|
Ethnography Of Argentina
Argentina has a racially and ethnically diverse population. The territory of what today is Argentina was first inhabited by numerous indigenous peoples. The first white settlers came during the period of Spanish colonization, beginning in the 16th century. The Spaniards imported African slaves, who would go on to become the first Afro-Argentines. Following independence from Spain in the 19th century and well into the 20th century, numerous migration waves took place, with Argentina being the second most popular destination for migrants in the early 20th century, after the United States. Most of these migrants came from Europe. Most modern-day Argentines are descendants of these 19th and 20th century immigrants, with about 97% of the population being of full or partial European ancestry, while an estimated 31% or 56% have some indigenous or mestizo ancestry, and 5% or 9% have some African or mulatto ancestry. In the , some 955,032 Argentines (2.38% of the population) ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
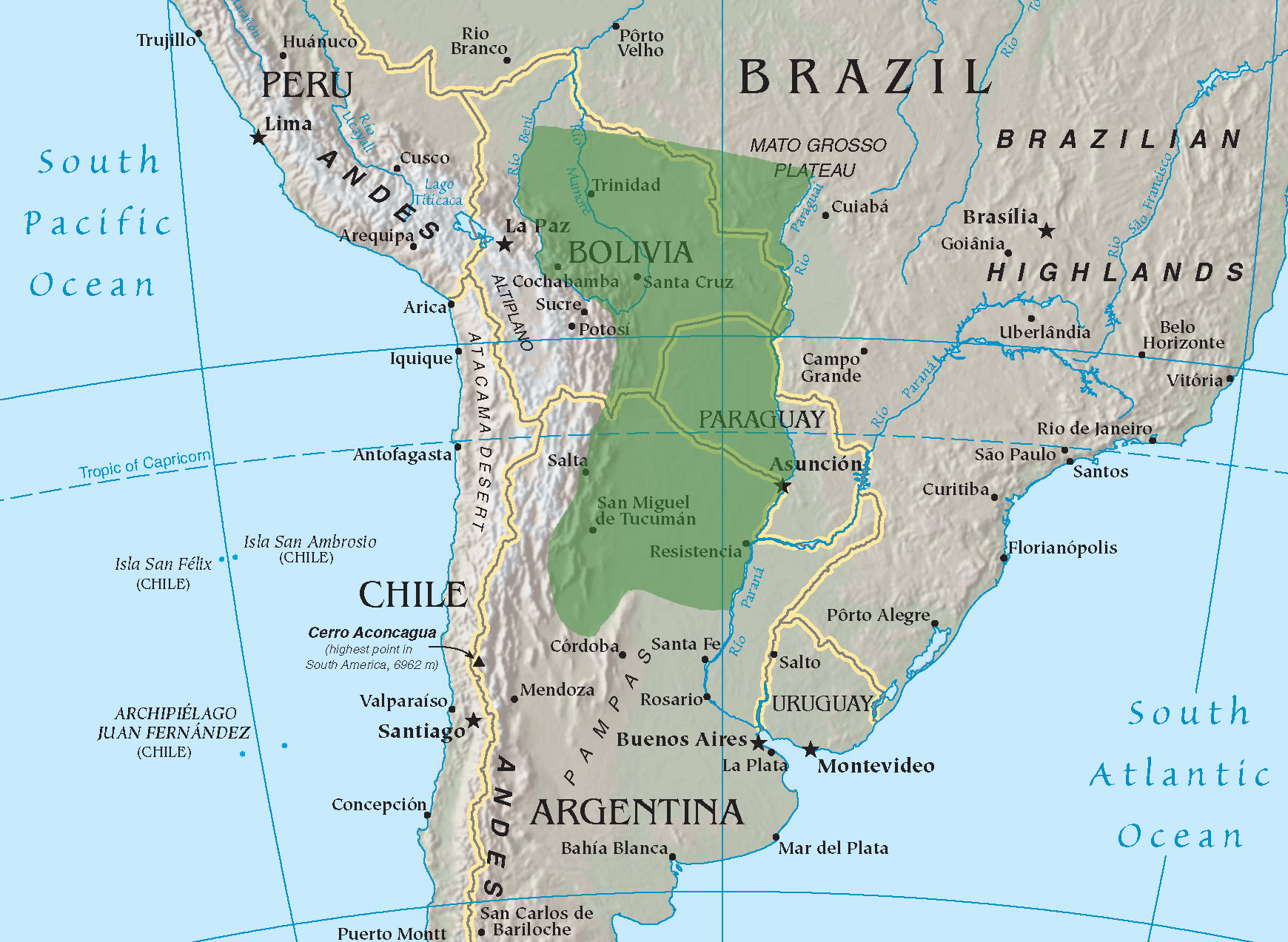
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, eighth-largest country in the world. Argentina shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a Federation, federal state subdivided into twenty-three Provinces of Argentina, provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and List of cities in Argentina by population, largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a Federalism, federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Argentine
Arab Argentine refers to Argentine citizens or residents whose ancestry traces back to various waves of immigrants, largely of Arab ethnic, cultural and linguistic heritage and/or identity originating mainly from what is now Lebanon and Syria (mainly descendants of Arab Christians). It also includes, individuals from the twenty-two countries which comprise the Arab world such as Palestine, Egypt and Morocco. Arab Argentines are one of the largest Arab diaspora groups in the world. Although a highly diverse group of Argentines — in ancestral origins, religion and historic identities — Arab Argentines hold a common identity in the Argentine consciousness, being universally known as ("Turks"), like in the rest of Latin American countries. The majority of the Arab Argentines are from either Lebanese or Syrian background with a smaller amount of Palestinian, Egyptian and Moroccan background. Interethnic marriage in the Arab community, regardless of religious affiliation, is v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
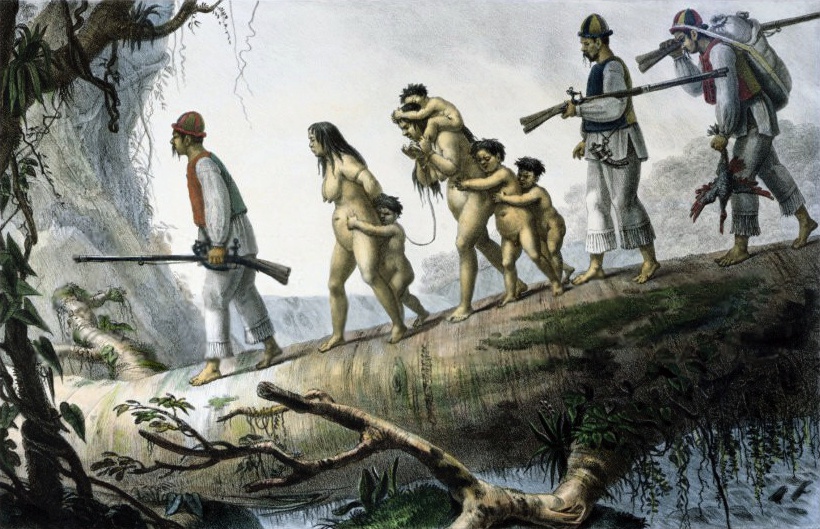
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa River, Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Pampas, Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
