|
Efficiency (economics)
In microeconomics, economic efficiency, depending on the context, is usually one of the following two related concepts: * Allocative or Pareto efficiency: any changes made to assist one person would harm another. * Productive efficiency: no additional output of one good can be obtained without decreasing the output of another good, and production proceeds at the lowest possible average total cost. These definitions are not equivalent: a market or other economic system may be allocatively but not productively efficient, or productively but not allocatively efficient. There are also other definitions and measures. All characterizations of economic efficiency are encompassed by the more general engineering concept that a system is efficient or optimal when it maximizes desired outputs (such as utility) given available inputs. Standards of thought There are two main standards of thought on economic efficiency, which respectively emphasize the distortions created by ''governments'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment and with national policies relating to these issues. Microeconomics also deal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
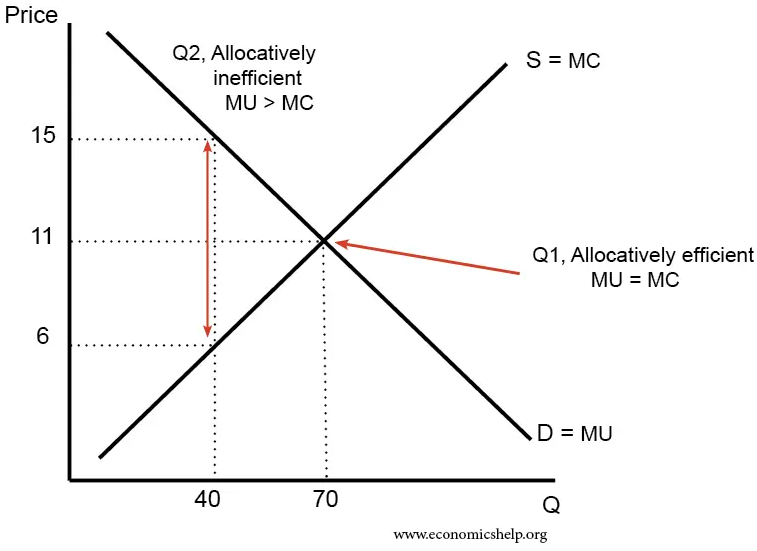
Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with consumer preferences; in particular, every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a marginal benefit to consumers equal to the marginal cost of producing. Description In contract theory, allocative efficiency is achieved in a contract in which the skill demanded by the offering party and the skill of the agreeing party are the same. Resource allocation efficiency includes two aspects: # At the macro aspect, it is the allocation efficiency of social resources, which is achieved through the economic system arrangements of the entire society. # The micro aspect is the use efficiency of resources, which can be understood as the production efficiency of the organization, which can be improved through innovation and progress within the organizations. Although there are different standards of evaluation for the concept of allocative efficiency, the basic principle ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
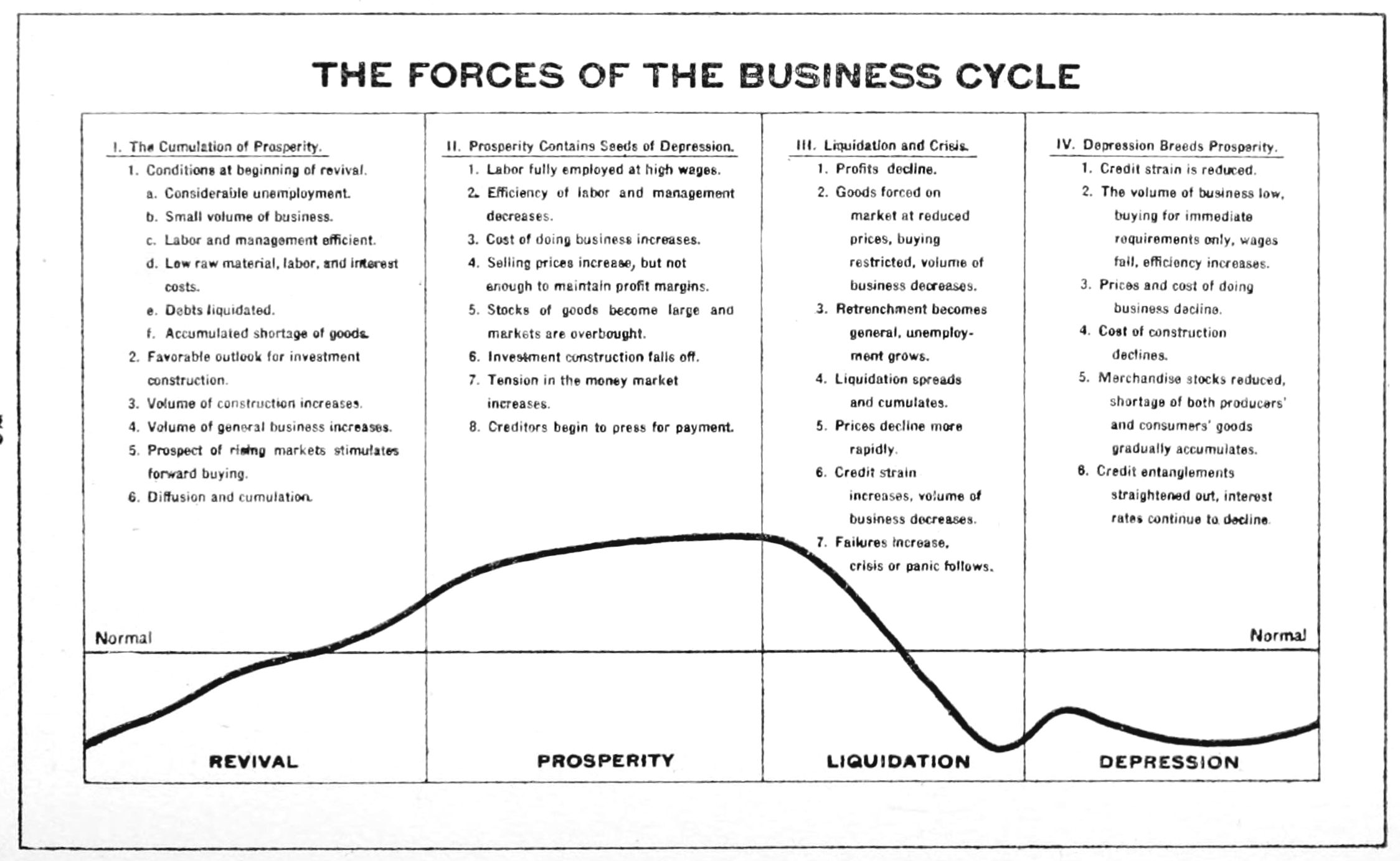
Economic Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often as an attempt to reduce inflation or the interest rate, to ensure price stability and general trust of the value and stability of the nation's currency. Monetary policy is a modification of the supply of money, i.e. "printing" more money, or decreasing the money supply by changing interest rates or removing excess reserves. This is in contrast to fiscal policy, which relies on taxation, government spending, and government borrowing as methods for a government to manage business cycle phenomena such as recessions. Further purposes of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to the stability of gross domestic product, to achieve and maintain low unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies. Monetary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection (taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation (which is considered "healthy" at the level in the range 2%–3%) and to increase employment. Additionally, it is designed to try to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Anderton
Alain G. Anderton is an author of business studies and economics textbooks for use in secondary education in the U.K. He has written GCSE and A-level The A-Level (Advanced Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational aut ... Economics textbooks (''Economics for GCSE'' and ''Economics'' respectively), as well as a book on business studies. References Living people Year of birth missing (living people) British economics writers British textbook writers British business writers {{UK-nonfiction-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers are unimpeded by price controls or restrictions on contract freedom. The major characteristic of a market economy is the existence of factor markets that play a dominant role in the allocation of capital and the factors of production. Market economies range from minimally regulated free-market and ''laissez-faire'' systems where state activity is restricted to providing public goods and services and safeguarding private ownership, to interventionist forms where the government plays an active role in serving special interests and promoting social welfare. State intervention can happen at the production, distribution, trade and consumption areas in the economy. The distribution of basic need services and goods like health care may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Curve
