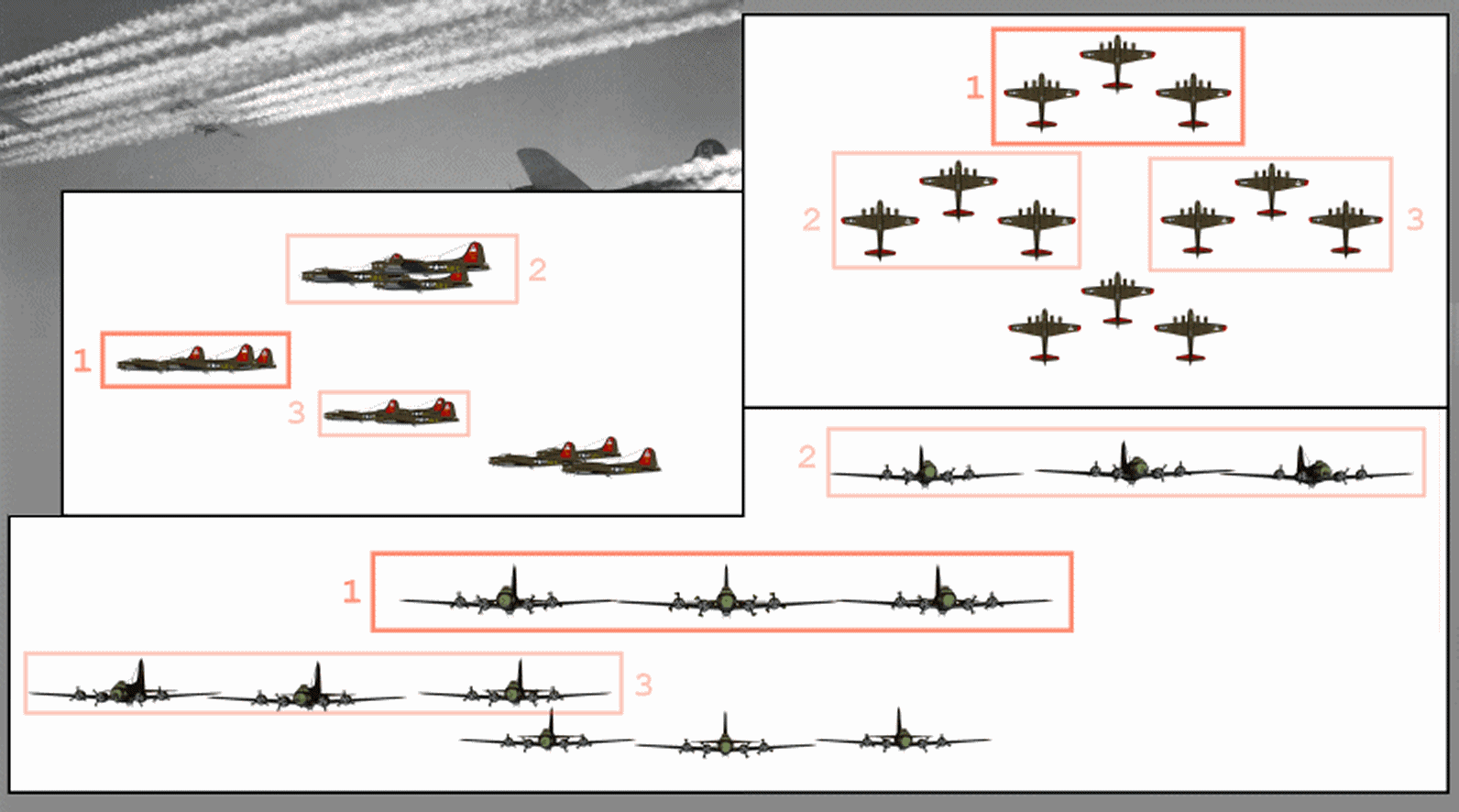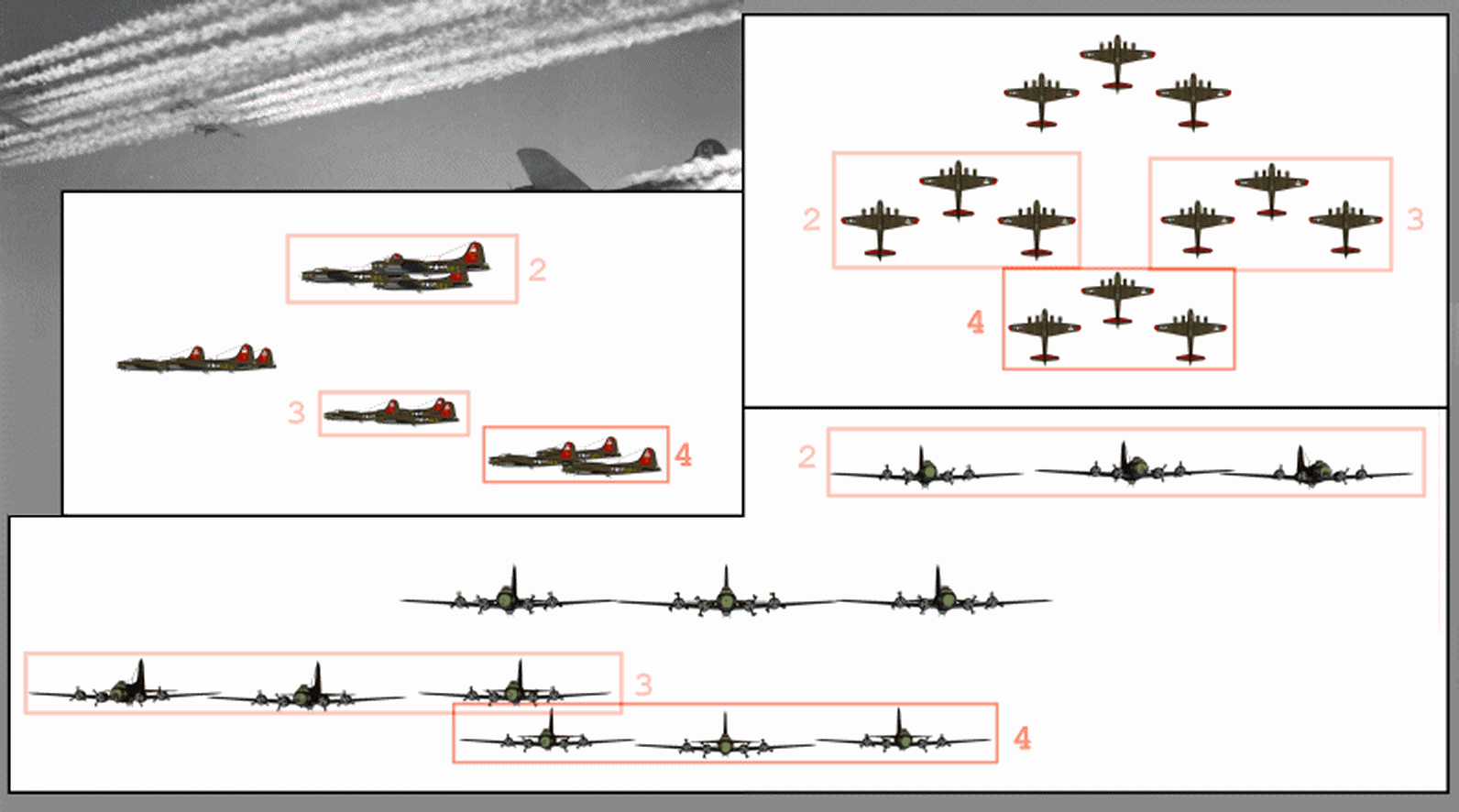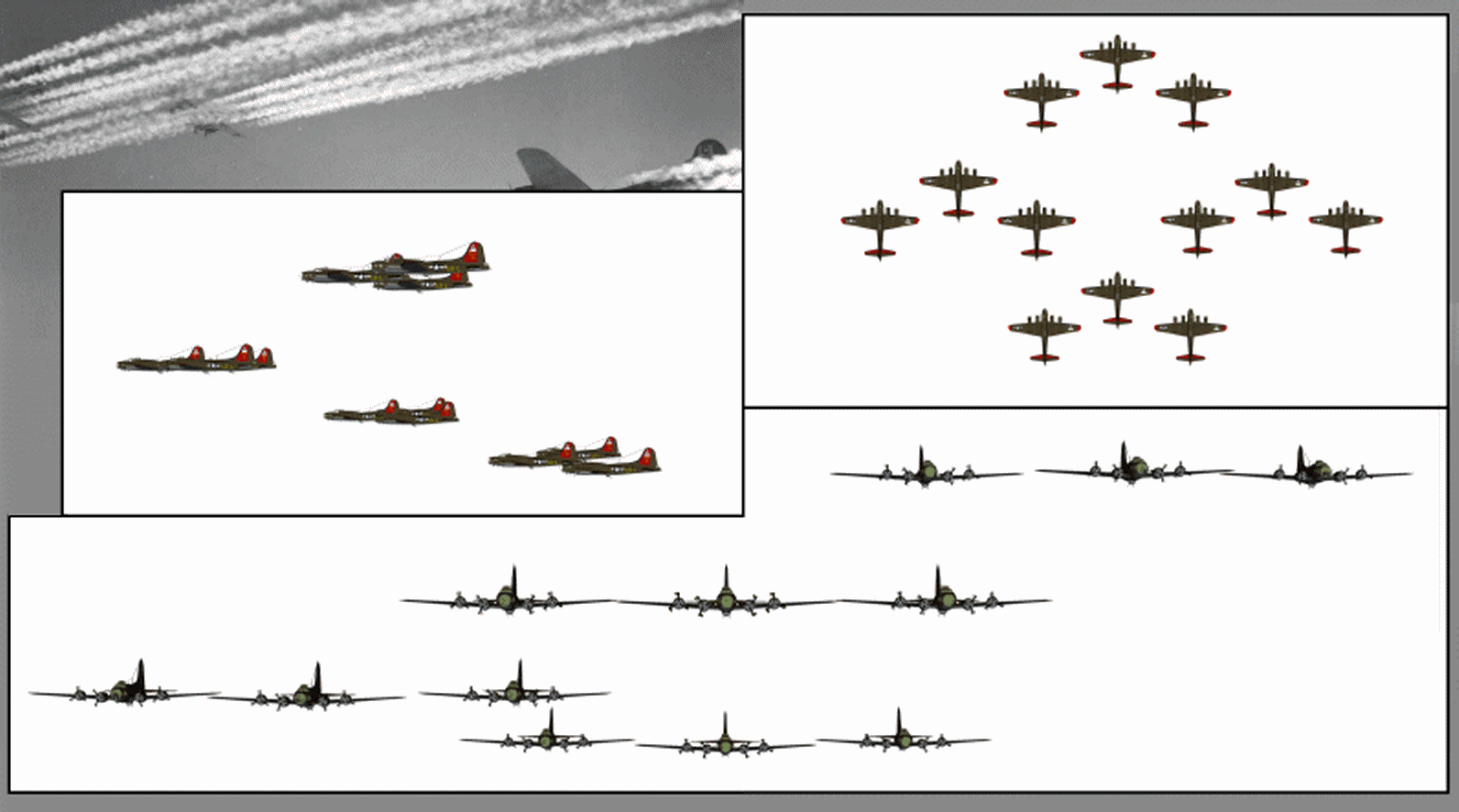
Combat Box
The combat box was a tactical formation used by heavy (strategic) bombers of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II. The combat box was also referred to as a "staggered formation". Its defensive purpose was in massing the firepower of the bombers' guns, while offensively it concentrated the release of bombs on a target. Initially formations were created in keeping with the pre-war Air Corps doctrine that massed bombers could attack and destroy targets in daylight without fighter escort, relying on interlocking fire from their defensive machine guns, almost exclusively the "light barrel" Browning AN/M2 .50 calibre (12.7 mm) gun. However the use of high altitudes by USAAF bombers resulted in factors that demanded a tighter bomb pattern and the combat box continued in use even after the advent of fighter escort – and especially starting in the spring of 1944 over Europe, with USAAF fighters flying far ahead of the combat boxes in air supremacy mode instead against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg-Peter Eder
Georg-Peter ''"Schorsch"'' Eder (8 March 1921 – 11 March 1986) was a German Luftwaffe military aviator and fighter ace during World War II. He is credited with 78 aerial victories achieved in 572 combat missions, including 150 combat missions with the Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighter. This figure includes 10 aerial victories on the Eastern Front, and further 68 victories over the Western Allies, including 36 four-engined bombers. Born in Oberdachstetten, Eder grew up in the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. He joined the military service in the Luftwaffe in 1939. Following flight training, he was posted to ''Jagdgeschwader'' 51 (JG 51—51st Fighter Wing) in late 1940. Flying with this wing, Eder claimed his first aerial victory on 22 June 1941, the first day of Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union. Following a ground accident in August 1941, he was assigned to a fighter pilot. In November 1942, Eder was posted to ''Jagdgeschwader'' 2 "R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-24 Liberator
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models designated as various LB-30s, in the Land Bomber design category. At its inception, the B-24 was a modern design featuring a highly efficient shoulder-mounted, high aspect ratio Davis wing. The wing gave the Liberator a high cruise speed, long range and the ability to carry a heavy bomb load. Early RAF Liberators were the first aircraft to cross the Atlantic Ocean as a matter of routine. In comparison with its contemporaries, the B-24 was relatively difficult to fly and had poor low-speed performance; it also had a lower ceiling and was less robust than the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress. While aircrews tended to prefer the B-17, General Staff favored the B-24 and procured it in huge numbers for a wide variety of roles. At approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater of Operations and dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during World War II. It is the third-most produced bomber of all time, behind the four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the multirole, twin-engined Junkers Ju 88. It was also employed as a transport, antisubmarine aircraft, drone controller, and search-and-rescue aircraft. In a USAAC competition, Boeing's prototype Model 299/XB-17 outperformed two other entries but crashed, losing the initial 200-bomber contract to the Douglas B-18 Bolo. Still, the Air Corps ordered 13 more B-17s for further evaluation, then introduced it into service in 1938. The B-17 evolved through numerous design advances but from its inception, the USAAC (later, the USAAF) promoted the aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II (1941–1945). It was created on 20 June 1941 as successor to the previous United States Army Air Corps and is the direct predecessor of the United States Air Force, today one of the six armed forces of the United States. The AAF was a component of the United States Army, which on 2 March 1942 was divided functionally by executive order into three autonomous forces: the Army Ground Forces, the United States Army Services of Supply (which in 1943 became the Army Service Forces), and the Army Air Forces. Each of these forces had a commanding general who reported directly to the Army Chief of Staff. The AAF administered all parts of military aviation formerly distributed among the Air Corps, General Headquarters Air Force, and the groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Cross
The War Order of the German Cross (german: Der Kriegsorden Deutsches Kreuz), normally abbreviated to the German Cross or ''Deutsches Kreuz'', was instituted by Adolf Hitler on 28 September 1941. It was awarded in two divisions: in gold for repeated acts of bravery or military leadership; and in silver for distinguished non-combat war service. The German Cross in Gold ranked higher than the Iron Cross First Class but below the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross, while the German Cross in Silver ranked higher than the War Merit Cross First Class with Swords but below the Knight's Cross of the War Merit Cross with Swords. Eligibility The German Cross was issued in two versions: gold and silver (the color of the laurel wreath around the swastika). The gold version was awarded to military personnel for repeated acts of bravery in combat, or of military leadership, with 6–8 acts as a rule of thumb. The silver version was awarded for multiple distinguished services in the war effort an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Cross Of The Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The Knight's Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of military valour. Presentations were made to members of the three military branches of the : the (army), the (navy) and the (air force), as well as the , the Reich Labour Service and the (German People storm militia), along with personnel from other Axis powers. The award was instituted on 1 September 1939, at the onset of the German invasion of Poland. The award was created to replace the many older merit and bravery neck awards of the German Empire. A higher grade, the Oak Leaves to the Knight's Cross, was instituted in 1940. In 1941, two higher grades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Of The Luftwaffe (1933–1945)