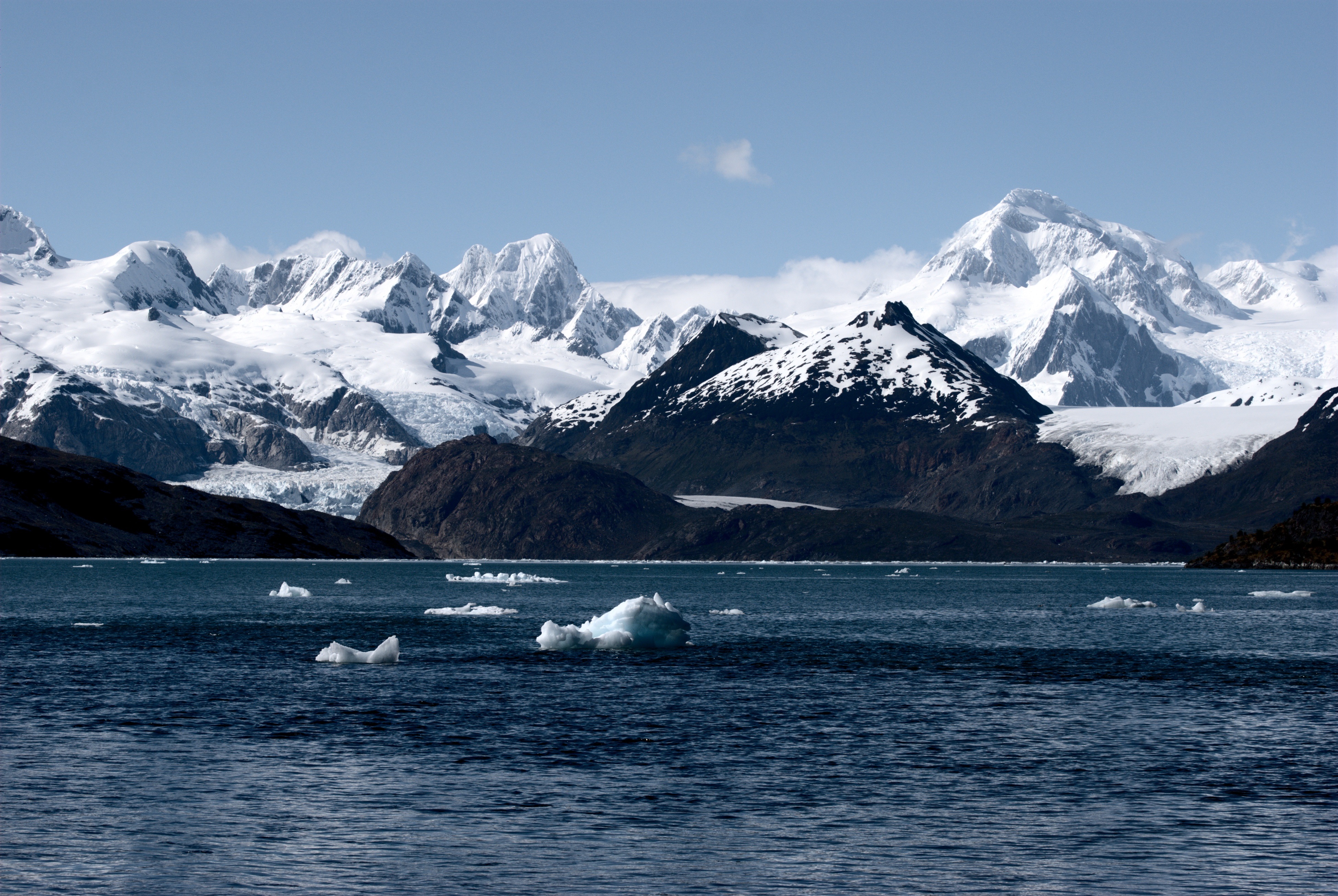
Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and Patagonian Desert, deserts, Plateaus, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The northern limit of the region is not precisely defined; the Colorado River, Argentina, Colorado and Barrancas River, Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes considered part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichí
The Wichí are a group indigenous people of South America. They are a large group of tribes, inhabiting the headwaters of the Bermejo River and the Pilcomayo River, in Argentina and Bolivia. Notes on designation This ethnic group was referred to by English settlers as Mataco, and is still widely known as such. The etymology of this term is obscure, but in several sources it is cited that the Wichí find the term derogatory. Among the Wichí exists a folk etymology for this term, which relates it to the Spanish verb ''matar'', to kill. Their preferred name and word for themselves is Wichi 'people' (), and their language is ''Wichí Lhamtés'' (). There is a pronunciation variant in some areas of Bolivia, , where the group refers to themselves as Weenhayek wichi, translated by Alvarsson (1988) as "''the different people''" (pl. ''Weenhayey''). Weenhayey informants of Alvarsson state that the old name was Olhamelh (), meaning simply ''us''. The subgroups within Wichí have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toba People
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Gran Chaco, Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta Province, Salta, Chaco Province, Chaco, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Formosa Province, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco Province, Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Tarija Department, Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of Orán, Salta, San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Chaco, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario, Santa Fe, Rosario and Santa Fe, Argentina, Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mocoví People
The Mocoví ( Mocoví: ''moqoit'') are an Indigenous people of the Gran Chaco region of South America. They speak the Mocoví language and are one of the ethnic groups belonging to the Guaycuru peoples. In the 2010 Argentine census, 22,439 people self-identified as Mocoví. Not much is known about them before the Spanish arrived. They were nomadic and lived off of their fishing, hunting and gathering. They hunted deer and rhea and slept on animal skins and flimsy shelters. They did not farm because the soil conditions were poor where they roamed and there was flooding. Trade routes were discovered in the Chaco forest, indicating trading and it was assumed they traded skins and feathers for gold, silver and copper objects. When the Jesuits arrived, they taught the Mocoví to farm with cattle and they became sedentary. In 1924, at least 200 Mocoví and Toba people The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in Argentina who historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaraní People
The Guarani are a group of culturally-related Indigenous peoples of South America. They are distinguished from the related Tupi people, Tupi by their use of the Guarani language. The traditional range of the Guarani people is in what is now Paraguay between the Paraná River and lower Paraguay River, the Misiones Province, Misiones Province of Argentina, southern Brazil once as far east as Rio de Janeiro, and parts of Uruguay and Bolivia. Although their demographic dominance of the region has been reduced by European colonization of the Americas, European colonisation and the commensurate rise of mestizos, there are contemporary Guarani populations in Paraguay and parts of Argentina and Bolivia. Most notably, the Guarani language, still widely spoken across traditional Guarani homelands, is one of the two official languages in Paraguay, the other one being Spanish. The Paraguayan population learns Guarani both informally from social interaction and formally in public schools. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara People
The Aymara or Aimara (, ) people are an Indigenous people in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America. Approximately 2.3 million Aymara live in northwest Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru. The ancestors of the Aymara lived in the region for many centuries before becoming a subject people of the Inca Empire in the late 15th or early 16th century and later of the Spanish in the 16th century. With the Spanish American wars of independence (1810–1825), the Aymaras became subjects of the new nations of Bolivia and Peru. After the War of the Pacific (1879–1883), Chile annexed territory with the Aymara population. Etymology The name of the Aymara people stems from the word ''Ayma-ra-mi'' meaning "a place with many communally owned farms". The word "Aymara" also refers to a group of language dialects of which the origin, spread and time-frame are debated. History Early history The early history of the Aymara people is uncertain. Various hypotheses have been voiced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolla People
The Qulla (Quechuan languages, Quechuan for ''south'', Hispanicized and mixed spellings: ''Colla, Kolla'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous people of western Bolivia, northern Chile, and the western portions of Jujuy Province, Jujuy and Salta Province, Salta provinces in Argentina. The 2004 Complementary Indigenous Survey reported 53,019 Qulla households living in Argentina. They moved freely between the borders of Argentina and Bolivia."Argentina: Current information on abuses committed against the Kolla." ''Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada.'' 1 June 1993 (retrieved 29 April 2011) While mostly living in arid highlands, their easternmost lands are part of the yungas, an altitude forests at the edge of the Amazon rainforest.< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaguita
The Diaguita people are a group of South American Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous people native to the Chilean Norte Chico, Chile, Norte Chico and the Argentine Northwest. Western or Chilean Diaguitas lived mainly in the Transverse Valleys that incise Semi-arid climate, semi-arid Andes, mountains. Eastern or Argentine Diaguitas lived in the provinces of La Rioja Province, Argentina, La Rioja and Catamarca Province, Catamarca and part of the provinces of Salta Province, Salta, San Juan Province, Argentina, San Juan and Tucumán Province, Tucumán. The term ''Diaguita'' was first applied to peoples and archaeological cultures by Ricardo E. Latcham in the early 20th century. Ancient Diaguitas were not a unified people; the language or dialects used by them seems to have varied from valley to valley and they were politically fragmented into several chiefdoms. Coastal and inland Chilean Diaguitas traded, as evidenced by the archaeological findings of mollusc shells in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua People
Quechua people (, ; ) , Quichua people or Kichwa people may refer to any of the Indigenous peoples of South America who speak the Quechua languages, which originated among the Indigenous people of Peru. Although most Quechua speakers are native to Peru, there are some significant populations in Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, and Argentina. The most common Quechua dialect is Southern Quechua. The Kichwa people of Ecuador speak the Kichwa language, Kichwa dialect; in Colombia, the Inga people speak Inga Kichwa. The Quechua word for a Quechua speaker is ''runa'' or ''nuna'' ("person"); the plural is ''runakuna'' or ''nunakuna'' ("people"). "Quechua speakers call themselves Runa -- simply translated, "the people". Some historical Quechua people are: * The Chanka people lived in the Huancavelica Region, Huancavelica, Ayacucho Region, Ayacucho, and Apurímac Region, Apurímac regions of Peru. * The Huanca people of the Junín Region of Peru spoke Quechua before the Incas did. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |