|
East Island (Tasmania)
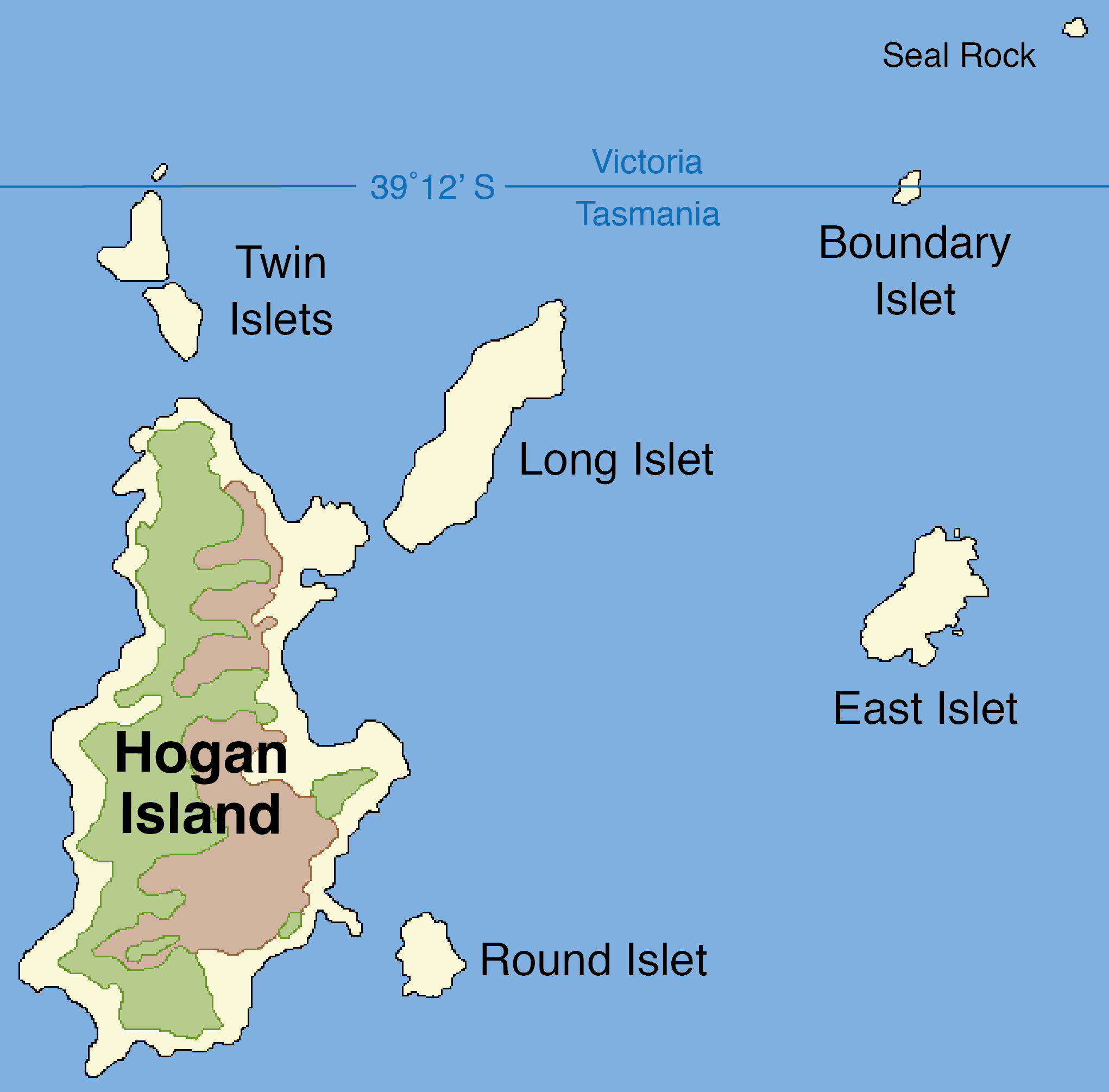
East Island is a granite island, with an area of 12.42 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Hogan Group, lying in northern Bass Strait between the Furneaux Group and Wilsons Promontory in Victoria. Fauna Recorded breeding seabird and wader species include little penguin, short-tailed shearwater, fairy prion, common diving petrel, Pacific gull and sooty oystercatcher. Reptiles present include White's skink and metallic skink.Brothers, Nigel; Pemberton, David; Pryor, Helen; & Halley, Vanessa. (2001). ''Tasmania’s Offshore Islands: seabirds and other natural features''. Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery: Hobart. Wrecks * Daphne (brig) in 1818. See also * List of islands of Tasmania Tasmania is the smallest and southernmost state of Australia. The Tasmanian mainland itself is an island, with an area of - 94.1% of the total land area of the state. The other islands have a combined area of , for a cumulative total of 99.75% o ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hogan Island Map
A hogan ( or ; from Navajo ' ) is the primary, traditional dwelling of the Navajo people. Other traditional structures include the summer shelter, the underground home, and the sweat house. A hogan can be round, cone-shaped, multi-sided, or square; with or without internal posts; timber or stone walls and packed with earth in varying amounts or a bark roof for a summer house, with the door facing east to welcome the rising sun for wealth and good fortune. Today, while some older hogans are now still used as dwellings and others are maintained for ceremonial purposes, new hogans are rarely intended as family dwellings. Traditional structured hogans are also considered pioneers of energy efficient homes. Using packed mud against the entire wood structure, the home was kept cool by natural air ventilation and water sprinkled on the dirt ground inside. During the winter the fireplace kept the inside warm well into the night. This concept is called thermal mass. Modern application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Penguin
The little penguin (''Eudyptula minor'') is a species of penguin from New Zealand. They are commonly known as little blue penguins or blue penguins owing to their slate-blue plumage and are also known by their Māori name . The Australian little penguin (''Eudyptula novaehollandiae'') from Australia and the Otago region of New Zealand is considered a separate species by a 2016 study and a 2019 study. Taxonomy The little penguin was first described by German naturalist Johann Reinhold Forster in 1781. Several subspecies are known, but a precise classification of these is still a matter of dispute. The holotypes of the subspecies ''E. m. variabilis'' and ''Eudyptula minor chathamensis'' are in the collection of the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. The white-flippered penguin (''E. m. albosignata'' or ''E. m. minor morpha albosignata'') is currently considered by most taxonomists to be a colour morph or subspecies of ''Eudyptula minor.'' In 2008, Shirihai treated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphne (brig)
''Daphne'' was a brig constructed in Java that arrived in Australia in 1814. She was wrecked without loss of life on 26 October 1819 in the Kent Group in Bass Strait. She was on a voyage from Port Jackson to India. On August 1819, ''Daphne'', Captain Howard, sailed from Hobart for Port Jackson with wheat and potatoes. ''Daphne'' departed Sydney bound for India on 10 October 1819 under the command of John Howard. As she passed through Bass Strait he stopped at several islands to purchase sealskins from sealers in the area. On 26 October a gale rose and Howard sheltered in the lee of East Island. Howard went ashore, probably to find sealers. On arriving on shore he noticed that ''Daphne'' was being driven towards the rocks. He returned on board but could do little to save the brig. He therefore ordered the passengers and crew to abandon ship. The passengers made it to shore safely but ''Daphne'' was totally destroyed. The longboat was badly damaged and it took Howard and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Skink
:''"Metallic skink" may also refer to the garden skink (Lampropholis delicata)''. ''Carinascincus metallicus'', the metallic cool-skink or metallic skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to Australia, found in southern Victoria, as well as in Tasmania where it is the most widespread and common lizard, occurring on many offshore islands in Bass Strait Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterwa ... as well as the mainland. It gives birth to live young. It is highly variable in colour and pattern, and may be a complex of closely related species.Cogger, H.G. (1979). ''Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia''. Reed: Sydney. References Carinascincus Skinks of Australia Endemic fauna of Australia Reptiles described in 1874 Taxa named by Arthu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White's Skink
White's skink (''Liopholis whitii)'', also known commonly as White's rock skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia. Etymology The specific name, ''whitii'', is in honour of Irish surgeon and naturalist John White. Geographic range ''L. whitii'' is widespread in south-eastern Australia, including Tasmania and many Bass Strait islands. Habitat The preferred natural habitats of ''L. whitii'' are forest, shrubland, and rocky areas, at altitudes from sea level to . White's skinks prefer a habitat with rocks, shrubby heathland and minimal human environmental disturbance. They also dig tunnels underground and have two entrances to the tunnel if needing an escape route. They also have well covered and hidden entrances to avoid predators. Description The White's skink is a stocky slow-growing medium-sized species, growing to a maximum snout-to-vent length (SVL) of about . That matures at ~ (SVL) in both sexes, this size is typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sooty Oystercatcher
The sooty oystercatcher (''Haematopus fuliginosus'') is a species of oystercatcher. It is a wading bird endemic to Australia and commonly found on its coastline. It prefers rocky coastlines, but will occasionally live in estuaries. All of its feathers are black. It has a red eye, eye ring and bill, and pink legs. Taxonomy John Gould described the sooty oystercatcher in 1845. Its species name is the Latin adjective ''fuliginosus'', "sooty". Two subspecies are recognised, the nominate from the coastline of southern Australia and subspecies ''ophthalmicus'' from northern Australia. The southern subspecies is larger and heavier than the northern. The northern one, with a more yellowish eye ring, is found from the Kimberleys across the top of the country to Mackay in central Queensland. There is considerable overlap, as the southern subspecies has been found up to Cape York. Subspecies ''ophthalmicus'' has been thought distinctive enough to warrant species status and needs further inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Gull
The Pacific gull (''Larus pacificus'') is a very large gull, native to the coasts of Australia. It is moderately common between Carnarvon in the west, and Sydney in the east, although it has become scarce in some parts of the south-east, as a result of competition from the kelp gull, which has "self-introduced" since the 1940s. Much larger than the ubiquitous silver gull, and nowhere near as common, Pacific gulls are usually seen alone or in pairs, loafing around the shoreline, steadily patrolling high above the edge of the water, or (sometimes) zooming high on the breeze to drop a shellfish or sea urchin onto rocks. Diet The gulls' diet consists of a number various fish species and invertebrates. They frequently consume crabs, most often the species ''Ovalipes australiensis'' and ''Paragrapsus gaimardii.'' They also commonly eat '' Platycephalus bassensis'' (sand flatheads) and cephalapods, both of which are sourced from their regular consumption of waste from fish which hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Diving Petrel
The common diving petrel (''Pelecanoides urinatrix''), also known as the smaller diving petrel or simply the diving petrel, is a diving petrel, one of four very similar auk-like small petrels of the southern oceans. It is native to South Atlantic islands and islands of the subantarctic southern Indian Ocean, islands and islets off New Zealand and south-eastern Australian islands. Taxonomy The common diving petrel was formally described in 1788 by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin. He placed it with the other petrels in the genus ''Procellaria'' and coined the binomial name ''Procellaria uriatrix''. Gmelin based his description on the "diving petrel" that had been described in 1785 by the English ornithologist John Latham in the second volume of his ''A General Synopsis of Birds''. Latham reported that they were found in great numbers in Queen Charlotte Sound at the northern end of South Island, New Zealand. The common diving petrel is now one of four petrels p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy Prion
The fairy prion (''Pachyptila turtur'') is a small seabird with the standard prion plumage of blue-grey upperparts with a prominent dark "M" marking and white underneath. The sexes are alike. This is a small prion of the low subantarctic and subtropic seas. Taxonomy The fairy prion was formally described in 1820 by the German naturalist Heinrich Kuhl under the binomial name ''Procellaria turtur''. It is now placed with the other prions in the genus ''Pachyptila'' that was introduced in 1811 by Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''pakhus '' meaning "dense" or "thick" with ''ptilon'' meaning "feather" or "plumage". The specific epithet ''turtur'' is Latin for "turtle dove". The word comes from the Ancient Greek word meaning "a saw", which is in reference to its serrated edges of its bill.Gotch, A. T. (1995) The fairy prion is a member of the genus ''Pachyptila'', and along with the blue petrel makes up the prions. They in turn are members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
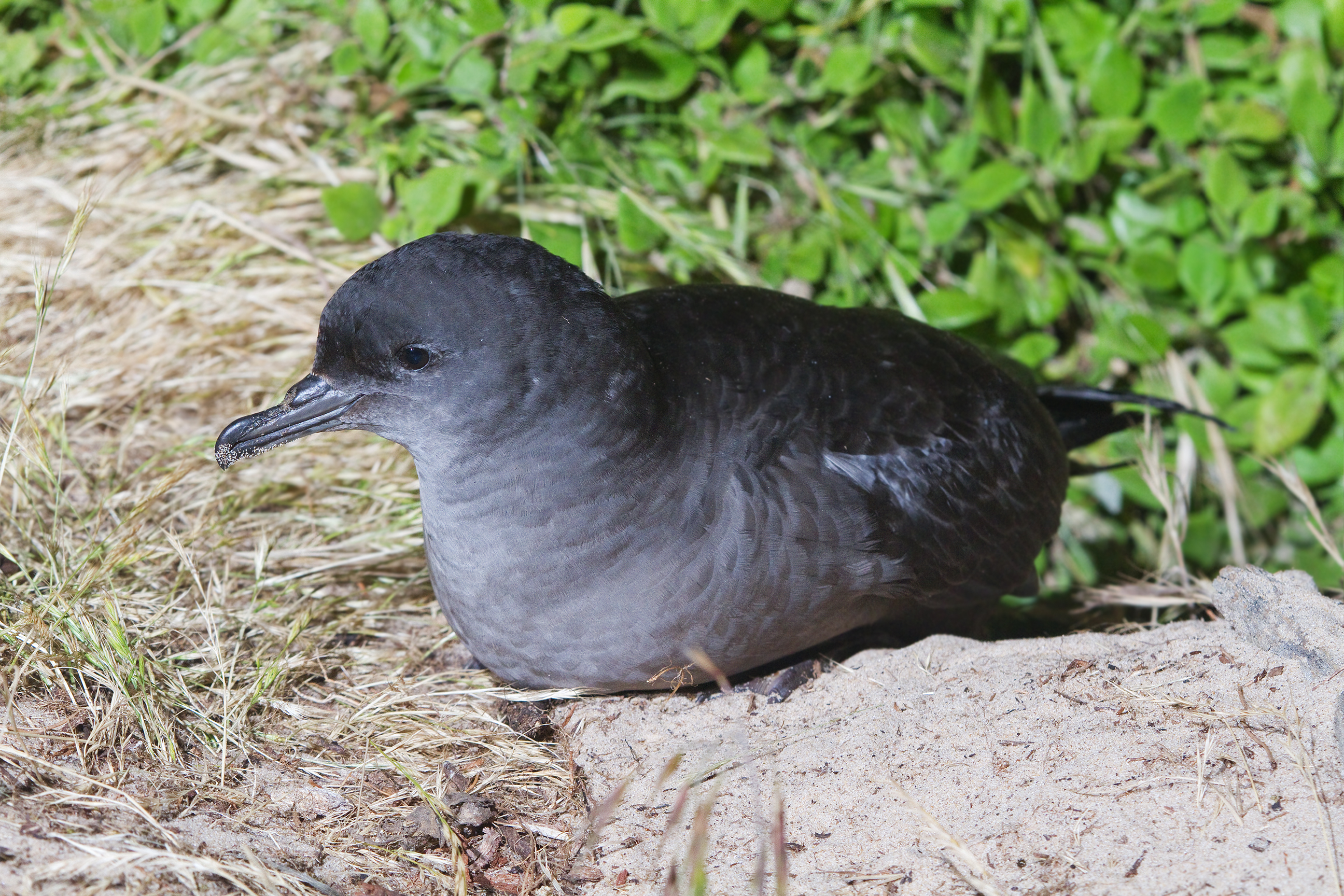
Short-tailed Shearwater
The short-tailed shearwater or slender-billed shearwater (''Ardenna tenuirostris''; formerly ''Puffinus tenuirostris''), also called yolla or moonbird, and commonly known as the muttonbird in Australia, is the most abundant seabird species in Australian waters, and is one of the few Australian native birds in which the chicks are commercially harvested. It is a migratory species that breeds mainly on small islands in Bass Strait and Tasmania and migrates to the Northern Hemisphere for the boreal summer. Taxonomy This shearwater appears to be related to the sooty and great shearwaters, which are also blunt-tailed, black-billed species, but its precise relationships are obscure (Austin, 1996; Austin ''et al.'', 2004). These are among the larger species of shearwater, which have been moved to a separate genus, ''Ardenna'' based on a phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA (Penhallurick & Wink, 2004). Ecology Each parent feeds the single chick for 2–3 days and then leaves for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wader
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflats in order to foraging, forage for food crawling or burrowing in the mud and sand, usually small arthropods such as aquatic insects or crustaceans. The term "wader" is used in Europe, while "shorebird" is used in North America, where "wader" may be used instead to refer to long-legged wading birds such as storks and herons. There are about 210 species of wader, most of which live in wetland or coastal environments. Many species of Arctic and temperate regions are strongly migratory, but tropical birds are often resident, or move only in response to rainfall patterns. Some of the Arctic species, such as the little stint, are amongst the longest distance migrants, spending the non- breeding season in the southern hemisphere. Many of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