In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible level of production, and the result is a cost curve. Profit-maximizing firms use cost curves to decide output quantities. There are various types of cost curves, all related to each other, including total and average cost curves; marginal ("for each additional unit") cost curves, which are equal to the differential of the total cost curves; and variable cost curves. Some are applicable to the short run, others to the long run. Notation There are standard acronyms for each cost concept, expressed in terms of the following descriptors: *SR = short-run (when the amount of physical capital cannot be adjusted) *LR = long-run (when all input amounts can be adjusted) *A = average (per unit of output) *M = marginal (for an additional unit of outp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a Market (economics), market will reach an Economic equilibrium, equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every Goods and services, product or service, including Workforce, labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum. Perfect competition provides both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency: * Such markets are ''allocatively efficient'', as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any Profit maximization, profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-run Equilibrium
In economics, the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. More specifically, in microeconomics there are no fixed factors of production in the long-run, and there is enough time for adjustment so that there are no constraints preventing changing the output level by changing the capital stock or by entering or leaving an industry. This contrasts with the short-run, where some factors are variable (dependent on the quantity produced) and others are fixed (paid once), constraining entry or exit from an industry. In macroeconomics, the long-run is the period when the general price level, contractual wage rates, and expectations adjust fully to the state of the economy, in contrast to the short-run when these variables may not fully adjust. History The diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." Having a business name does not separate the business entity from the owner, which means that the owner of the business is responsible and liable for debts incurred by the business. If the business acquires debts, the creditors can go after the owner's personal possessions. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. The term is also often used colloquially (but not by lawyers or by public officials) to refer to a company, such as a corporation or cooperative. Corporations, in contrast with Sole proprietorship, sole proprietors and partnerships, are a separate legal entity and provide limited liability for their owners/members, as well as being su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarcity
In economics, scarcity "refers to the basic fact of life that there exists only a finite amount of human and nonhuman resources which the best technical knowledge is capable of using to produce only limited maximum amounts of each economic good."Samuelson, P. Anthony., Samuelson, W. (1980). Economics. 11th ed. / New York: McGraw-Hill. If the conditions of scarcity didn't exist and an "infinite amount of every good could be produced or human wants fully satisfied ... there would be no economic goods, i.e. goods that are relatively scarce..." Scarcity is the limited availability of a commodity, which may be in demand in the market or by the commons. Scarcity also includes an individual's lack of resources to buy commodities. The opposite of scarcity is abundance. Scarcity plays a key role in economic theory, and it is essential for a "proper definition of economics itself."Montani G. (1987) Scarcity. In: Palgrave Macmillan (eds) ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics''. Palgrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpeg)