|
Estonia–Germany Relations
Estonia–Germany relations (; ) are foreign relations between Estonia and Germany. Estonia has an embassy in Berlin. Germany has an embassy in Tallinn. Both countries are full members of the European Union, NATO, OECD, OSCE, Council of Europe, Council of the Baltic Sea States, HELCOM and WTO. History During the final stages of World War I, Estonia was occupied by Germany, shortly after the Estonian Declaration of Independence of 24 February 1918. Germany first recognised Estonia's independence on 9 July 1921. In 1939, Germany signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union, which allowed the Soviet invasion of Estonia in 1940 during World War II. From 1941 to 1944 Germany occupied Estonia. Both countries re-established diplomatic relations on 28 August 1991. Military cooperation The German Air Force takes part in the NATO Baltic Air Policing mission to guard the airspace over the Baltic states including Estonia. See also *Foreign relations of Estonia *Foreign r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,300 other islands and islets on the east coast of the Baltic Sea. Its capital Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest List of cities and towns in Estonia, urban areas. The Estonian language is the official language and the first language of the Estonians, majority of its population of nearly 1.4 million. Estonia is one of the least populous members of the European Union and NATO. Present-day Estonia has been inhabited since at least 9,000 BC. The Ancient Estonia#Early Middle Ages, medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last pagan civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity following the Northern Crusades in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia–Germany Relations
Estonia–Germany relations (; ) are foreign relations between Estonia and Germany. Estonia has an embassy in Berlin. Germany has an embassy in Tallinn. Both countries are full members of the European Union, NATO, OECD, OSCE, Council of Europe, Council of the Baltic Sea States, HELCOM and WTO. History During the final stages of World War I, Estonia was occupied by Germany, shortly after the Estonian Declaration of Independence of 24 February 1918. Germany first recognised Estonia's independence on 9 July 1921. In 1939, Germany signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union, which allowed the Soviet invasion of Estonia in 1940 during World War II. From 1941 to 1944 Germany occupied Estonia. Both countries re-established diplomatic relations on 28 August 1991. Military cooperation The German Air Force takes part in the NATO Baltic Air Policing mission to guard the airspace over the Baltic states including Estonia. See also *Foreign relations of Estonia *Foreign r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsch-Baltische Gesellschaft
The Deutsch-Baltische Gesellschaft ("German-Baltic Society") is an organization which represents Baltic German refugees expelled from Estonia and Latvia during World War II and its aftermath. It was established in 1950 as the Deutsch-Baltische Landsmannschaft im Bundesgebiet. The organization is based in Darmstadt, Hesse. Its youth organization is the Deutschbaltischer Jugend- und Studentenring. Society Chairman * Georg von Manteuffel-Szoege (1950-1962) * Axel de Vries (1962-1963 comm.) * Erik von Sivers (1963-1973) * Rudolf von Wistinghausen (1973-1980) * Klas Lackschewitz (1980-1984) * Hans Erich Seuberlich (1984) * Runar of Sivers (1985-1989) * Waltraut Dame von Tiesenhausen (1989-1996) * Heinz-Adolf Treu (1996-2005) * Eckhart Neander (2005-2010) * Frank von Auer (2010-2015) * Christian von Boetticher (since October 31, 2015) Corporate members * Carl-Schirren-Gesellschaft e. V. - German-Baltic cultural work * German Baltic youth and student ring e. V. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Baltic Germans
This is a list of notable Baltic Germans. Art and literature Architects *Alfred Aschenkampff (1858–1914), architect (Latvia) *Paul Max Bertschy (1840–1911), city architect of Liepāja (Latvia) *Bernhard Bielenstein (1877–1959), architect (Latvia) *Wilhelm Bockslaff (1858–1945), architect (Latvia) *Johann Felsko (1813–1902), architect (Latvia) *Karl Felsko, (1844–1918), architect (Latvia) *Christoph Haberland (1750–1803), architect (Latvia) *Otto Pius Hippius (1826–1883), architect (Estonia) *Erich Jacoby (1885–1941), architect (Estonia) *Paul Mandelstamm (1872–1941), architect (Latvia) *Robert Natus (1890–1950), architect (Estonia) *Robert Pflug (1832–1885), architect (Latvia) *August Reinberg (1860–1908), architect (Latvia) *Jacques Rosenbaum (1878–1944), architect (Estonia) *Alfred Rosenberg (1893–1946), politician, Nazi ideologist and architect (Germany) *Max Scherwinsky (1859–1909), architect and designer (Latvia) *Edmund von Trompowsky (1851� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Knighthoods
Baltic Noble Corporations of Courland, Livonia, Danish Estonia, Estonia, and Oesel (Ösel) were medieval fiefdoms formed by German nobles in the 13th century under vassalage to the Teutonic Knights and Denmark in modern Latvia and Estonia. The territories continued to have semi-autonomous status from 16th to early 20th century under Swedish and Russian rule. The four knighthoods are united in the Verband der Baltischen Ritterschaften. Eingetragener Verein, e.V. ( ''Association of Baltic Noble Corporations'' ) History The Teutonic Knights entered the area of what is now Latvia and Estonia in the beginning of the 13th century in order to Christianize the region. After the conquest much of the Order's land was divided among the German noble families originally from Westphalia and regions along the Rhine river. The towns also saw the development of a German mercantile class. The noble families constituted a minority amongst the local German-speaking population, and overall, the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans ( or , later ) are ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their resettlement in 1945 after the end of World War II, Baltic Germans have drastically declined as a geographically determined ethnic group in the region, with diaspora generally relocating to Germany proper and beyond. Since the late Middle Ages, native German-speakers formed the majority of merchants and clergy, and the large majority of the local landowning nobility who effectively constituted a ruling class over indigenous Latvian and Estonian non-nobles. By the time a distinct Baltic German ethnic identity began emerging in the 19th century, the majority of self-identifying Baltic Germans were non-nobles belonging mostly to the urban and professional middle class. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Catholic German traders and crusaders (''see '') began settling in the eastern Baltic territories. With the decline of Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of Germany
The Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) is a Central European country and member of the European Union, G4, G7, the G20, the Organizations for Economic Co-operation and Development and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It maintains a network of 229 diplomatic missions abroad and holds relations with more than 190 countries. As one of the world's leading industrialized countries it is recognized as a major power in European and global affairs. History The history of German foreign policy covers diplomatic developments and international history since 1871. Before 1866, Habsburg Austria and its German Confederation were the nominal leader in German affairs, but the Hohenzollern Kingdom of Prussia exercised increasingly dominant influence in German affairs, owing partly to its ability to participate in German Confederation politics through its Brandenburg holding, and its ability to influence trade through its Zollverein network. The question of excluding or includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of Estonia
The Republic of Estonia gained its independence from the Russian Empire on 24 February 1918 and established diplomatic relations with many countries via membership of the League of Nations. The forcible incorporation of Estonia into the Soviet Union in 1940 was not generally recognised by the international community and the Estonian diplomatic service continued to operate in some countries. Following the restoration of independence from the Soviet Union, Russia was one of the first nations to re-recognize Estonia's independence (the first country to do so was Iceland on 22 August 1991). Estonia's immediate priority after regaining its independence was the withdrawal of Russian (formerly Soviet) forces from Estonian territory. In August 1994, this was completed. However, relations with Moscow have remained strained primarily because Russia decided not to ratify the border treaty it had signed with Estonia in 1999. Trends following re-independence Since regaining independence, Est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Air Policing
The Baltic air-policing mission is a NATO air defence Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) in order to guard the airspace above the three Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Mission Within the Alliance, preserving airspace integrity is conducted as a collective task jointly and collectively using fighter aircraft for air policing. Air policing is a purely defensive mission. Since the 1970s, NATO has established a comprehensive system of air surveillance and airspace management means, as well as Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) assets for intercepts (QRA(I)) provided by its member nations. By means of radar sites, remote data transmission, Control and Reporting Centres (CRCs) and Combined Air Operations Centres (CAOCs) the Alliance ensures constant surveillance and control of its assigned airspace 24 hours a day and 365 days a year. NATO exploits these facilities to react within seconds to air traffic incidents in the Allies’ airspace. This structure of weapon systems, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Air Force
The German Air Force (, ) is the aerial warfare branch of the , the armed forces of Germany. The German Air Force (as part of the ) was founded in 1956 during the era of the Cold War as the aerial warfare branch of the armed forces of West Germany. After the reunification of West and East Germany in 1990, it integrated parts of the air force of the former German Democratic Republic, which itself had been founded in 1956 as part of the National People's Army. There is no organizational continuity between the current Luftwaffe of the Bundeswehr and the former Luftwaffe of the Wehrmacht founded in 1935, which was completely disbanded in 1945/46 after World War II. The term that is used for both the historic and the current German air force is the German-language generic designation of any air force. The commander of the German Air Force is Lieutenant General Ingo Gerhartz. As of 2015, the German Air Force uses eleven air bases, two of which host no flying units. Furthermore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
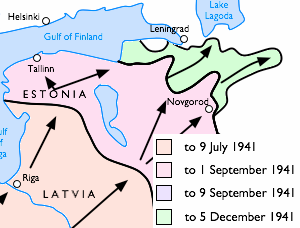
German Occupation Of Estonia During World War II
In the course of Operation Barbarossa, Nazi Germany invaded Estonia in July–December 1941, and occupied the country until 1944. Estonia had gained Estonian War of Independence, independence in 1918 from the then-warring German Empire, German and Russian Empires. However, in the wake of the August 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Nazi-Soviet Pact, the Soviet Union had Occupation of the Baltic states, invaded and occupied Estonia in June 1940, and the country was formally annexed into the USSR in August 1940. In the summer of 1941, the German invaders were at first seen by most Estonians as liberators from Soviet terror, since the Germans arrived only a week after the June deportation, mass deportation of tens of thousands of people from Estonia and other territories Soviet occupation of the Baltic states (1940), occupied by the USSR in 1939–1941: Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, eastern Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, Soviet deportations from Bessarabia and Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |