|
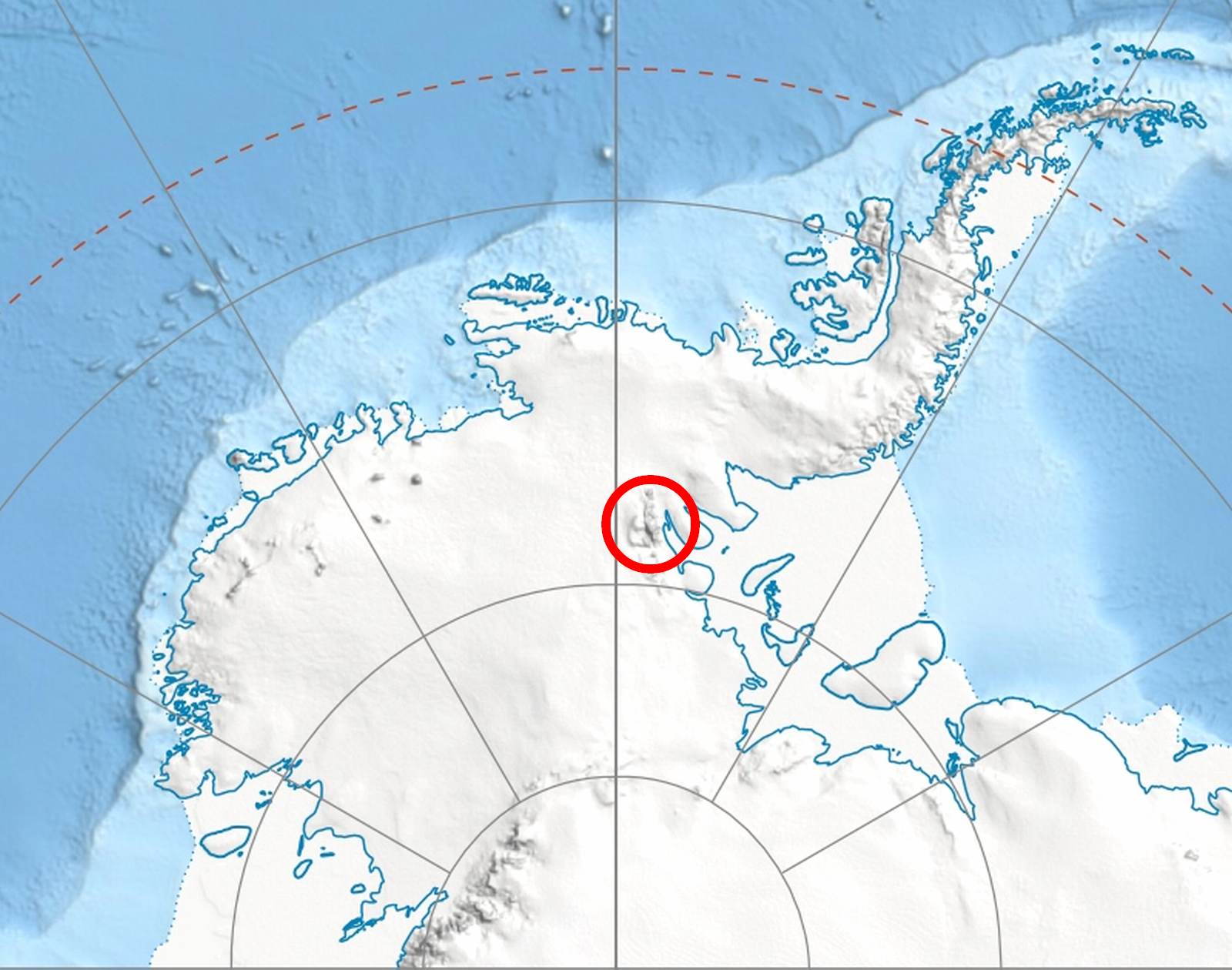
Evans Peak
Evans Peak () is a prominent rock peak, high, standing east-northeast of Mount Ostenso in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It overlooks Rumyana Glacier to the north and Patton Glacier to the south. The peak was named by the University of Minnesota Geological Party to these mountains, 1963–64, for John Evans, a geologist with the party. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. References External links SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Ostenso
Mount Ostenso () is a mountain (4,180 m) 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Mount Giovinetto in the main ridge of the Sentinel Range, Antarctica. First mapped by the Marie Byrd Land Traverse Party (1957–58) led by Charles R. Bentley, and named for Ned A. Ostenso, traverse seismologist at Byrd Station (1957) and a member of the party. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... References * Ellsworth Mountains Mountains of Ellsworth Land Four-thousanders of Antarctica {{EllsworthLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Range
The Sentinel Range is a major mountain range situated northward of Minnesota Glacier and forming the northern half of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The range trends NNW-SSE for about and is 24 to 48 km (15 to 30 mi) wide. Many peaks rise over and Vinson Massif (4892 m) in the southern part of the range is the highest elevation on the continent.Sentinel Range. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. Sentinel Range comprises a main ridge (featuring Vinson Massif in its southern portion) and a number of distinct heights, ridges and mountains on its east side, including (south to north) , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellsworth Mountains
The Ellsworth Mountains are the highest mountain ranges in Antarctica, forming a long and wide chain of mountains in a north to south configuration on the western margin of the Ronne Ice Shelf in Marie Byrd Land. They are bisected by Minnesota Glacier to form the Sentinel Range to the north and the Heritage Range to the south. The former is by far the higher and more spectacular with Mount Vinson () constituting the highest point on the continent.Bockheim, J.G., Schaefer, C.E., 2015. ''Soils of Ellsworth Land, the Ellsworth Mountains''. In: Bockheim, J.G. (Ed.), ''The Soils of Antarctica. World Soils Book Series'', Springer, Switzerland, pp. 169–181. The mountains are located within the Chilean Antarctic territorial claim but outside of the Argentinian and British ones. Discovery The mountains were discovered on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth in the course of a trans-Antarctic flight from Dundee Island to the Ross Ice Shelf. He gave them the descriptive name Sentinel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumyana Glacier
Rumyana Glacier ( bg, ледник Румяна, lednik Rumyana, ) is the long and wide glacier on the east side of north-central Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica, situated northwest of Patton Glacier and southeast of Delyo Glacier. It drains the east slopes of Mount Giovinetto and the north slopes of Evans Peak, and flows northeastwards to join Ellen Glacier northwest of Mount Jumper. The glacier is named after the Bulgarian woman rebel leader Rumyana Voyvoda (19th century). Location Rumyana Glacier is centred at . US mapping in 1961, updated in 1988. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, c ... Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patton Glacier
Patton Glacier () is a broad tributary glacier in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. It drains the east slope of the main ridge between Mounts Ostenso and Tyree, flows east-northeastwards between Evans Peak and Versinikia Peak on the north and Mount Bearskin on the south, and enters Ellen Glacier northeast of Zalmoxis Peak and southeast of Mount Jumper. The feature was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59. It was named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Sgt. Richard J. Patton, United States Air Force (USAF), the first to parachute land at the South Pole, November 26, 1956. He gave valuable assistance on the ground in directing the air drops from Globemaster aircraft, used in transporting supplies to establish the South Pole Station. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota, formally the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, (UMN Twin Cities, the U of M, or Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The Twin Cities campus comprises locations in Minneapolis and Falcon Heights, Minnesota, Falcon Heights, a suburb of St. Paul, approximately apart. The Twin Cities campus is the oldest and largest in the University of Minnesota system and has the List of United States university campuses by enrollment, ninth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 52,376 students at the start of the 2021–22 academic year. It is the Flagship#Colleges and universities in the United States, flagship institution of the University of Minnesota System, and is organized into 19 colleges, schools, and other major academic units. The Minnesota Territorial Legislature drafted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Evans (geologist)
John Evans may refer to: Academics *John Evans (archaeologist) (1823–1908), English archaeologist and geologist *John Evans (topographical writer) (1768–c. 1812), writer on Wales * John Cayo Evans (1879–1958), Welsh mathematician *John Davies Evans (1925–2011), English archaeologist * John Gwenogvryn Evans (1852–1930), Welsh minister and paleographer * John Robert Evans (1929–2015), Canadian cardiologist and civic leader *John V. Evans (astronomer) (born 1933), British-American * John Wainwright Evans (1909–1999), solar astronomer * John William Evans (geologist) (1857–1930), British * John William Evans (entomologist), British entomologist Entertainment *John Evans (actor) (1693–1734), Irish * John Evans (19th-century writer) (died 1832), English writer * John Evans (artist) (1932–2012), American * John Evans (director), American film director and screenwriter *John Evans (special effects), on five James Bond films * John Bryan Evans (born 1980), Welsh filmmak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains In Antarctica ...
This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atlantic Sources * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Ultras Of Antarctica Antarctica Ultras * Ultras Ultras are a type of association football fans who are renowned for their fanatical support. The term originated in Italy, but is used worldwide to describe predominantly organised fans of association football teams. The behavioural tende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |