|
Enhanced External Counterpulsation
External counterpulsation therapy (ECP) is a procedure that may be performed on individuals with angina, heart failure, or cardiomyopathy. Medical uses The FDA approved the CardiAssist ECP system for the treatment of angina, acute myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock under a 510(k) submission in 1980 Since then, additional ECP devices have been cleared by the FDA for use in treating stable or unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, cardiogenic shock, and congestive heart failure. Studies have found EECP to be beneficial for patients with erectile dysfunction and some COPD patients. Additionally, improvements in exercise endurance in the non-diseased patient has been found in research studies. Some reviews did not find sufficient evidence that it was useful for either angina or heart failure. Other reviews found tentative benefit in those with angina that does not improve with medications. For stroke due to lack of blood flow, a 2012 Cochrane review fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of partial obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The main mechanism of coronary artery obstruction is atherosclerosis as part of coronary artery disease. Other causes of angina include abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure and, less commonly, anemia. The term derives , and can therefore be translated as "a strangling feeling in the chest". An urgent medical assessment is suggested to rule out serious medical conditions. There is a relationship between severity of angina and degree of oxygen deprivation in the heart muscle. However, the severity of angina does not always match the degree of oxygen deprivation to the heart or the risk of a heart attack (myocardial infarction). Some people may experience sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood. Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, Fatigue (medical), excessive fatigue, and bilateral peripheral edema, leg swelling. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, hypertension, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, alcohol use disorder, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering the structure or the function of the heart or in some cases both. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. As of 2013, cardiomyopathies are defined as "disorders characterized by morphologically and functionally abnormal myocardium in the absence of any other disease that is sufficient, by itself, to cause the observed phenotype." Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', and ''metron'', 'measure'. Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry: telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
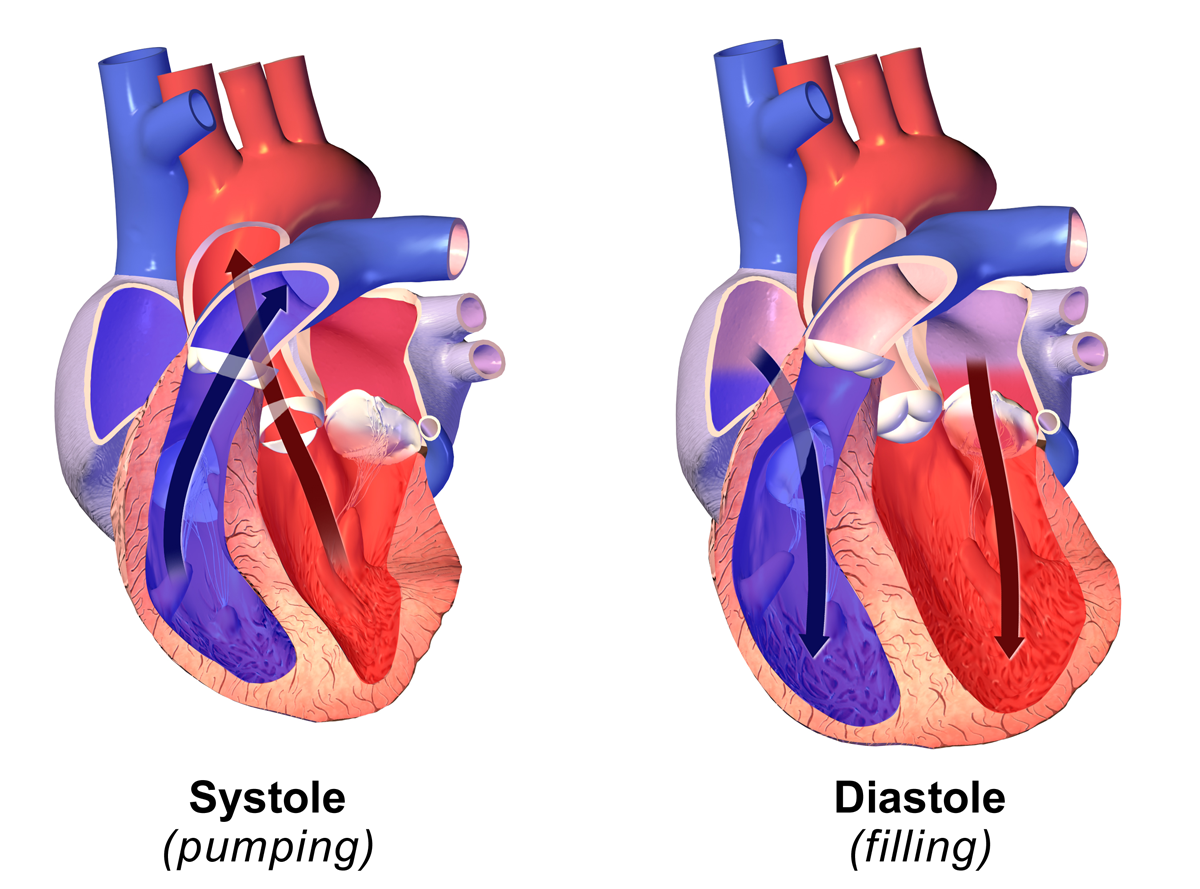
Diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole (medicine)
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. Etymology The term originates, via Neo-Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. Terminology, general explanation The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MmHg
A millimetre of mercury is a manometric unit of pressure, formerly defined as the extra pressure generated by a column of mercury one millimetre high. Currently, it is defined as exactly , or approximately 1 torr = atmosphere = pascals.Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC of the It is denoted mmHg or mm Hg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress or force per unit area is: \tau = ,where is the force applied and is the cross-sectional area. The area involved corresponds to the material face (geometry), face parallel to the applied force vector, i.e., with surface normal vector perpendicular to the force. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as:\tau_w := \mu\left.\frac\_,where is the dynamic viscosity, is the flow velocity, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |