|
Estemmenosuchus
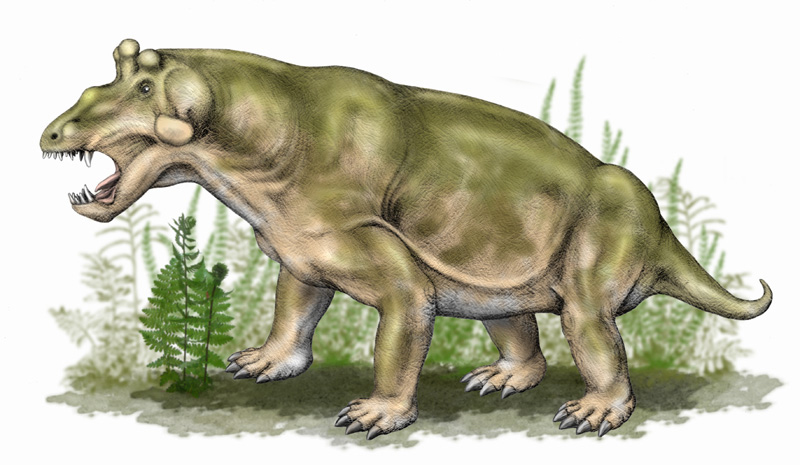
''Estemmenosuchus'' (meaning "crowned crocodile" in Greek) is an extinct genus of large, early omnivorous therapsid. It is believed and interpreted to have lived during the middle part of the Middle Permian around 267 million years ago. The two species, ''E. uralensis'' and ''E. mirabilis'', are characterised by distinctive horn-like structures, which were probably used for intra-specific display. Both species of ''Estemmenosuchus'' are from the Perm (or Cis-Urals) region of Russia. Two other estemmenosuchids, ''Anoplosuchus'' and ''Zopherosuchus'', are now considered females of the species ''E. uralensis''. There were many complete and incomplete skeletons found together. Description ''Estemmenosuchus'' could reach a body length of more than . Its skull was long and massive, up to in length, and possessed several sets of large horns, somewhat similar to the antlers of a moose, growing upward and outward from the sides and top of the head. The animal had a sprawling post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estemmenosuchus Tyrrell
''Estemmenosuchus'' (meaning "crowned crocodile" in Greek) is an extinct genus of large, early omnivorous therapsid. It is believed and interpreted to have lived during the middle part of the Middle Permian around 267 million years ago. The two species, ''E. uralensis'' and ''E. mirabilis'', are characterised by distinctive horn-like structures, which were probably used for intra-specific display. Both species of ''Estemmenosuchus'' are from the Perm (or Cis-Urals) region of Russia. Two other estemmenosuchids, ''Anoplosuchus'' and ''Zopherosuchus'', are now considered females of the species ''E. uralensis''. There were many complete and incomplete skeletons found together. Description ''Estemmenosuchus'' could reach a body length of more than . Its skull was long and massive, up to in length, and possessed several sets of large horns, somewhat similar to the antlers of a moose, growing upward and outward from the sides and top of the head. The animal had a sprawling posture a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estemmenosuchus Uralensis
''Estemmenosuchus'' (meaning "crowned crocodile" in Greek) is an extinct genus of large, early omnivorous therapsid. It is believed and interpreted to have lived during the middle part of the Middle Permian around 267 million years ago. The two species, ''E. uralensis'' and ''E. mirabilis'', are characterised by distinctive horn-like structures, which were probably used for intra-specific display. Both species of ''Estemmenosuchus'' are from the Perm (or Cis-Urals) region of Russia. Two other estemmenosuchids, ''Anoplosuchus'' and ''Zopherosuchus'', are now considered females of the species ''E. uralensis''. There were many complete and incomplete skeletons found together. Description ''Estemmenosuchus'' could reach a body length of more than . Its skull was long and massive, up to in length, and possessed several sets of large horns, somewhat similar to the antlers of a moose, growing upward and outward from the sides and top of the head. The animal had a sprawling posture a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from " pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals ( Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styracocephalus
''Styracocephalus platyrhynchus'' ('spike head') is an extinct species of tapinocephalian therapsids that lived during the Guadalupian epoch. ''Styracocephalus''s head ornament meant that it could be recognised from a distance. The most striking feature of ''Styracocephalus'' are the large backward-protruding tabular horns. The crest stuck upwards and backwards, but there is some variation in its shape, and this suggests that it changed throughout life and that it may be sexually dimorphic. ''Styracocephalus'' was a herbivore A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ... that may have been fully terrestrial or partly aquatic like the modern hippopotamus. It may have evolved from the estemmenosuchids. Its remains are known from South Africa but it probably had a wider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabular Bone
The tabular bones are a pair of triangular flat bones along the rear edge of the skull which form pointed structures known as tabular horns in primitive Teleostomi Teleostomi is an obsolete clade of jawed vertebrates that supposedly includes the tetrapods, bony fish, and the wholly extinct acanthodian fish. Key characters of this group include an operculum and a single pair of respiratory openings, feat .... References Fish anatomy Amphibian anatomy {{vertebrate-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocher Assemblage Zone
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. * Yellow ochre, , is a hydrated iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre. * Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite, which is an anhydrous iron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belebei Formation
Belebey (russian: Белебе́й; ba, Бәләбәй) is a town in the Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia, located on the bank of the Usen River, from Ufa. Population: History Belebey was established in 1715 and granted town status in 1781. Between 1865 and 1919 it was part of Ufa Governorate. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Belebey serves as the administrative center of Belebeyevsky District, even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the town of republic significance of Belebey—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, the town of republic significance of Belebey is incorporated within Belebeyevsky Municipal District as Belebey Urban Settlement.Law #126-z Demographics Ethnic composition: *Russians: 46.9% *Tatars: 23.6% *Chuvash people: 12% *Bashkirs , native_name_lang = bak , flag = File: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochyor
Ochyor (russian: Очёр), alternatively spelled Ocher, is a town and the administrative center of Ochyorsky District in Perm Krai, Russia, located on the Ochyor River (Kama's tributary), west of Perm, the administrative center of the krai. Population: History The settlement was founded in 1759 in connection with the construction of the Ocher iron foundry and ironworks, owned by Count Stroganov. In 1918, on the site of the old factory, the Ocher Machine-Building Plant was established, which produces bulldozers, pipe-layers, depth-pumping rods, etc. The city industry is represented by a casting-mechanical plant, a food processing plant, a bakery and a dairy plant. In Ocher suburbs there are concentrated deposits of gravel, peat, there are outlets of soda waters. In 1924 Ocher district was formed. On February 25, 1929 Ocher was granted a status of the settlement, on June 19, 1950 - status of the city. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotitanosuchus Olsoni
''Eotitanosuchus'' ("dawn giant crocodile") is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids whose fossils were found in the town of Ochyor in Perm Krai, Russia. It lived about 267 million years ago. The only species is ''Eotitanosuchus olsoni''. Description ''Eotitanosuchus'' is known from a single large skull without a lower jaw. The skull was , but the overall length may have been over , possibly up to and more than in weight for adult specimens. Like ''Biarmosuchus tener'', it was primitive in that, though it was a predator, the temple opening behind the eye was small, giving it a weak bite. The temple was, however, larger at the top than in other biarmosuchians. Paleoecology ''Eotitanosuchus'' fossils were found in the Perm (or Cis-Urals) region of Russia. ''Eotitanosuchus'' was without doubt a dominant animal of its environment. Found preserved in flood deposits (once coastal bogs) containing many skeletons of estemmenosuchids, it has been suggested that this large pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biarmosuchus Tener
''Biarmosuchus'' is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids that lived around 267 mya during the Middle Permian period. ''Biarmosuchus'' was discovered in the Perm region of Russia. The first specimen was found in channel sandstone that was deposited by flood waters originating from the young Ural Mountains. Description ''Biarmosuchus'' was a medium-sized predator, similar in size to a large dog, grew up to 1.5–2 m in length with a skull length 15 cm (immature) to 21 cm. It was a lightly built, probably agile animal that would have fed on smaller tetrapods. Their legs are quite long, and the animals were probably quite agile in spite of their size. A large opening for the eye and a small temple opening common in primitive stem-mammals, this lends to a weak bite but how it ate is pure speculation. The teeth contained eight small incisors on the palate, followed by a canine tooth and a further five canine teeth. So together the species contained fourteen uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



