|
Environmentally Extended Input–output Analysis
Environmentally extended input–output analysis (EEIOA) is used in environmental accounting as a tool which reflects production and consumption structures within one or several economies. As such, it is becoming an important addition to material flow accounting. Introduction In recognition of the increasing importance of global resource use mediated by international trade for environmental accounting and policy, new perspectives have been and are currently being developed within environmental accounting. The most prominent among these are consumption-based accounts compiled using environmentally extended input-output analysis. Consumption-based indicators of material use are commonly referred to as “material footprints” (comparable to carbon footprints and water footprints) or as raw material equivalents (RME) for imported and exported goods. Raw material equivalents or material footprints of traded goods comprise the material inputs required along the entire supply chain associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Accounting
Environmental accounting is a subset of accounting proper, its target being to incorporate both economic and environmental information. It can be conducted at the corporate level or at the level of a national economy through the System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting, a satellite system to the National Accounts of Countries (among other things, the National Accounts produce the estimates of gross domestic product otherwise known as GDP). Environmental accounting is a field that identifies resource use, measures and communicates costs of a company's or national economic impact on the environment. Costs include costs to clean up or remediate contaminated sites, environmental fines, penalties and taxes, purchase of pollution prevention technologies and waste management costs. An environmental accounting system consists of environmentally differentiated conventional accounting and ecological accounting. Environmentally differentiated accounting measures effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Accounting
Greenhouse gas inventories are emission inventories of greenhouse gas emissions that are developed for a variety of reasons. Scientists use inventories of natural and anthropogenic (human-caused) emissions as tools when developing atmospheric models. Policy makers use inventories to develop strategies and policies for emissions reductions and to track the progress of those policies. Regulatory agencies and corporations also rely on inventories to establish compliance records with allowable emission rates. Businesses, the public, and other interest groups use inventories to better understand the sources and trends in emissions. Unlike some other air emission inventories, greenhouse gas inventories include not only emissions from source categories, but also removals by carbon sinks. These removals are typically referred to as carbon sequestration. Greenhouse gas inventories typically use Global warming potential (GWP) values to combine emissions of various greenhouse gases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Economics
Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied subject due to growing environmental concerns in the twenty-first century. Environmental economics "undertakes theoretical or empirical studies of the economic effects of national or local environmental policies around the world. ... Particular issues include the costs and benefits of alternative environmental policies to deal with air pollution, water quality, toxic substances, solid waste, and global warming." Environmental economics is distinguished from ecological economics in that ecological economics emphasizes the economy as a subsystem of the ecosystem with its focus upon preserving natural capital. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing "strong" sustainability and rejecting the proposition that human-made ("physical") capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wassily Leontief
Wassily Wassilyevich Leontief (russian: Васи́лий Васи́льевич Лео́нтьев; August 5, 1905 – February 5, 1999), was a Soviet-American economist known for his research on input–output analysis and how changes in one economic sector may affect other sectors. Leontief won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1973, and four of his doctoral students have also been awarded the prize (Paul Samuelson 1970, Robert Solow 1987, Vernon L. Smith 2002, Thomas Schelling 2005). Biography Early life Wassily Leontief was born on August 5, 1905, in Munich, Germany, the son of Wassily W. Leontief (professor of Economics) and Zlata (German spelling ''Slata''; later Evgenia) Leontief (née Becker). Wassily Leontief Sr. belonged to a family of Russian old-believer merchants living in St. Petersburg since 1741. Evgenia (Genya) Becker belonged to a wealthy Jewish family from Odessa. At 15 in 1921, Wassily Jr. entered University of Leningrad in present-day St. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Metabolism
Urban metabolism is a scientific modelling, model to facilitate the description and analysis of the material flow, flows of the materials and energy transfer, energy within cities, such as undertaken in a material flow analysis of a city. It provides researchers with a metaphorical framework to study the interactions of natural and human systems in specific regions.Pincetl, S., Bunje, P., & Holmes, T. (2012). An expanded urban metabolism method: Toward a systems approach for assessing urban energy processes and causes. Landscape and Urban Planning, 193-202. From the beginning, researchers have tweaked and altered the parameters of the urban metabolism model. C. Kennedy and fellow researchers have produced a clear definition in the 2007 paper ''The Changing Metabolism of Cities'' claiming that urban metabolism is "the sum total of the technical and socio-economic process that occur in cities, resulting in growth, production of energy and elimination of waste."Kennedy, C., Cuddihy, J., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Metabolism
Social metabolism or socioeconomic metabolism is the set of flows of materials and energy that occur between nature and society, between different societies, and within societies. These human-controlled material and energy flows are a basic feature of all societies but their magnitude and diversity largely depend on specific cultures, or sociometabolic regimes. El metabolismo social: una nueva teoría socioecológica. Relaciones. 2013. Social or socioeconomic metabolism is also described as "the self-reproduction and evolution of the structures of human soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Flow Analysis
