|
Estesia
''Estesia'' (in honour of Richard Estes) is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous anguimorph lizard found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. It was discovered in June 1990 by a joint expedition made up of Mongolian and American palaeontologists, and described in 1992 by Mark Norell, Malcolm McKenna and Michael Novacek. This animal is of interest to palaeontologists, not only because it is close to the lineage of modern Gila monsters (''Heloderma''), but also because its dentition shows evidence that it was venomous. The type species is ''E. mongoliensis'', after Mongolia, where it was found. Material Material for ''Estesia'' has been collected in various localities in the Gobi Desert, including the Barun Goyot Formation, the Djadochta Formation and Ukhaa Tolgod. *IGM M3/14 (holotype): A well-preserved skull with mandible, from Lizard Hill, Khulsan (Barun Goyot Formation) *IGM 3/15: Partial skeleton with associated braincase, from Khermeen Tsav (Barun Goyot Formation), discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monstersauria
Monstersauria is a clade of anguimorph lizards, defined as all taxa more closely related to ''Heloderma'' than '' Varanus''. It includes ''Heloderma'', as well as several extinct genera, such as ''Estesia'', '' Primaderma'' and ''Gobiderma'', but it was found to be polyphyletic in the most recent and complete squamate phylogenetic analysis by Reeder ''et al.'' (2015). Classification Traditionally, Monstersauria was thought to include the modern Helodermatidae along with fossil genera such as ''Gobiderma'' and ''Estesia'' on the finding that it was a sister to Varanidae. But in more recent years, such as 2004 and 2008, more precise molecular studies have shown that the extant ''Heloderma'' is closer to Anguidae & kin than to Varanoidea. A large-scale integrated analysis on squamate phylogeny incorporating 737 characters of morphological and molecular data in 2015 analyzed the traditionally-monstersaurian fossil taxa along with the rest of the dataset, and what it found was a well- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanoidea
Varanoidea is a superfamily of lizards, including the well-known family Varanidae (the monitors and goannas). Also included in the Varanoidea are the Lanthanotidae (earless monitor lizards), and the extinct Palaeovaranidae. Throughout their long evolutionary history, varanoids have exhibited great diversity, both in habitat and form. This superfamily includes the largest-known terrestrial lizard, Megalania (5–6 meters), and the largest extant lizard, the Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis'', 3+ meters). Evolution Either synonymous with, or a subgroup of, the group Platynota, the varanoids first appear in the fossil record in the latter part of Early Cretaceous, but possible varanoid ancestors have been traced back as far as Early Jurassic times. Among the earliest known varanoids are the monitor-like necrosaurids '' Palaeosaniwa canadensis'' from the Campanian (roughly 71-82 mya) of North America and '' Estesia mongoliensis'' and '' Telmasaurus grangeri'', both from the Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barun Goyot Formation
The Barun Goyot Formation (also known as Baruungoyot Formation or West Goyot Formation) is a geological formation dating to the Late Cretaceous Period. It is located within and is widely represented in the Gobi Desert Basin, in the Ömnögovi Province of Mongolia. Description It was previously known as the Lower Nemegt Beds occurring beneath the Nemegt Formation and above the Djadokhta Formation. It has been suggested that the Djadokhta and Barun Goyot Formations are lower and upper parts, respectively, of the same lithological unit and the boundary between the two does not exist. The stratotype of the Barun Goyot Formation is the Khulsan locality, east of Nemegt. At Nemegt, only the uppermost barungoyotian beds are visible. The ''Red Beds of Khermeen Tsav'' are also considered part of the Barun Goyot Formation. It is approximately in thickness,Gradzinski, R.; & Jerzykiewicz, T. (1974). Sedimentation of the Barun Goyot formation. Palaeontologica Polonica, 30, 111-146. and was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djadochta Fauna