Between 1933 and 1945, the organization of the Luftwaffe underwent several changes. Originally, the German military high command, for their air warfare forces, decided to use an organizational structure similar to the army and navy, treating the aviation branch as a strategic weapon of war. Later on, during the period of rapid rearmament, the Luftwaffe was organized more in a geographical fashion. Under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles (1919), Germany was prohibited from having an air force, with the former German Empire's '' Luftstreitkräfte'' disbandment in 1920. German pilots were secretly trained for military aviation, first in the Soviet Union during the late 1920s, and then in Germany in the early 1930s. In Germany, the training was done under the guise of the German Air Sports Association (german: Deutscher Luftsportverband (DLV)) at the Central Commercial Pilots School (german: Zentrale der Verkehrs Fliegerschule (ZVF)). Following its 15 May 1933 formation in secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdgeschwader 2
Jagdgeschwader 2 (JG 2) "Richthofen" was a German fighter wing during World War II. JG 2 operated the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and Focke-Wulf Fw 190 single-seat, single-engine interceptor aircraft. Named after the famed World War I flying ace Manfred von Richthofen, the origins of the wing can be traced to 1934. Following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 which began World War II, JG 2 served protecting the German border with France during the Phoney War. On 10 May 1940 it served in the Battle of Belgium and Battle of France. Thereafter it fought in the Battle of Britain and then remained on the English Channel front until September 1944. Elements of JG 2 fought in the latter stages of the North African Campaign, notably in the Battle of Tunisia in 1942 and 1943. After the expulsion of German forces from France and Belgium following the Normandy landings, JG 2 served in the Defence of the Reich and fought on the Western Front, most notably at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |