|
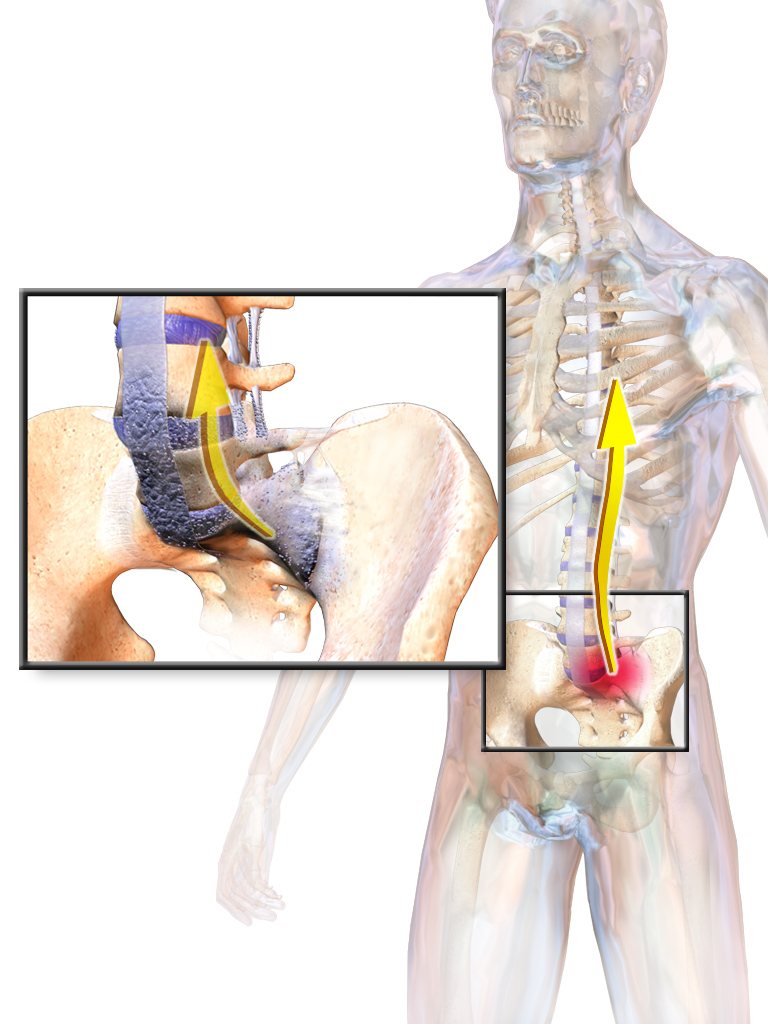
Entheses
The enthesis (plural entheses) is the connective tissue between tendon or ligament and bone. There are two types of entheses: ''Fibrous entheses'' and ''fibrocartilaginous entheses''. In a fibrous enthesis, the collagenous tendon or ligament directly attaches to the bone. In a fibrocartilaginous enthesis, the interface presents a gradient that crosses four transition zones: # Tendinous area displaying longitudinally oriented fibroblasts and a parallel arrangement of collagen fibres # Fibrocartilaginous region of variable thickness where the structure of the cells changes to chondrocytes # Abrupt transition from cartilaginous to calcified fibrocartilage—often called 'tidemark' or 'blue line' # Bone Clinical significance A disease of the entheses is known as an ''enthesopathy'' or ''enthesitis''. Enthetic degeneration is characteristic of spondyloarthropathy and other pathologies. The enthesis is the primary site of disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Society and culture Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthesopathy
An enthesopathy refers to a disorder involving the attachment of a tendon or ligament to a bone. This site of attachment is known as the enthesis (pl. entheses). If the condition is known to be inflammatory, it can more precisely be called an enthesitis. Forms Enthesopathy can occur at the shoulder, elbow, wrist, carpus, hip, knee, ankle, tarsus, or heel bone, among other regions. Enthesopathies may take the form of spondyloarthropathies (joint diseases of the spine) such as ankylosing spondylitis, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendinitis. Further examples include: * Adhesive capsulitis of shoulder * Rotator cuff syndrome of shoulder and allied disorders * Periarthritis of shoulder * Scapulohumeral fibrositis * Synovitis of hand or wrist * Periarthritis of wrist * Gluteal tendinitis * Iliac crest spur * Psoas tendinitis * Trochanteric tendinitis Causes Generalized involvement of the entheses with calcification of tendon and ligament insertions and of joint capsules has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthesitis
Enthesitis is inflammation of the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone. It is an enthesopathy, a pathologic condition of the entheses. Early clinical manifestations are an aching sensation akin to "working out too much", and it gets better with activity. It is worse in the morning (after sleeping and not moving). The muscle insertion hurts very focally as it joins into the bone, but there is little to no pain at all with passive motion. There are some cases of isolated, primary enthesitis which are very poorly studied and understood. It is known to be associated with other autoimmune diseases, like spondyloarthropathies and psoriasis (thought to often precede psoriatic arthritis). A common autoimmune enthesitis is at the heel, where the Achilles tendon attaches to the calcaneus. It is associated with HLA B27 arthropathies, such as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. Symptoms include multiple points of tenderness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondyloarthropathy
Spondyloarthropathy or spondyloarthrosis refers to any joint disease of the vertebral column. As such, it is a class or category of diseases rather than a single, specific entity. It differs from spondylopathy, which is a disease of the vertebra itself, but many conditions involve both spondylopathy and spondyloarthropathy. Spondyloarthropathy with inflammation is called axial spondyloarthritis. In the broadest sense, the term spondyloarthropathy includes joint involvement of vertebral column from any type of joint disease, including rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, but the term is often used for a specific group of disorders with certain common features, which are often specifically termed seronegative spondylarthropathies. They have an increased incidence of HLA-B27, as well as negative rheumatoid factor and ANA. Enthesopathy is also sometimes present in association with seronegative . Non-vertebral signs and symptoms of degenerative or other not directly infected inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips, eye and bowel problems may occur as well as back pain. Joint mobility in the affected areas generally worsens over time. Although the cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 85% of those affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no known cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, exercise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioarchaeology
The term bioarchaeology has been attributed to British archaeologist Grahame Clark who, in 1972, defined it as the study of animal and human bones from archaeological sites. Redefined in 1977 by Jane Buikstra, bioarchaeology in the United States now refers to the scientific study of human remains from archaeological sites, a discipline known in other countries as osteoarchaeology, osteology or palaeo-osteology. Compared to bioarchaeology, osteoarchaeology is the scientific study that solely focus on the human skeleton. The human skeleton is used to tell us about health, lifestyle, diet, mortality and physique of the past. Furthermore, palaeo-osteology is simple the study of ancient bones. In contrast, the term bioarchaeology is used in Europe to describe the study of all biological remains from archaeological sites. Although Clark used it to describe just human remains and animal remains (zoology/archaeozoology), increasingly modern archaeologists also include botanical remains (bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioarchaeology
The term bioarchaeology has been attributed to British archaeologist Grahame Clark who, in 1972, defined it as the study of animal and human bones from archaeological sites. Redefined in 1977 by Jane Buikstra, bioarchaeology in the United States now refers to the scientific study of human remains from archaeological sites, a discipline known in other countries as osteoarchaeology, osteology or palaeo-osteology. Compared to bioarchaeology, osteoarchaeology is the scientific study that solely focus on the human skeleton. The human skeleton is used to tell us about health, lifestyle, diet, mortality and physique of the past. Furthermore, palaeo-osteology is simple the study of ancient bones. In contrast, the term bioarchaeology is used in Europe to describe the study of all biological remains from archaeological sites. Although Clark used it to describe just human remains and animal remains (zoology/archaeozoology), increasingly modern archaeologists also include botanical remains (bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpey's Fibres
Sharpey's fibres (bone fibres, or perforating fibres) are a Matrix (biology), matrix of connective tissue consisting of bundles of strong predominantly type I Collagen, collagen fibres connecting periosteum to bone. They are part of the outer fibrous layer of periosteum, entering into the outer circumferential and interstitial Lamellae (zoology), lamellae of bone tissue. Sharpey's fibres are also used to attach muscle to the periosteum of bone by merging with the fibrous periosteum and underlying bone as well. A good example is the attachment of the rotator cuff muscles to the blade of the scapula. In the Tooth, teeth, Sharpey's fibres are the terminal ends of principal fibres (of the periodontal ligament) that insert into the cementum and into the periosteum of the alveolar bone. A study on rats suggests that the three-dimensional structure of Sharpey's fibres intensifies the continuity between the periodontal ligament fibre and the Dental alveolus, alveolar bone (tooth socket), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Field
In linguistics, a semantic field is a lexical set of words grouped semantically (by meaning) that refers to a specific subject.Howard Jackson, Etienne Zé Amvela, ''Words, Meaning, and Vocabulary'', Continuum, 2000, p14. The term is also used in anthropology,Ingold, Tim (1996). ''Key debates in anthropology''. Routledge. , . Source(accessed: Sunday May 2, 2010), p.127 computational semiotics, and technical exegesis. Definition and usage Brinton (2000: p. 112) defines "semantic field" or "semantic domain" and relates the linguistic concept to hyponymy: Related to the concept of hyponymy, but more loosely defined, is the notion of a semantic field or domain. A semantic field denotes a segment of reality symbolized by a set of related words. The words in a semantic field share a common semantic property. A general and intuitive description is that words in a semantic field are not necessarily synonymous, but are all used to talk about the same general phenomenon.Adrian Akma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Muscle
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Types There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or "voluntary muscle", is a striated muscle tissue that primarily joins to bone with tendons. Skeletal muscle enables movement of bones, and maintains posture. The widest part of a muscle that pulls on the tendons is known as the belly. Muscle slip A muscle slip is a slip of muscle that can either be an anatomical variant, or a branching of a muscle as in rib connections of the serratus anterior muscle. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in parts of the body where it conveys action without conscious intent. The majority of this type of muscle tissue is found in the digestive and urinary systems where it acts by propelling forward food, chyme, and feces in the forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcific Tendinitis
Calcific tendinitis is a common condition where calcium deposits form in a tendon, sometimes causing pain at the affected site. Deposits can occur in several places in the body, but are by far most common in the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Around 80% of those with deposits experience symptoms, typically chronic pain during certain shoulder movements, or sharp acute pain that worsens at night. Calcific tendinitis is typically diagnosed by physical exam and X-ray imaging. The disease often resolves completely on its own, but is typically treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, rest and physical therapy to promote healing, and in some cases various procedures to breakdown and/or remove the calcium deposits. Adults aged 30–50 are most commonly affected by calcific tendinitis. It is twice as common in women as men, and is not associated with exercise. Calcifications in the rotator cuff were first described by Ernest Codman in 1934. The name, "calcifying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |