|
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships among living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment; life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium."Biosphere" in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. By the most general [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or more or less. Bacteria allows for the cycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen and sulphur. The community begins with relatively few pioneering plants and animals and develops through increasing complexity until it becomes stable or self-perpetuating as a climax community. The "engine" of succession, the cause of ecosystem change, is the impact of established organisms upon their own environments. A consequence of living is the sometimes subtle and sometimes overt alteration of one's own environment. Succession is a process by which an ecological community undergoes more or less orderly and predictable changes following a disturbance or the initial colonization of a new habitat. Succession may be initiated either by formation of new, unoccupied habitat, such as from a lava flow or a severe lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by change in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations that interlock with those of the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass (ecology)
The biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Biomass can refer to ''species biomass'', which is the mass of one or more species, or to ''community biomass'', which is the mass of all species in the community. It can include microorganisms, plants or animals. The mass can be expressed as the average mass per unit area, or as the total mass in the community. How biomass is measured depends on why it is being measured. Sometimes, the biomass is regarded as the natural mass of organisms ''in situ'', just as they are. For example, in a salmon fishery, the salmon biomass might be regarded as the total wet weight the salmon would have if they were taken out of the water. In other contexts, biomass can be measured in terms of the dried organic mass, so perhaps only 30% of the actual weight might count, the rest being water. For other purposes, only biological tissues count, and teeth, bones and shells are excluded. In some appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
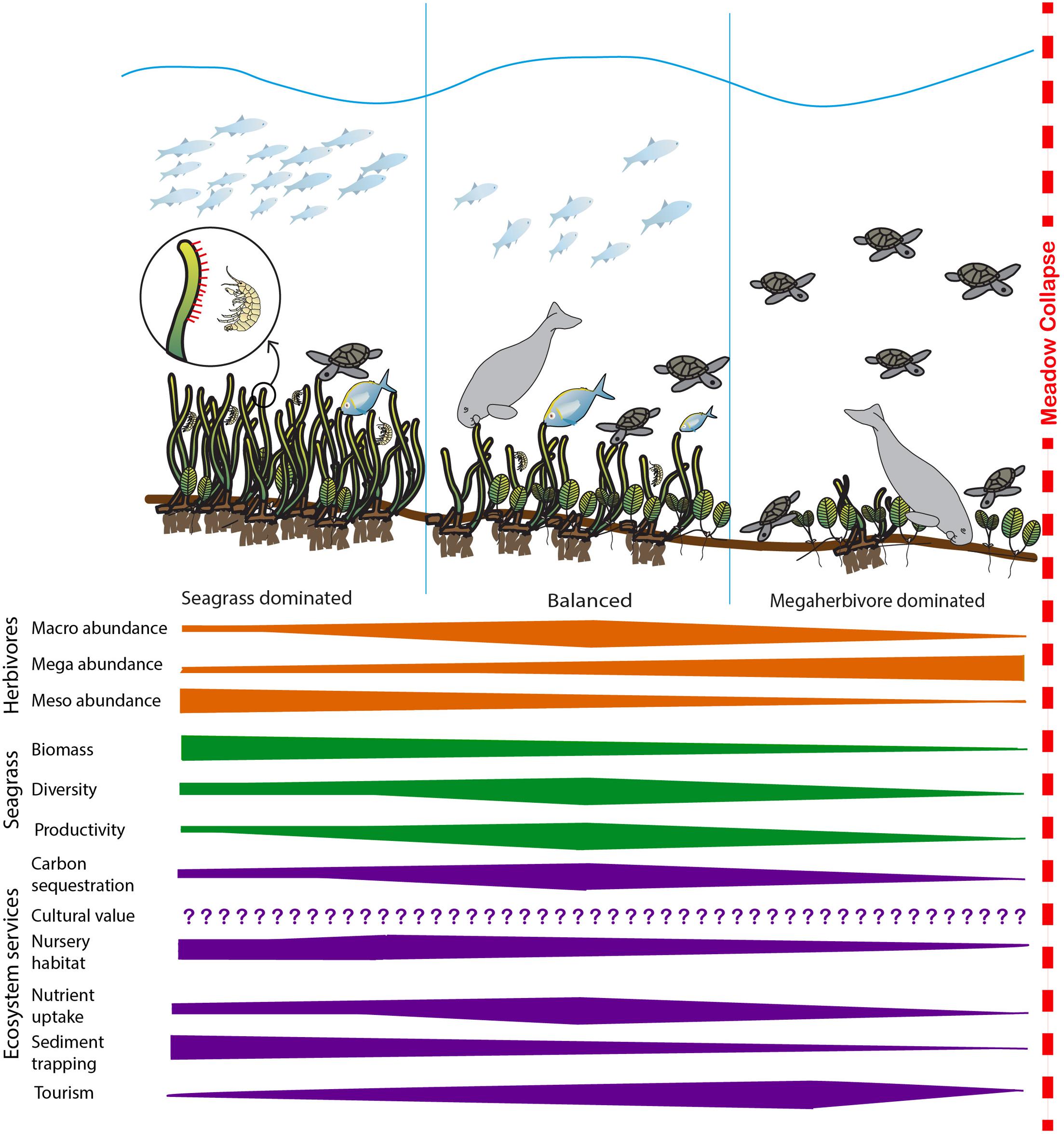
Abundance (ecology)
In ecology, local abundance is the relative representation of a species in a particular ecosystem. It is usually measured as the number of individuals found per sample. The ratio of abundance of one species to one or multiple other species living in an ecosystem is referred to as relative species abundances. Both indicators are relevant for computing biodiversity. A variety of sampling methods are used to measure abundance. For larger animals, these may include spotlight counts, track counts and roadkill counts, as well as presence at monitoring stations. In many plant communities the abundances of plant species are measured by plant cover, i.e. the relative area covered by different plant species in a small plot. Abundance is in simplest terms usually measured by identifying and counting every individual of every species in a given sector. It is common for the distribution of species to be skewed so that a few species take up the bulk of individuals collected. Relative species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmentalism
Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the impact of changes to the environment on humans, animals, plants and non-living matter. While environmentalism focuses more on the environmental and nature-related aspects of green ideology and politics, ecologism combines the ideology of social ecology and environmentalism. ''Ecologism'' is more commonly used in continental European languages, while ''environmentalism'' is more commonly used in English but the words have slightly different connotations. Environmentalism advocates the preservation, restoration and improvement of the natural environment and critical earth system elements or processes such as the climate, and may be referred to as a movement to control pollution or protect plant and animal diversity. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethology
Ethology is the scientific study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait. Behaviourism as a term also describes the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, usually referring to measured responses to stimuli or to trained behavioural responses in a laboratory context, without a particular emphasis on evolutionary adaptivity. Throughout history, different naturalists have studied aspects of animal behaviour. Ethology has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Charles O. Whitman, Oskar Heinroth, and Wallace Craig. The modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, the three recipients of the 1973 Nobel Prize in Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |