|
Epitaph Of Pugu Yitu
The epitaph of Pugu Yitu is an inscription found inside the tomb of Pugu Yitu (; 635-678). It dates to 678 and was found in 2009 by a joint Russian-Mongolian team in Zaamar sum, Tov Province, 160 km west of Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia about 2.5 km north-east from the banks of the Tuul River and close to the 10th-century Khitan town of Khermen Denzh on the banks of the Tuul River. The inscription is currently displayed at the Zanabazar Fine Arts Museum in Ulaanbaatar. The tomb of Pugu Yitu, also called the Shoroon Dov Kurgan, showed signs of attempted looting in ancient times. The nearby tomb of Shoroon Bumbagar was never looted and therefore was found to hold far more artifacts including an intact door, many statues and wall paintings of people, dragons and temples, although there was no inscription. The tomb of Pugu Yitu is unusual in that it has an inscription. Apart from the cover inscription of Pugu Yitu measuring 75 cm x 75 cm with 4 lines of 3 characters each, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign nation. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous land empire in history. His grandson Kublai Khan conquered China proper and established the Yuan dynasty. After the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
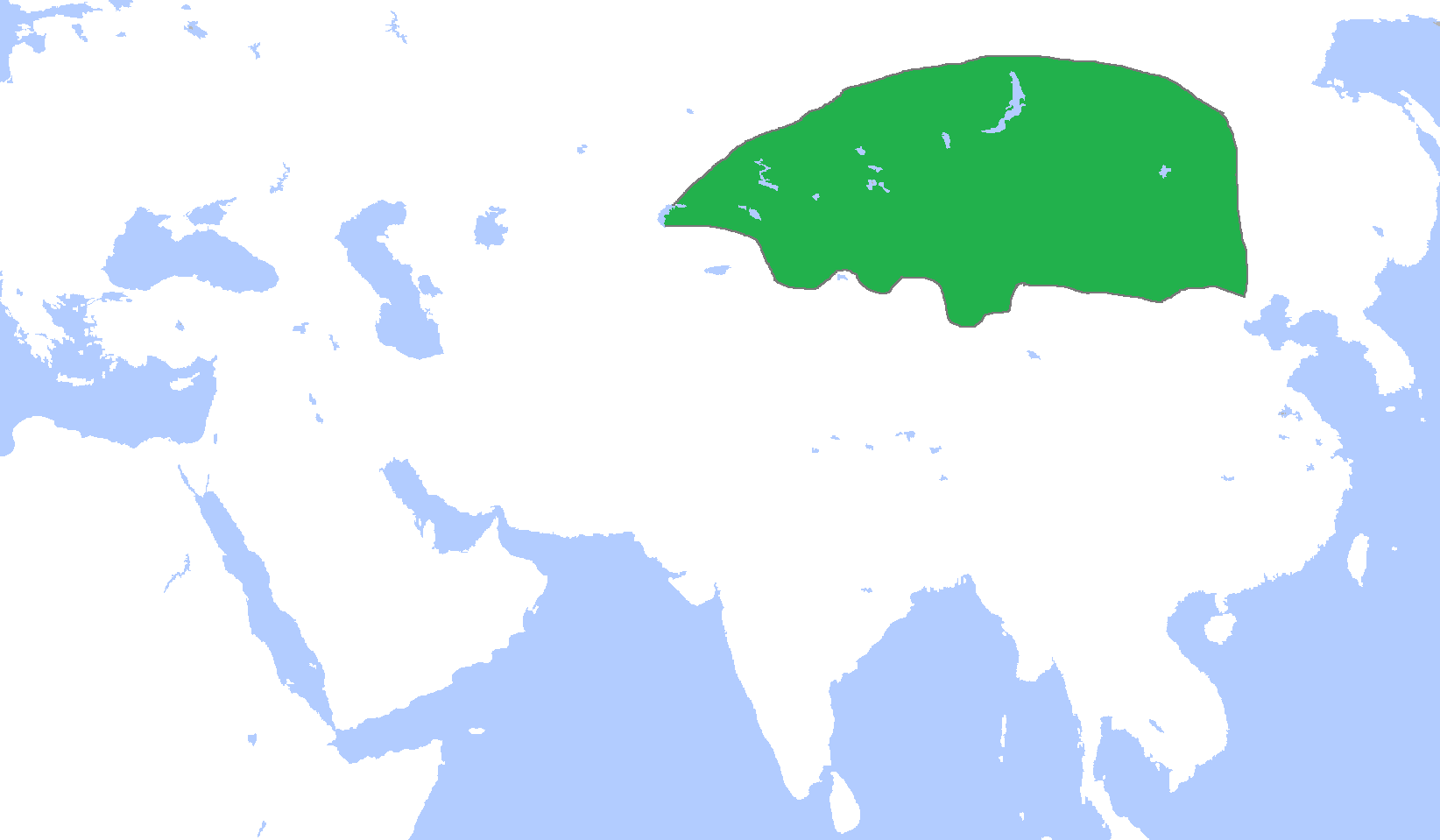
Eastern Turkic Khaganate
The Eastern Turkic Khaganate () was a Turkic khaganate formed as a result of the internecine wars in the beginning of the 7th century (AD 581–603) after the First Turkic Khaganate (founded in the 6th century in the Mongolian Plateau by the Ashina clan) had splintered into two polities – one in the east and the other in the west. Finally, the Eastern Turkic Khaganate was defeated and absorbed by the Tang dynasty, and Xueyantuo occupied the territory of the former Turkic Khaganate. History Outline In 552-555 the Göktürks replaced the Rouran Khaganate as the dominant power on the Mongolian Plateau, forming the First Turkic Khaganate (552-630). They quickly spread west to the Caspian Sea. Between 581 and 603 the Western Turkic Khaganate in Central Asia separated from the Eastern Khaganate in the Mongolian Plateau. In the early period the Central Plain regimes were weak and paid tribute to the Turks at times. The Tang dynasty eventually overthrew the Eastern Turks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Mongolia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Arts Zanabazar Museum
The Fine Arts Zanabazar Museum ( Mongolian: Занабазарын нэрэмжит Дүрслэх урлагийн музей) is an art museum located in Ulaanbaatar, capital of Mongolia, and founded in 1966. It exhibits collections of Mongolian masters of fine arts from the 18th to the 20th century and works in cooperation with the UNESCO for improving the presentation of its collections. History The building where the museum is located was built by a Russian merchant in 1905. During this time it was used as a bank. In 1965, the chairman of the Mongolian Craftsmen's Union Committee proposed the idea of creating an art museum to help preserve Mongolia's heritage. On July 23, 1966, the museum opened to the public for the first time. In the period from 1966 to 1989, the museum's exhibitions were held in Moscow, Kyiv, Sofia, Bratislava, Baku, Budapest, Saint Petersburg, Tashkent, Ulan-Ude and Erfurt. In 1968, about 194 exhibitions from the People's Republic of China were transferre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bain Tsokto Inscriptions
The Tonyukuk inscriptions (), also called the Bain Tsokto inscriptions are Turkic inscriptions of the 8th century located in modern-day Mongolia. They are the oldest written attestations of the Turkic language family, predating the Orkhon inscriptions (Khöshöö Tsaidam monuments) by several years. Geography The inscriptions are in Tuul River valley at (southeast of Ulan Bator and Nalaikh). They are often confused with, or considered as a part of, the Orkhon inscriptions (Khöshöö Tsaidam inscriptions), although the Orkhon inscriptions are actually located about to the west of Bain Tsokto. History Bain Tsokto inscriptions are about Tonyukuk, the counselor of four Turkic khagans -- Ilterish Khagan, Kapaghan Khagan, Inel Khagan and Bilge Khagan -- of the Second Turkic Khaganate. He died in the 720s. Unlike the two other Orkhon inscriptions which were erected after the hero had died, Bain Tsokto inscriptions were erected by Tonyukuk himself around the year 716. (His deeds af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 38th king, Trisong Detsen. The 821–823 treaty concluded between the Tibetan Empire and the Tang dynasty delineated the former as being in possession of an area larger than the Tibetan Plateau, stretching east to Chang'an, west beyond modern Afghanistan, and south into modern India and the Bay of Bengal. The Yarlung dynasty was founded in 127 BC in the Yarlung Valley. The Yarlung capital was moved to Lhasa by the 33rd king Songsten Gampo, and into the Red Fort during the imperial period which continued to the 9th century. The beginning of the imperial period is marked in the reign of the 33rd king of the Yarlung dynasty, Songtsen Gampo. The power of Tibet's military empire gradually increased over a diverse terrain. During the reign of Tris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohe People
The Mohe, Malgal, or Mogher, or Mojie, were an East Asian Tungusic people who lived primarily in the modern geographical region of Northeast Asia. The two most powerful Mohe groups were known as the Heishui Mohe, located along the Amur River, and the Sumo Mohe, named after the Songhua River. The Mohe constituted a major part of the population in the kingdom of Balhae in northeast Asia, which lasted from the late 7th century to early 10th century. After the fall of Balhae, few historical traces of the Mohe can be found, though they are considered to be the primary ethnic group from whom the Jurchen people descended. The Heishui Mohe in particular are considered to be the direct ancestors of the Jurchens, from whom the 17th century Manchu people and Qing dynasty founders originated.Huang, P.: "New Light on the origins of the Manchu," ''Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies'', vol. 50, no.1 (1990): 239-82. Retrieved from JSTOR database July 18, 2006. The Mohe practiced a sedentary agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Tai
Mount Tai () is a mountain of historical and cultural significance located north of the city of Tai'an. It is the highest point in Shandong province, China. The tallest peak is the '' Jade Emperor Peak'' (), which is commonly reported as being tall. Mount Tai is known as the eastern mountain of the Sacred Mountains of China. It is associated with sunrise, birth, and renewal, and is often regarded the foremost of the five. Mount Tai has been a place of worship for at least 3,000 years and served as one of the most important ceremonial centers of China during large portions of this period. Because of its sacred importance and dramatic landscape, it was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987. It meets 7 of the 10 evaluation standards of World Heritage, and is listed as a World Heritage site that meets the most standards, along with the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area in Australia. An earthquake or thunderstorm occurred in Mount Tai in 1831 BC or 1652 BC, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gaozong Of Tang
Emperor Gaozong of Tang (21 July 628 – 27 December 683), personal name Li Zhi, was the third emperor of the Tang dynasty in China, ruling from 649 to 683; after January 665, he handed power over the empire to his second wife Empress Wu (the future Wu Zetian), and her decrees were carried out with greater force than the decrees of Emperor Gaozong's. Emperor Gaozong was the youngest son of Emperor Taizong and Empress Zhangsun; his elder brothers were Li Chengqian and Li Tai. Emperor Gaozong's reign saw the primacy of Empress Wu, who became the effective power behind the Tang rule. Emperor Gaozong was aided in his rule by Empress Wu during the later years of his reign after a series of strokes left him incapacitated. Emperor Gaozong effectively after January 665 delegated all matters of state to his strong wife; After that Empress Wu acted as the power behind the emperor, "hanging the curtain and listening to politics" (''Chuílián tīngzhèng'' 垂簾聼政). Gaozong's person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xueyantuo
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele people, Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, Eastern Göktürks. Names Xue ''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ''Xinli'' 薪犁 in Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian, vol. 110 but were not referred to again until the 7th century. Peter B. Golden, Golden (2011) proposed that 薛 Xue's Old Turkic form ''Sir'' derived from Sanskrit ''Shri, Śrī'' "fortunate, auspicious" Yantuo The etymology of ''Yantuo'' 延陀 is much debated. It was first identified with ''Tarduš'', one of two divisions, besides ''Töliš'', of the short-lived Xueyantuo Qaghanate, by Western Orientalists (like Vilhelm Thomsen) who considered ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' to be tribal names. The ethnonym is thus reconstructable as Syr-Tardush. However, Chinese scholars viewed ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' as names of political organizations or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaamar
Zaamar ( mn, Заамар) is a sum of Töv Province in Mongolia. It is one of the largest sums in Mongolia with a total area of 2,900 square kilometres and a population of 37,500 and 7,500 households. Geography The Zaamar range is home to birch, poplar, and ebony trees. Wildlife consists of wolves, red deer, foxes, corsac fox, gazelle, roe deer, and marmot Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, w .... Districts of Töv Province {{Mongolia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)