|
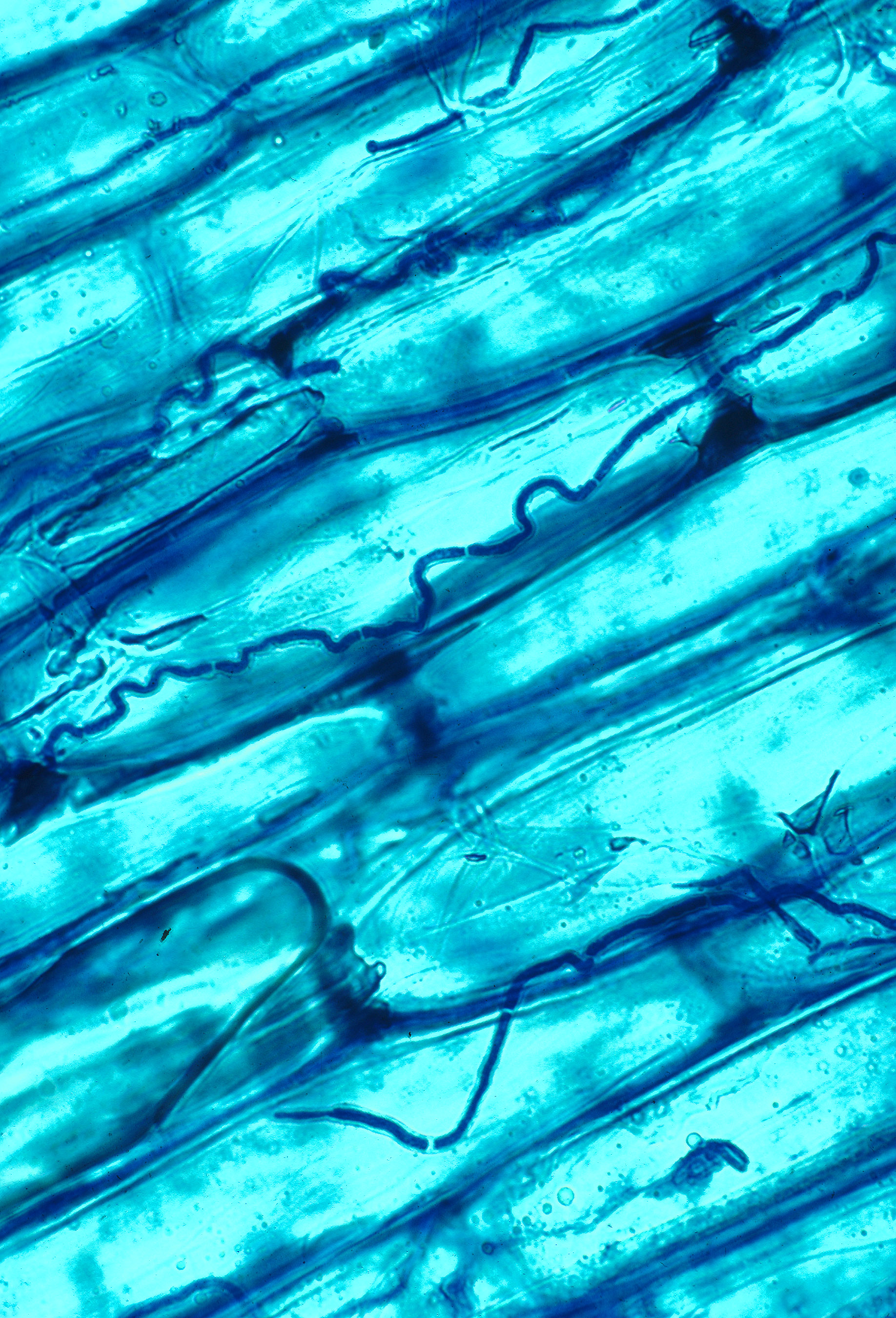
Epichloë Bromicola
''Epichloë bromicola'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. A systemic and seed-transmissible grass symbiont first described in 1998, ''Epichloë bromicola'' is a sister lineage to '' Epichloë elymi''. ''Epichloë bromicola'' is found from Europe to Asia, where it has been identified in many species of grasses. In Europe, it has been associated with '' Bromus benekenii'', ''Bromus erectus'', '' Bromus ramosus'', '' Elymus repens'', '' Hordelymus europaeus'' and ''Hordeum brevisubulatum''. In Asia, it has been found in '' Leymus chinensis'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis''. The sexual phase has been observed on ''Bromus erectus'', '' Elymus repens'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis''. Seed transmission has been seen in '' Bromus benekenii'', '' Bromus ramosus'', '' Hordelymus europaeus'', ''Hordeum brevisubulatum'', '' Leymus chinensis'' and ''Elymus tsukushiensis'', but is known to be absent in ''Bromus erectus ''Bromus erectus'', commonly known as erect br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats ( stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Elymi
''Epichloë elymi'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. A systemic and seed-transmissible grass symbiont first described in 1999, ''Epichloë elymi'' is a sister lineage to ''Epichloë bromicola''. ''Epichloë elymi'' is found in North America, where it has been identified in ''Bromus kalmii'' and some species of ''Elymus'', including ''E. patula'' and ''E. virginicus''. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Epichloe elymi elymi The Elymians ( grc-gre, Ἔλυμοι, ''Élymoi''; Latin: ''Elymi'') were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity. Origins According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, the Elymians ... Fungi described in 1999 Fungi of North America Fungus species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromus Benekenii
''Bromus benekenii'' is a species of grass in the family Poaceae Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns an .... Its native range is Northwestern Africa, Europe to China. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q165102 benekenii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromus Erectus
''Bromus erectus'', commonly known as erect brome, upright brome or meadow brome, is a dense, course, tufted perennial grass. It can grow to . Like many brome grasses the plant is hairy. The specific epithet ''erectus'' is Latin, meaning "erect". The diploid number of the grass is 56. Description ''Bromus erectus'' is a perennial, tufted grass with basal tufts of cespitose leaves that is nonrhizomatous. The culms grow between in height. The internodes are typically glabrous. The flattened cauline leaves have pubescent or glabrous sheaths. The leaf blades are long and wide. The grass lacks auricles and the ligule is blunt but finely serrated, sometimes with hairy edges. The contracted and ellipsoid panicle is usually upright, rather than nodding, measuring long. The lanceolate spikelets are long and have five to twelve flowers. The glume In botany, a glume is a bract (leaf-like structure) below a spikelet in the inflorescence (flower cluster) of grasses (Poaceae) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromus Ramosus
''Bromus ramosus'', the hairy brome, is a bunchgrass in the grass family Poaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The name '' Bromus'' comes from the term brome, meaning oats. Unlike most other bromes (''Bromus'' sp.), it grows in shady sites under trees. Description ''Bromus ramosus'' is a perennial herbaceous bunchgrass, typically reaching tall. The leaves are long, usually drooping, long and wide, and finely hairy.Umberto Quattrocchi (2006) ''CRC World Dictionary of Grasses: Common Names, Scientific Names, Eponyms, Synonyms, and Etymology'' Volume I The flower A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechani ... spike is gracefully arched with pendulous spikelets on long slender stems in pairs on the main stem. Subspecies *''Bromus ramosus'' subsp. ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymus Repens
''Elymus repens'', commonly known as couch grass, is a very common perennial species of grass native to most of Europe, Asia, the Arctic biome, and northwest Africa. It has been brought into other mild northern climates for forage or erosion control, but is often considered a weed. Other names include common couch, twitch, quick grass, quitch grass (also just quitch), dog grass, quackgrass, scutch grass, and witchgrass.Flora of NW Europe''Elytrigia repens''/ref>Flora of China''Elytrigia repens''/ref> Description It has creeping rhizomes which enable it to grow rapidly across grassland. It has flat, hairy leaves with upright flower spikes. The stems ( 'culms') grow to 40–150 cm tall; the leaves are linear, 15–40 cm long and 3–10 mm broad at the base of the plant, with leaves higher on the stems 2–8.5 mm broad. The flower spike is 10–30 cm long, with spikelets 1–2 cm long, 5–7 mm broad and 3 mm thick with three to eight florets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hordelymus Europaeus
''Hordelymus'' is a genus of European, north African, and southwest Asian plants in the grass family. The only known species is ''Hordelymus europaeus,'' native to Europe (from Sweden + Ireland to Spain, Italy, and Russia) as well as North Africa (Algeria + Morocco) and southwestern Asia (Turkey + Caucasus). Wood-barley is a common name for ''H. europaeus''. ;formerly included see ''Taeniatherum ''Taeniatherum'' is a genus of Eurasian and North African plants in the grass family known by the common name medusahead. The only recognized species is ''Taeniatherum caput-medusae'' and is native to southern and central Europe (from Portugal ...'' * ''Hordelymus asper - Taeniatherum caput-medusae'' * ''Hordelymus caput-medusae - Taeniatherum caput-medusae'' References Pooideae Monotypic Poaceae genera Flora of Europe {{Pooideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hordeum Brevisubulatum
''Hordeum brevisubulatum'' is a widespread species of wild barley ''Hordeum spontaneum'', commonly known as wild barley or spontaneous barley, is the wild form of the grass in the family Poaceae that gave rise to the cereal barley (''Hordeum vulgare''). Domestication is thought to have occurred on two occasio ... native to temperate and subarctic Eastern Europe and Asia. A halophyte, it prefers to grow in saline grasslands. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q12218925 brevisubulatum Plants described in 1844 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leymus Chinensis
''Leymus chinensis'', commonly known as false wheatgrass or Chinese rye grass, is a species of wild rye Wild rye is a common name used for several grasses. Wild ryes belong to any of three genera: * '' Elymus'' (wheatgrasses) * ''Leymus ''Leymus'' is a genus of plants in the grass family Poaceae (Gramineae). It is widespread across Europe, Asia, ... native to China, Korea, Mongolia and Russia. Description ''Leymus chinensis'' is a perennial plant that is normally 40–90 cm tall and is native to northern China. It is a plant that can potentially be used as a food source in future generations. Scientists have tested the effects of various stimuli on ''Leymus chinensis''. If optimum conditions for the growth of this plant are discovered, then this plant has the capability to eventually become a potential food source for humanity. Temperature and light effects on germination Temperature and light greatly affect the germination of several species of grasses. ''Leymus chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymus Tsukushiensis
{{disambig ...
Elymus may refer to: * ''Elymus'' (plant), a genus of grasses * Elymus (mythology), the mythical ancestor of the Elymians * A man killed by Gorge (mythology) In Greek mythology, Gorge( grc, Γόργη, comes from the adjective ''gorgos,'' "terrible" or "horrible") may refer to: *Gorge, a Libyan princess as one of the Danaïdes, daughters of King Danaus. Her mother was either the hamadryads Atlanteia or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1998
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |