|
Eutrema Penlandii
''Eutrema penlandii'' is a rare species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common names Penland's alpine fen mustard and Penland's eutrema. It is endemic to Colorado in the United States, where it is known only from a small strip of unique mountain habitat measuring 40 kilometers long.''Eutrema penlandii''. . It is threatened by and associated environmental changes in this part of the |
Reed Clark Rollins
Reed Clark Rollins (7 December 191128 April 1998) was an American botanist, professor at Harvard University Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ... and one of the founders of both the International Association for Plant TaxonomyCowan, R. S. and Stafleu, F. A. (1982) "The origin and early history of IAPT" ''Taxon'' 31(3): pp. 415–420 and the Organization for Tropical Studies. He was also the second president of each of them. accessed 6 April 2009 Sources * Al- ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilia Globularis
''Gilia'' is a genus of between 25 and 50 species of flowering plants in the Polemoniaceae family and is related to phlox. These Western native plants are best sown in sunny, well-draining soil in the temperate and tropical regions of the Americas, where they occur mainly in desert or semi-desert habitats They are summer annuals, rarely perennials, growing to 10–120 cm tall. The leaves are spirally arranged, usually pinnate (rarely simple), forming a basal rosette in most species. The flowers are produced in a panicle, with a five-lobed corolla, which can be blue, white, pink or yellow. ''Gilia'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including ''Schinia aurantiaca'' and ''Schinia biundulata ''Schinia biundulata'' is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in western North America, including Arizona, California, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, Texas and Utah. The wingspan is 20–22 mm. Food ''Gilia cana'' is used as an excl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
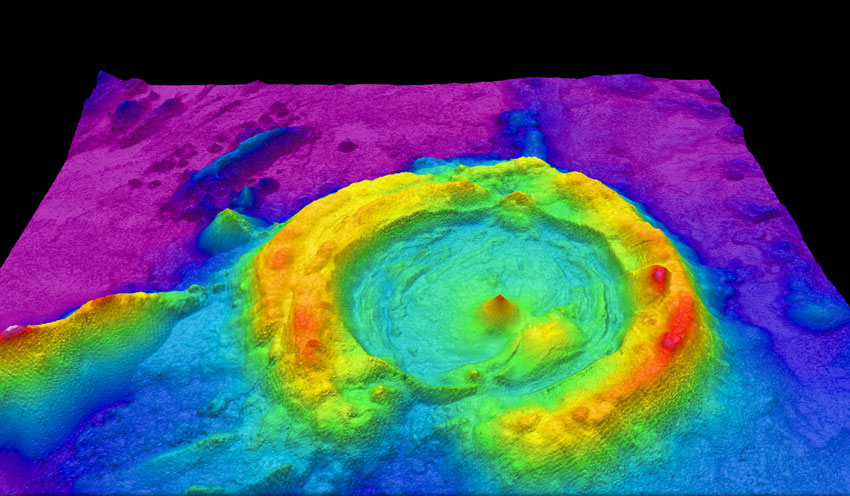
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loveland Pass
Loveland Pass is a high mountain pass in north-central Colorado, at an elevation of above sea level in the Rocky Mountains of the Western United States. Background It is located on the Continental Divide in the Front Range, west of Denver on U.S. Highway 6 (US 6). The twisty road is considered to be especially treacherous during the winter months. A steep, steady 6.7% grade, along with numerous hairpin turns on either side, make it difficult to snowplow the road regularly. The pass is named for William A.H. Loveland, the president of the Colorado Central Railroad and a resident of Golden during the late 19th century. The city of Loveland, in Larimer County near Fort Collins, is also named after him. Loveland held a railroad charter and was an advocate for a wagon road between Denver and Leadville. In 1869, he opened this section of wagon road now known as Loveland Pass. It would be abandoned in 1906 and then restored for vehicle use in 1920 by the U.S. forest Service. Lovelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Evans
Mount Evans is the highest peak in the Mount Evans Wilderness in the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The prominent 14,271-foot (4,350 m) fourteener is located southwest by south ( bearing 214°) of Idaho Springs in Clear Creek County, Colorado, United States, on the drainage divide between Arapaho National Forest and Pike National Forest. The peak is one of the characteristic Front Range peaks, dominating the western skyline of the Great Plains along with Pikes Peak, Longs Peak, and nearby Mount Bierstadt. Mount Evans can be seen from over to the east, and many miles in other directions. Mount Evans dominates the Denver metropolitan area skyline, rising over above the area. Mount Evans can be seen from points south of Castle Rock, up to ( south) and as far north as Fort Collins ( north), and from areas near Limon ( east). In March 2022, Clear Creek County approved a proposal to rename the peak to Mount Blue Sky, pending state and federal review, due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Sherman
Mount Sherman is a Elevation, high mountain summit in the Mosquito Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The fourteener is located east by south (Absolute bearing, bearing 103°) of the Leadville, Colorado, City of Leadville, Colorado, United States, on the drainage divide separating Lake County, Colorado, Lake County from Park County, Colorado, Park County. The mountain was named in honor of General William Tecumseh Sherman. Mountain Mount Sherman is one of the most nondescript of the fourteeners, and one of the easiest to climb; it is recommended as a beginner fourteener. It is also the only fourteener that has had a successful aircraft landing on its summit.Louis W. Dawson II, ''Dawson's Guide to Colorado's Fourteeners, Volume 1'', Blue Clover Press, 1994, Sherman Mine The Sherman mine, located in upper Iowa Gulch at and above 12,200 ft. on the west flank of Mt. Sherman, produced over 10 million ounces of silver, mostly between 1968 and 1982, with a value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito Pass
Mosquito Pass, with an elevation of , is a high mountain pass in the Mosquito Range of central Colorado in the United States. It lies on the boundary between Lake and Park counties between Leadville (west) and Fairplay (east). It also lies on the divide between the Arkansas and South Platte Rivers, which is the informal demarcation between the northern and southern parts of Colorado, east of the Continental Divide. One of the highest passes in the state, Mosquito Pass can be traversed only on foot, on an offroad motorcycle or with a proper four-wheel drive Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case ... (4WD) vehicle. 2WD vehicles will find the road difficult due to the stream crossings and high rocky sections. Even with 4WD, it is typically passable only during the summer months ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Silverheels
Mount Silverheels is a high and prominent mountain summit in the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The thirteener is located in Pike National Forest, northeast ( bearing 41°) of the Town of Alma in Park County, Colorado, United States. Mount Silverheels is just east of two fourteeners: Mount Bross and Mount Lincoln. Legend of Silverheels The mountain was named for Silverheels, a dance hall girl in the nearby mining camp of Buckskin Joe, now a ghost town. She was nicknamed "Silverheels" because of the silver shoes she wore while dancing. She wore a blue or white mask so as to conceal her face, and her actual name is unknown. Well-compensated by the trappers and prospectors who watched her dance, Silverheels was personally generous, having used her own money to bring in doctors during a smallpox epidemic in Buckskin Joe. After the disease waned, Silverheels left Buckskin Joe and was never heard from again. In the words of Frank H. Mayer, a United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient carbon sink on the planet, because peatland plants capture carbon dioxide (CO2) naturally released from the peat, maintaining an equilibrium. In natural peatlands, the "annual rate of biomass production is greater than the rate of decomposition", but it takes "thousands of years for peatlands to develop the deposits of , which is the average depth of the boreal orthernpeatlands", which store around 415 gigatonnes (Gt) of carbon (about 46 times 2019 global CO2 emissions). Globally, peat stores up to 550 Gt of carbon, 42% of all soil carbon, which exceeds the carbon stored in all other vegetation types, including the world's forests, although it covers just 3% of the land's surface. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