Material flow analysis (MFA), also referred to as substance flow analysis (SFA), is an analytical method to quantify flows and stocks of materials or substances in a well-defined system. MFA is an important tool to study the bio-physical aspects of human activity on different spatial and temporal scales. It is considered a core method of industrial ecology or anthropogenic, urban, social and industrial metabolism. MFA is used to study material, substance, or product flows across different industrial sectors or within ecosystems. MFA can also be applied to a single industrial installation, for example, for tracking nutrient flows through a waste water treatment plant. When combined with an assessment of the costs associated with material flows this business-oriented application of MFA is called material flow cost accounting. MFA is an important tool to study the circular economy and to devise material flow management. Since the 1990s, the number of publications related to mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
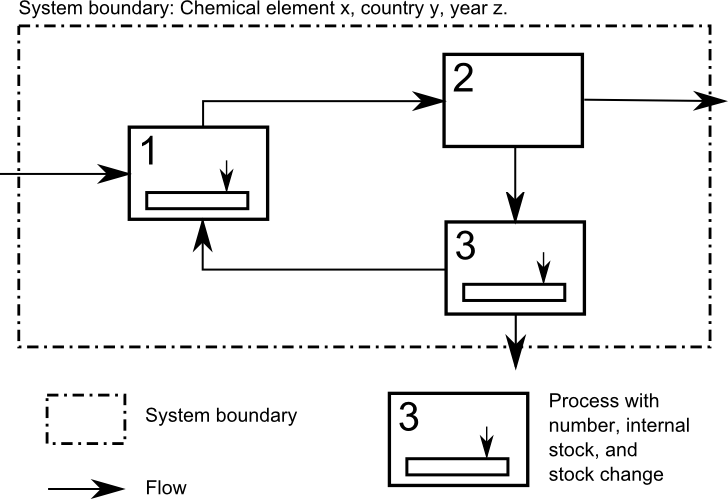
Material Flow Accounting
Material flow accounting (MFA) is the study of material flows on a national or regional scale. It is therefore sometimes also referred to as regional, national or economy-wide material flow analysis. Introduction Material flow accounting provides economy-wide data on material use. Through international standardization, this data has become reliable and comparable across countries. Increasingly, the data are also being made available in medium- to long-term time series allowing for the analysis of past trends as well as potential future developments. Material flow accounts provide information on the material inputs into, the changes in material stock within, and the material outputs in the form of exports to other economies or discharges to the environment of an economy. Material flow accounting can be used in national planning, especially for scarce resources, and also allows for forecasting. The method can be used to assess environmental burdens associated with the economic activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Metabolism
Industrial metabolism is a concept to describe the material and energy turnover of industrial systems. It was proposed by Robert Ayres in analogy to the biological metabolism as "the whole integrated collection of physical processes that convert raw materials and energy, plus labour, into finished products and wastes..." In analogy to the biological concept of metabolism, which is used to describe the whole of chemical reactions in, for example, a cell to maintain its functions and reproduce itself, the concept of industrial metabolism describes the chemical reactions, transport processes, and manufacturing activities in industry. Industrial metabolism presupposes a connection between different industrial activities by seeing them as part of a larger system, such as a material cycle or the supply chain of a commodity. System scientists, for example in industrial ecology, use the concept as paradigm to study the flow of materials or energy through the industrial system in order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Emissions
One way of attributing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is to measure the embedded emissions of goods that are being consumed (also referred to as "embodied emissions", "embodied carbon emissions", or "embodied carbon"). This is different from the question of to what extent the policies of one country to reduce emissions affect emissions in other countries (the "spillover effect" and "carbon leakage" of an emissions reduction policy). The UNFCCC measures emissions according to production, rather than consumption. Consequently, embedded emissions on imported goods are attributed to the exporting, rather than the importing, country. The question of whether to measure emissions on production instead of consumption is partly an issue of equity, i.e., who is responsible for emissions. The 37 Parties listed in Annex B to the Kyoto Protocol have agreed to legally binding emission reduction commitments. Under the UNFCCC accounting of emissions, their emission reduction commitments do not in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Flow Accounting
Material flow accounting (MFA) is the study of material flows on a national or regional scale. It is therefore sometimes also referred to as regional, national or economy-wide material flow analysis. Introduction Material flow accounting provides economy-wide data on material use. Through international standardization, this data has become reliable and comparable across countries. Increasingly, the data are also being made available in medium- to long-term time series allowing for the analysis of past trends as well as potential future developments. Material flow accounts provide information on the material inputs into, the changes in material stock within, and the material outputs in the form of exports to other economies or discharges to the environment of an economy. Material flow accounting can be used in national planning, especially for scarce resources, and also allows for forecasting. The method can be used to assess environmental burdens associated with the economic activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Accounts
System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA)System of Environmental-Economic Accounting 2012: Central Framework – final, official publication 2012, UN, EC, IMF, OECD and World Ban"System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting" United Nations, European Commission, International Monetary Fund, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and World Bank 2012, 378 pp. is a framework to compile statistics linking environmental statistics to economic statistics. SEEA is described as a satellite system to the United Nations System of National Accounts (SNA).EC, IMF, OECD, UN & World Ban"System of National Accounts 2008" European Commission, International Monetary Fund, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, United Nations and World Bank, New York, Dec. 2009, 1993, lvi + 662 pp. This means that the definitions, guidelines and practical approaches of the SNA are applied to the SEEA. This system enables environmental statistics to be compared t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |