|
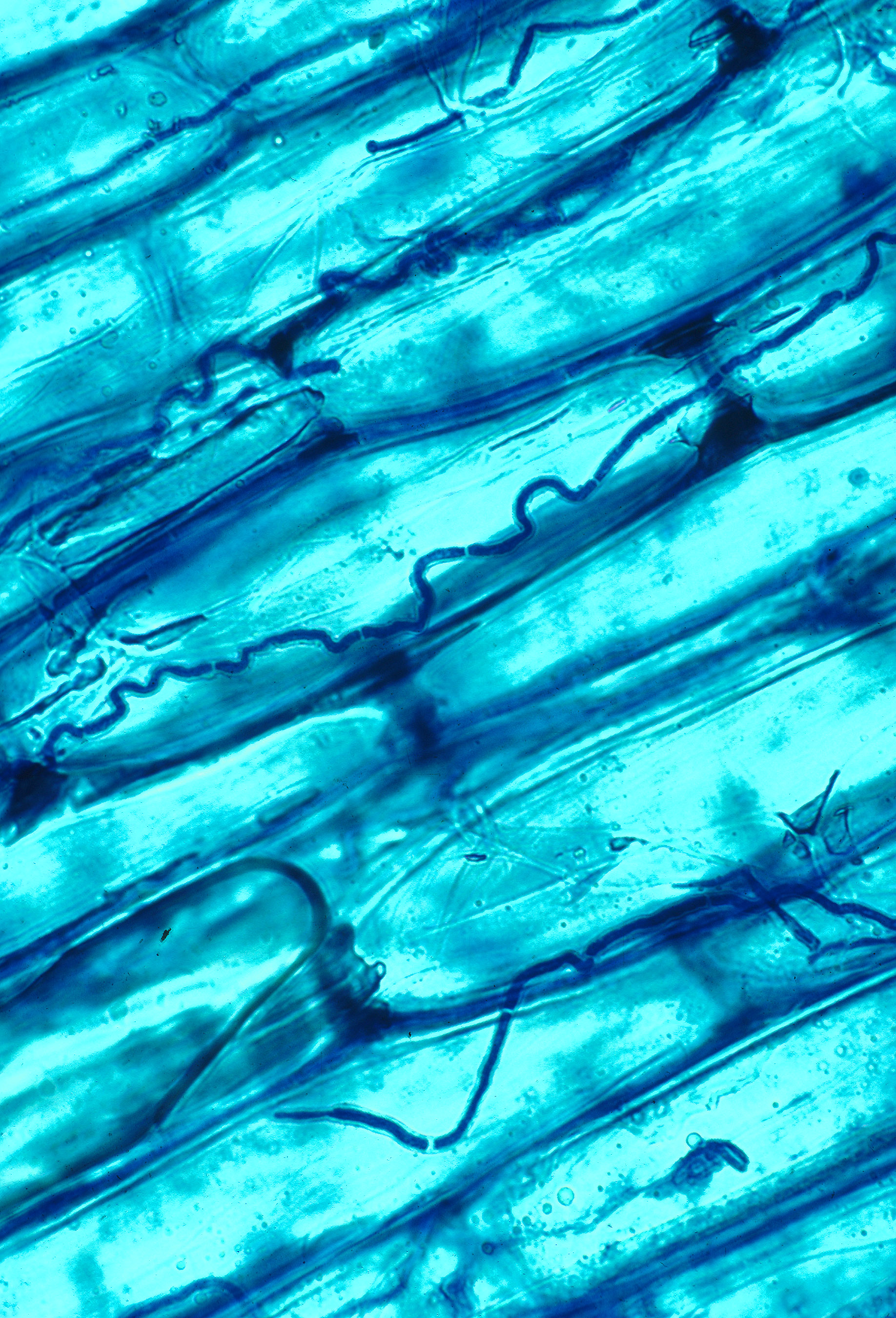
Epichloë Elymi
''Epichloë elymi'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. A systemic and seed-transmissible grass symbiont first described in 1999, ''Epichloë elymi'' is a sister lineage to ''Epichloë bromicola''. ''Epichloë elymi'' is found in North America, where it has been identified in ''Bromus kalmii'' and some species of ''Elymus'', including ''E. patula'' and ''E. virginicus''. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Epichloe elymi elymi The Elymians ( grc-gre, Ἔλυμοι, ''Élymoi''; Latin: ''Elymi'') were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity. Origins According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, the Elymians ... Fungi described in 1999 Fungi of North America Fungus species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymus Virginicus
''Elymus virginicus'', or Virginia wildrye, is a perennial bunchgrass located in Virginia and the eastern United States. Virginia wild rye is one of the few cool season native grasses found in the east Texas area. It is extremely palatable to livestock and will decrease without proper grazing management. It spreads via seed and tillering. It can be confused with Canadian wild rye which is a more robust plant with longer awns. It should be cut early in the season when used for hay to avoid ergot contamination. Northern Missouri Germplasm Virginia wild rye was released in 1999 by the Missouri Plant Material Center for use in northern Missouri. Description * Cool season * Perennial * Bunch grass * Variable color, green - silver blue * 2 – 4 feet tall * Seed head has dense, medium length awns * Seed head 2 - 6 inches in length ;Uses * Pasture and hay * Restoration * Erosion control * Wildlife habitat * Buffer strips ;Key characteristics * Seed head remains straight at maturity * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats ( stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Bromicola
''Epichloë bromicola'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. A systemic and seed-transmissible grass symbiont first described in 1998, ''Epichloë bromicola'' is a sister lineage to '' Epichloë elymi''. ''Epichloë bromicola'' is found from Europe to Asia, where it has been identified in many species of grasses. In Europe, it has been associated with '' Bromus benekenii'', ''Bromus erectus'', '' Bromus ramosus'', '' Elymus repens'', '' Hordelymus europaeus'' and ''Hordeum brevisubulatum''. In Asia, it has been found in '' Leymus chinensis'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis''. The sexual phase has been observed on ''Bromus erectus'', '' Elymus repens'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis''. Seed transmission has been seen in '' Bromus benekenii'', '' Bromus ramosus'', '' Hordelymus europaeus'', ''Hordeum brevisubulatum'', '' Leymus chinensis'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis'', but is known to be absent in ''Bromus erectus ''Bromus erectus'', commonly known as erect br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromus Kalmii
''Bromus kalmii'', Kalm's brome, is a species of Bromus, brome grass. It is a native bunchgrass in the North-central and Northeastern United States, the Great Lakes region (North America), Great Lakes region, and eastern Canada. The Botanical name#Components of plant names, specific epithet ''kalmii'' refers to its discoverer Pehr Kalm. Description ''Bromus kalmii'' is a perennial grass, with solitary or slightly tufted Culm (botany), culms that grow tall. The culms are pubescent just below the nodes. The grass typically has three to five and occasionally six leaf blades. The firm and scabrous leaf blades are either pubescent or glabrous and are long and wide. The glabrous or sometimes shaggy sheaths are mostly shorter than the Internode (botany), internodes and each have a V-shaped cleft. The ligule is typically long. The narrow, crowded panicle is long. The lower branches of the panicle are very slender and each bear one or two spikelets. The five to eleven flowered spike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymus (plant)
''Elymus'' is a genus of perennial plants with approximately 150 species in the grass family, related to rye, wheat, and other widely grown cereal grains. ''Elymus'' is a cosmopolitan genus, represented by species across all continents of the world. Common names include couch grass, wildrye and wheatgrass. Species Species accepted by the Plants of the World Online as of 2021: ref name=POWO> *''Elymus abolinii'' *''Elymus aenaeanus'' *'' Elymus afghanicus'' *'' Elymus africanus'' *'' Elymus alaskanus'' *'' Elymus albicans'' *'' Elymus alienus'' *'' Elymus alpinus'' *'' Elymus altissimus'' *'' Elymus amgensis'' *'' Elymus angsaiensis'' *''Elymus angulatus'' *'' Elymus angustispiculatus'' *''Elymus anthosachnoides'' *'' Elymus antiquus'' *'' Elymus × apiculatus'' *''Elymus arcuatus'' *''Elymus aristiglumis'' *''Elymus arizonicus'' *''Elymus athericus'' *''Elymus atratus'' *''Elymus bakeri'' *''Elymus barbicallus'' *''Elymus barystachyus'' *''Elymus bori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymus Hystrix
''Elymus hystrix'', known as eastern bottlebrush grass, or bottle-brush-grass, is a bunchgrass in the grass family, Poaceae. It is native to the Eastern United States and Eastern Canada. Description ''Elymus hystrix'' is a herbaceous plant with alternate, simple leaves, on erect stems. The flowers are white and bloom in spring. ''Elymus hystrix'' ranges from approximately two and a half to four and a half feet in height. There are usually two spikelets at each of the five to nine nodes of the plant. Unlike some similar native grasses, the blades of ''Elymus hystrix'' do not have glumes surrounding its spikelets. ''Elymus hystrix'' is self-compatible; that is, it can reproduce using its own pollen. ''Elymus hystrix'' is a perennial meaning it does not completely die at the end of each season, but comes back the next year. ''Elymus hystrix'' has four copies of its genome, exhibiting a type of polyploidy called tetraploidy. Taxonomy ''Elymus hystrix'' was first described by Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1999
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of North America
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |