|
Equal Franchise Society
The Equal Franchise Society (EFS) was a state-by-state organization that advocated women's suffrage in the United States. Created and joined by women of wealth, it was a conduit through which the energies of upper-class women could be channeled into political activism conducted within a socially comfortable milieu. The New York branch of the Society, for example, often held suffrage rallies at which members spoke in the street outside the Colony Club, to which many of them belonged. After the public rally, Club members would eat luncheon inside their Club. The EFS also invited anti-suffragists to meet with them for the purposes of debate. History Katherine Duer Mackay founded the Equal Franchise Society (EFS) in New York City in 1908 and also served as its president. The first meeting was held at her house on December 21, where the Constitution for the group was adopted and officers were elected. Mackey later leased offices for the group's meetings in the Madison Square Buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Franchise Society Legislative Series C
Equal(s) may refer to: Mathematics * Equality (mathematics). * Equals sign (=), a mathematical symbol used to indicate equality. Arts and entertainment * Equals (film), ''Equals'' (film), a 2015 American science fiction film * Equals (game), ''Equals'' (game), a board game * The Equals, a British pop group formed in 1965 * "Equal", a 2016 song by Chrisette Michele from ''Milestone (Chrisette Michele album), Milestone'' * "Equal", a 2022 song by Odesza featuring Låpsley from ''The Last Goodbye (album), The Last Goodbye'' * "Equals", a 2009 song by Set Your Goals from ''This Will Be the Death of Us'' * Equal (TV series), ''Equal'' (TV series), a 2020 American docuseries on HBO * = (album), ''='' (album), a 2021 album by Ed Sheeran * "=", a 2022 song by J-Hope from ''Jack in the Box (album), Jack in the Box'' Other uses * Equal (sweetener), a brand of artificial sweetener. * EQUAL Community Initiative, an initiative within the European Social Fund of the European Union. See also [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeanne Wier
Jeanne Elizabeth Wier (April 8, 1870 – April 1950) was a teacher, historian, and founder of the Nevada Historical Society. Early life Jeanne Wier was born in Grinnell, Iowa on April 8, 1870 to parents Adolphus William Wier and Elizabeth Greenside Rood Wier. She graduated as class valedictorian from Clear Lake High School, in Clear Lake, Iowa in 1886. She entered the didactics program at the Iowa State Normal School in Cedar Falls, and graduated with a bachelor's degree in 1893. In the 1890s, Wier’s family left Iowa and moved to Heppner, Oregon, where she was an assistant principal of the high school from 1893 to 1895. In that year Wier began her studies at Stanford University, where she majored in history, studying under Professor George Elliott Howard. In 1897 she began field work for her thesis in northern Nevada studying the Washoe Indians. Nevada State University In 1899, Anne Henrietta Martin, who had been teaching in the history department of Nevada State University, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Women's Rights In The United States
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Women In The United States
The history of women in the United States encompasses the lived experiences and contributions of women throughout American history. The earliest women living in what is now the United States were Native Americans. During the 19th century, women were primarily restricted to domestic roles in keeping with Protestant values. The campaign for women's suffrage in the United States culminated with the adoption of the Nineteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1920. During World War II, many women filled roles vacated by men fighting overseas. Beginning in the 1960s, the second-wave feminist movement changed cultural perceptions of women, although it was unsuccessful in passing the Equal Rights Amendment. In the 21st century, women have achieved greater representation in prominent roles in American life. The study of women's history has been a major scholarly and popular field, with many scholarly books and articles, museum exhibits, and courses in schools and universities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Voting Rights In The United States
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Suffrage In The United States
In the 1700's to early 1800's New Jersey did allow Women the right to vote before the passing of the 19th Amendment, but in 1807 the state restricted the right to vote to "...tax-paying, white male citizens..." Women's legal right to vote was established in the United States over the course of more than half a century, first in various states and localities, sometimes on a limited basis, and then nationally in 1920 with the passing of the 19th Amendment. The demand for women's suffrage began to gather strength in the 1840s, emerging from the broader movement for women's rights. In 1848, the Seneca Falls Convention, the first women's rights convention, passed a resolution in favor of women's suffrage despite opposition from some of its organizers, who believed the idea was too extreme. By the time of the first National Women's Rights Convention in 1850, however, suffrage was becoming an increasingly important aspect of the movement's activities. The first national suffrage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
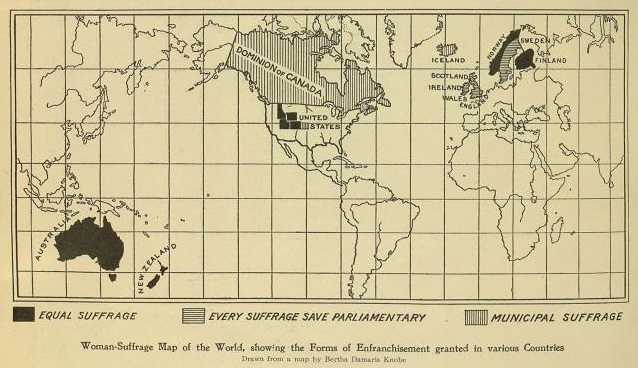
Timeline Of Women's Suffrage
Women's suffrage Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ... – the right of women to vote – has been achieved at various times in countries throughout the world. In many nations, women's suffrage was granted before universal suffrage, so women and men from certain classes or Race (classification of human beings), races were still unable to vote. Some countries granted suffrage to both sexes at the same time. This timeline lists years when women's suffrage was enacted. Some countries are listed more than once, as the right was extended to more women according to age, land ownership, etc. In many cases, the first voting took place in a subsequent year. Some women in the Isle of Man (geographically part of the British Isles but not part of the United Kingdom) gained the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Suffragists And Suffragettes
This list of suffragists and suffragettes includes noted individuals active in the worldwide women's suffrage movement who have campaigned or strongly advocated for women's suffrage, the organisations which they formed or joined, and the publications which publicized – and, in some nations, continue to publicize – their goals. Suffragists and suffragettes, often members of different groups and societies, used or use differing tactics. "Suffragette" in the British usage denotes a more " militant" type of campaigner, while suffragettes in the United States organized such nonviolent events as the Suffrage Hikes, the Woman Suffrage Procession of 1913, and the Silent Sentinels. Argentina *Cecilia Grierson (1859–1934) – the first woman physician in Argentina; supporter of women's emancipation, including suffrage *Julieta Lanteri (1873–1932) – physician, freethinker, and activist; the first woman to vote in Argentina *Alicia Moreau de Justo (1885–198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Suffrage Organizations And Publications
Major women's suffrage organizations International *International Alliance of Women – founded in 1904 to promote women's suffrage. *Woman's Christian Temperance Union – active in the suffrage movement, especially in the U.S. and New Zealand. Australia * '' Victorian Women's Suffrage Society'', founded in 1884, the local suffrage organisation of Victoria and the first suffrage organisation in Australia Belgium *''Ligue belge du droit des femmes'' (Belgian League for the Rights of Women), founded 1892, concerned with voting rights from 1912. Britain *National Society for Women's Suffrage – Britain's first large suffrage organization, founded in 1867 by Lydia Becker. *Women's Franchise League – major British group created in 1889 by Emmeline Pankhurst. *Women's Freedom League – British group founded in 1907 by 70 members of the Women's Social and Political Union in a breakaway following rules changes by Christabel Pankhurst. Bulgaria *Bulgarian Women's Union (''Bulgarski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 7th-most extensive, the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 32nd-most populous, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, Nevada, Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise, NV MSA, Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City, Nevada, Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vote, increasing the number of those parties' potential constituencies. National and international organizations formed to coordinate efforts towards women voting, especially the International Woman Suffrage Alliance (founded in 1904 in Berlin, Germany). Many instances occurred in recent centuries where women were selectively given, then stripped of, the right to vote. The first place in the world to award and maintain women's suffrage was New Jersey in 1776 (though in 1807 this was reverted so that only white men could vote). The first province to ''continuously'' allow women to vote was Pitcairn Islands in 1838, and the first sovereign nation was Norway in 1913, as the Kingdom of Hawai'i, which originally had universal suffrage in 1840, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colour") include blue-collar jobs, and most pink-collar jobs. Members of the working class rely exclusively upon earnings from wage labour; thus, according to more inclusive definitions, the category can include almost all of the working population of industrialized economies, as well as those employed in the urban areas (cities, towns, villages) of non-industrialized economies or in the rural workforce. Definitions As with many terms describing social class, ''working class'' is defined and used in many different ways. The most general definition, used by many socialists, is that the working class includes all those who have nothing to sell but their labour. These people used to be referred to as the proletariat, but that term has gone out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)

.png)