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. The type locality is the Bayn Dzak locality, famously known as the Flaming Cliffs. Dinosaur, mammal, and other reptile remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Excavation history The Djadochta Formation was first documented and explored—though only a single locality—during paleontological expeditions of the American Museum of Natural History in 1922–1925, which were part of the Central Asiatic Expeditions. The expeditions were led by Roy Chapman Andrews, in company of Walter Willis Granger as chief paleontologist and field team. The team did extensive exploration at the Bayn Dzak (formerly Shabarakh Usu) region, which they nicknamed Flaming Cliffs given that at sunset th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguimorph
The Anguimorpha is a suborder of squamates. The group was named by Fürbringer in 1900 to include all autarchoglossans closer to '' Varanus'' and ''Anguis'' than ''Scincus''. These lizards, along with iguanians and snakes, constitute the proposed "venom clade" Toxicofera of all venomous reptiles. Evolution The oldest widely accepted member of Anguimorpha is ''Dorsetisaurus'' from the Late Jurassic of Europe and North America. In 2022, the genus ''Cryptovaranoides'' was described from the latest Triassic (Rhaetian) of England. ''Cryptovaranoides'' was recovered in the study as a crown-group Anguimorph, and therefore the oldest crown group-squamate, 35 million years older than any previously known crown-group squamate. Families Anguidae There are 9 genera found within the Anguidae family. They are characterized by being heavily armored with non-overlapping scales, and almost all having well-developed ventrolateral folds (excluding ''Anguis''). Anguidae members can, however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. The type locality is the Bayn Dzak locality, famously known as the Flaming Cliffs. Dinosaur, mammal, and other reptile remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Excavation history The Djadochta Formation was first documented and explored—though only a single locality—during paleontological expeditions of the American Museum of Natural History in 1922–1925, which were part of the Central Asiatic Expeditions. The expeditions were led by Roy Chapman Andrews, in company of Walter Willis Granger as chief paleontologist and field team. The team did extensive exploration at the Bayn Dzak (formerly Shabarakh Usu) region, which they nicknamed Flaming Cliffs given that at sunset th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
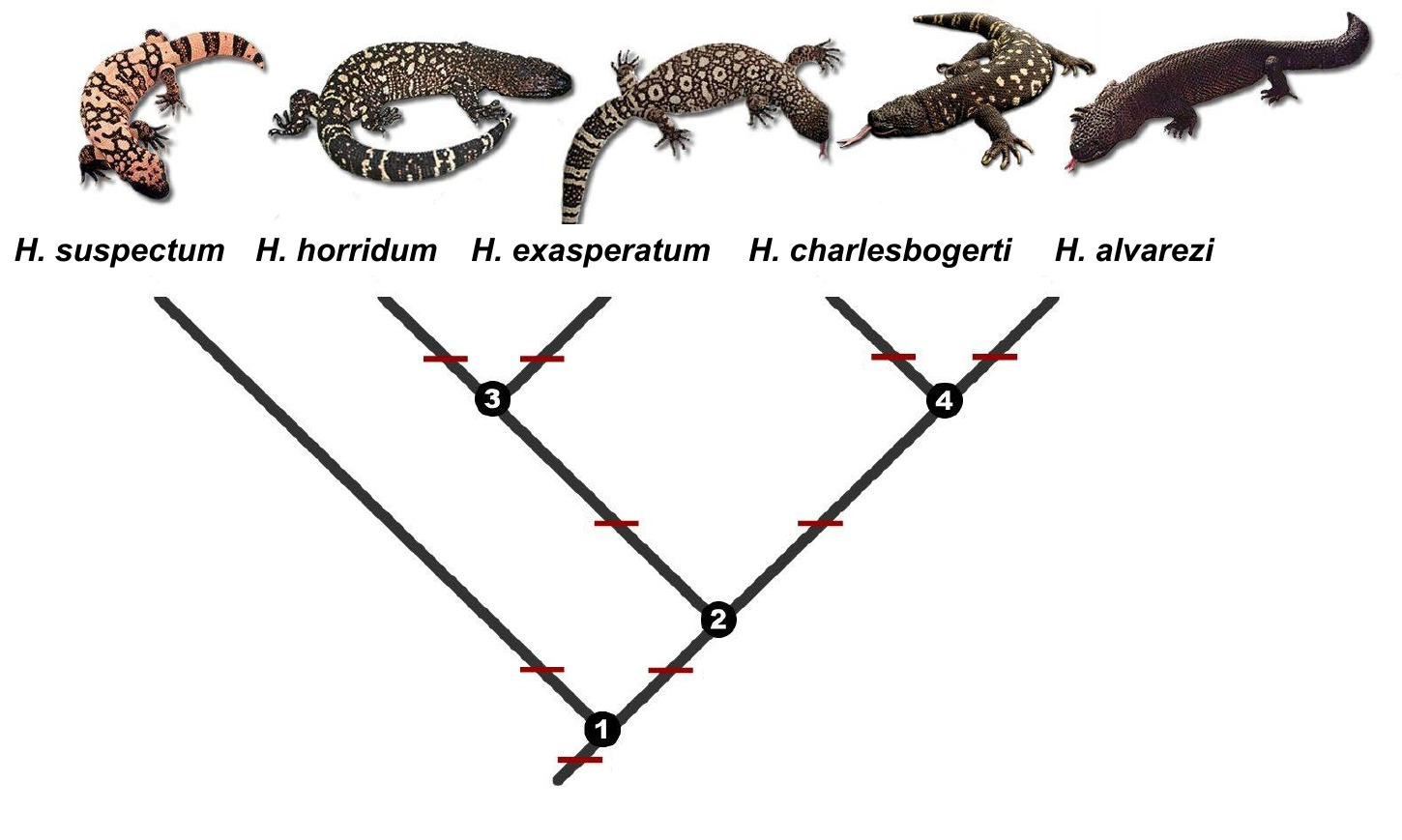
Heloderma
''Heloderma'' is a genus of toxicoferan lizards that contains five species, all of which are venomous. It is the only extant genus of the family Helodermatidae. Description The genus ''Heloderma'' contains the Gila monster (''H. suspectum'') and four species of beaded lizards. The Gila monster is a large, stocky, most of the time slow-moving reptile that prefers arid deserts. Beaded lizards are seen to be more agile and seem to prefer more humid surroundings. The tails of all species of ''Heloderma'' are used as fat storage organs. The scales of the head, back and tail are bead-like, containing osteoderms for better protection. The scales of the belly are free from osteoderms. Most species are dark in color, with yellowish or pinkish markings. Venom The venom glands of ''Heloderma'' are located at the end of the lower jaws, unlike snakes' venom glands, which are located behind the eyes. Also, unlike snakes, the Gila monster and beaded lizards lack the musculature to inject veno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1992
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous Lepidosaurs Of Asia
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Norell
Mark Allen Norell (born July 26, 1957) is an American paleontologist, acknowledged as one of the most important living vertebrate paleontologists. He is currently the chairman of paleontology and a research associate at the American Museum of Natural History. He is best known as the discoverer of the first theropod embryo and for the description of feathered dinosaurs. Norell is credited with the naming of the genera ''Apsaravis'', '' Byronosaurus'', ''Citipati'', ''Tsaagan'', and ''Achillobator''. His work regularly appears in major scientific journals (including cover stories in Science and Nature) and was listed by Time magazine as one of the ten most significant science stories of 1993, 1994 and 1996. Norell is both a fellow of the Explorer's Club and the Willi Hennig Society. Career Norell's research has encompassed a number of different areas, from the theoretical study of diversity through time, his doctoral dissertation on alligator phylogeny, and his postdoctoral work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(Varanus_exanthematicus).png)