|
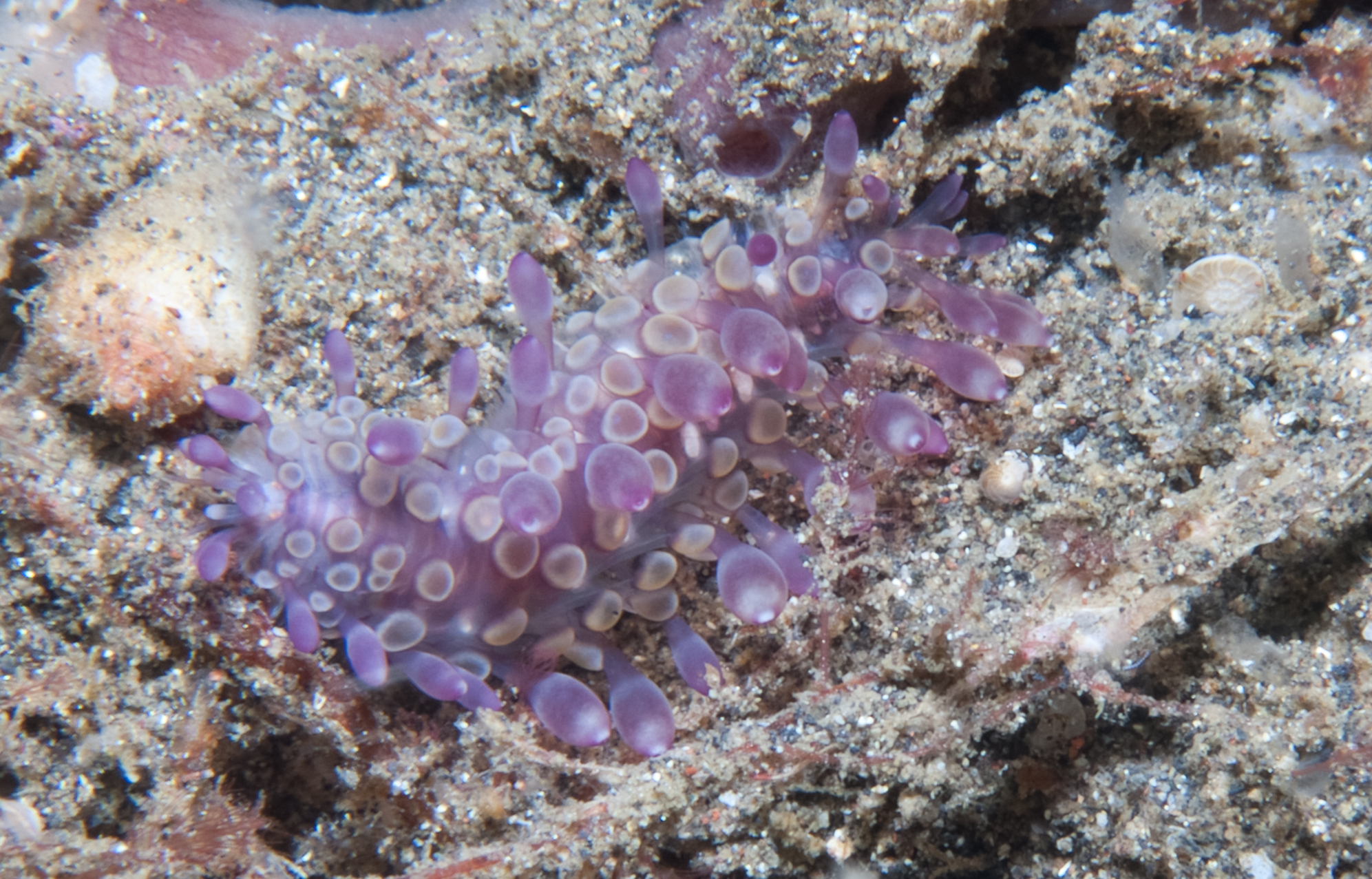
Eulagisca Gigantea
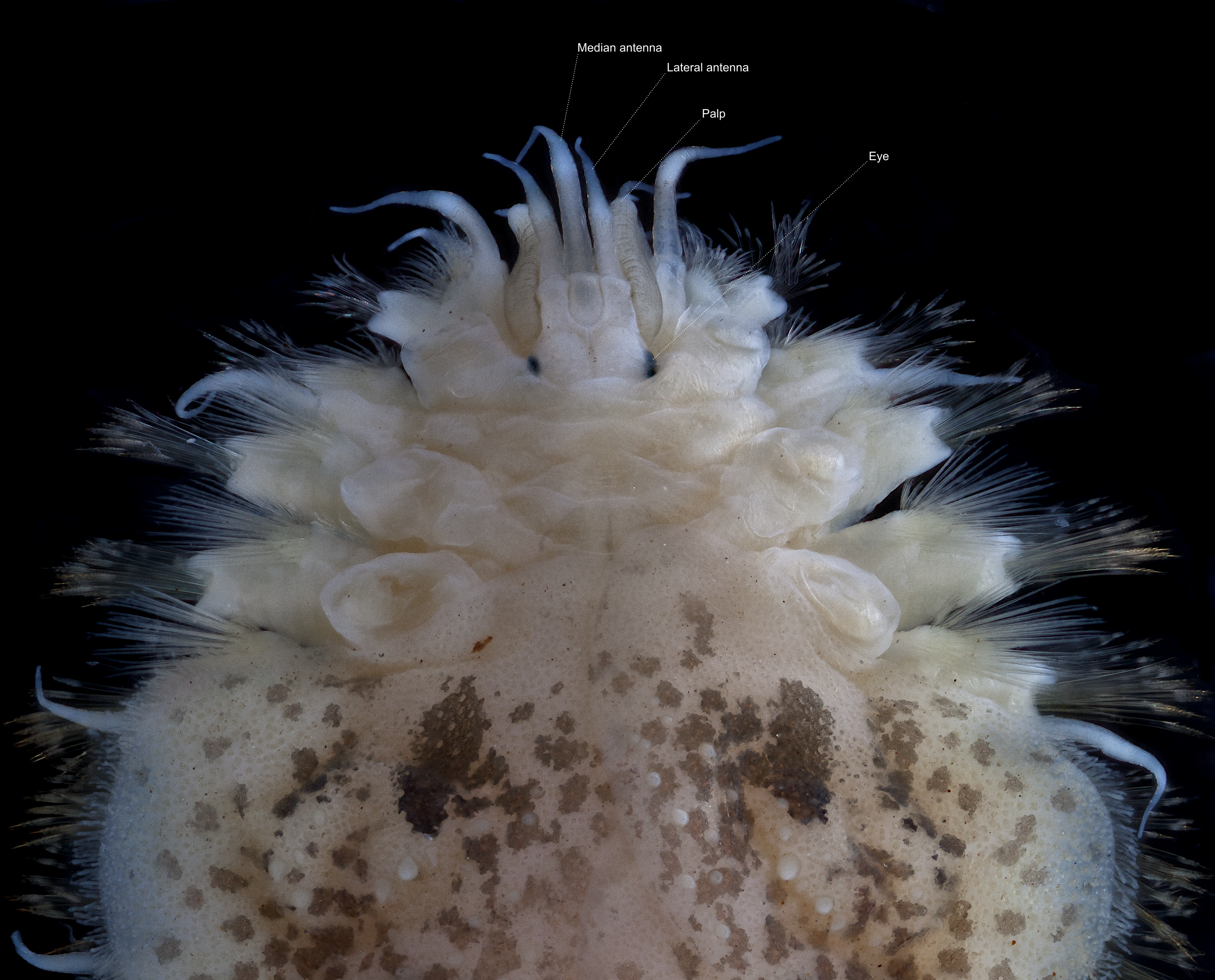
''Eulagisca gigantea'' is a scale worm that is widely distributed around Antarctica and the Southern Ocean at depths of about . Description ''Eulagisca gigantea'' can grow to a length of and a width of . It is dorso-ventrally flattened and has 40 segments with 15 pairs of elytra. The prostomium is oval and the back part is concealed by a nuchal fold. The lateral antennae are inserted terminally on the anterior margin of the prostomium. The notochaetae are about as thick as the neurochaetae, but bidentate neurochaetae absent. The eversible proboscis A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ... bears a pair of large jaws and is about a quarter of the length of the whole organism. It is a greyish-brown colour and without patterning. References Further reading * {{Taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in ''Eulagisca gigantea'' and ''Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those preda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem. By way of his voyages in the 1770s, James Cook proved that waters encompassed the southern latitudes of the globe. Since then, geographers have disagreed on the Southern Ocean's northern boundary or even existence, considering the waters as various parts of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, instead. However, according to Commodore John Leech of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), recent oceanographic research has discovered the importance of Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A '' Eunoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete prostomia have a posterior extension or ridge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala or thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms are characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cracks and crevices in bedrock. A few construct tubes in which they live and some are pelagic, swimming through the water column. There are estimated to be more than 4,600 accepted species in the order. Characteristics Phyllodocida are segmented worms and range in size from a few millimetres long to over a metre. Each segment bears a pair of paddle-like parapodia. The prostomium generally has one or two pairs of eyes, a dorsal pair of antennae, a ventral pair of sensory palps and a pair of organs on the neck. The peristomium is a ring, often hidden dorsally by the prostomium and the first segment. There is a muscular proboscis with one or more pairs of jaws. The next few segments tend to differ from those further back in having enlarged do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_2.jpg)