|
English Ship Aid (1562)
''Aid'' or ''Ayde''The 'HMS' prefix was not used until the middle of the 18th century, but is sometimes applied retrospectively was an 18-gun ship of the Royal Navy. She was built at Deptford Dockyard, being launched on 6 October 1562. She was rebuilt in 1580 and was broken up in 1599. For the majority of her service, she was commanded by Sir Martin Frobisher. Service history Le Havre (1562) ''Aid'' was one of three ships built in 1562 due to the threat of war with France. Her first duty, in autumn of that year, was to help supply the English garrison at Le Havre.Paine (2000), pp2–3 This continued until the port was captured by French loyalist forces from the Huguenots in August the following year. Service off the coast of Scotland (1565) Anthony Jenkinson was sent in ''Aid'' to Scotland during the political crisis of the Chaseabout Raid. He sailed into the Firth of Forth on 25 September 1565. Jenkinson had intended to blockade Leith to prevent Lord Seton bringing mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, link up with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas. The Spanish were opposed by an English fleet based in Plymouth. Faster and more manoeuvrable than the larger Spanish galleons, they were able to attack the Armada as it sailed up the Channel. Several subordinates advised Medina Sidonia to anchor in The Solent and occupy the Isle of Wight, but he refused to devia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Henry Coote
Charles Henry Coote (1840–1899) was a librarian at the British Museum. He obtained during his long service of 41 years in the Museum such an intimate acquaintance with the details of old maps that he became of the first authorities on the subject. In 1878 he published in the New Shakspere Society's ''Transactions'' a paper on "Shakspere's New Map in Twelfth Night". In 1886, with E. Delmar Morgan, he prepared for the Hakluyt Society ''Early Voyages to Russia and Persia''; in 1888 he edited, with an introduction and bibliography, ''A Reproduction of Johann Schöner's Globe of 1523''; in 1894 he published, with prologue and notes, ''The Voyage from Lisbon to India, 1505-6, by Albericus Vespuccius''; and in 1894-95 he supplied the explanatory text to F. Muller and Co.'s reproductions of ''Remarkable Maps of the Fifteenth, Sixteenth, and Seventeenth Centuries.'' He also wrote the introduction to the Earl of Crawford's ''Autotype Facsimiles of Three Mappemondes''. C. H. Coote contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frobisher Bay
Frobisher Bay is an inlet of the Davis Strait in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the southeastern corner of Baffin Island. Its length is about and its width varies from about at its outlet into the Labrador Sea to roughly towards its inner end.Frobisher Bay in The capital of Nunavut, , known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, lies near the innermost end of the bay. Geography Frobisher Bay has a tapered shape formed by two flanking[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Strait
Hudson Strait (french: Détroit d'Hudson) links the Atlantic Ocean and Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Resolution Island off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km long with an average width of 125 km, varying from 70 km at the eastern entrance to 240 km at Deception Bay. English navigator Sir Martin Frobisher was the first European to report entering the strait, in 1578. He named a tidal rip at the entrance the Furious Overfall and called the strait ''Mistaken Strait'', since he felt it held less promise as an entrance to the Northwest Passage than the body of water that was later named Frobisher Bay. John Davis sailed by the entrance to the strait during his voyage of 1587. The first European to explore the strait was George Weymouth who sailed 300 nautical miles beyond the Furious Overfall in 1602. The strait was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters. For centuries, European explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus in 1492, sought a navigable passage as a possible trade route to Asia, but were blocked by North, Central, and South America, by ice, or by rough waters (e.g. Tierra del Fuego). An ice-bound northern route was discovered in 1850 by the Irish explorer Robert McClure. Scotsman John Rae explored a more southerly area in 1854 through which Norwegian Roald Amundsen f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnaq
Arnaq or Egnock (died November 1577) was the name given by the English to an Inuk woman from what is now Baffin Island, Nunavut, who was taken hostage by Sir Martin Frobisher on his second journey to find the Northwest Passage. She, her infant son (named by the English as Nutaaq) and an Inuk man named as Kalicho were among the first Inuit and first indigenous people from North America to visit England and among the best documented of the Tudor period. They were brought back to the English port of Bristol at the end of September 1577 and died in November of the same year. Life Arnaq was most likely born in the Frobisher Bay area of Nunavut in the 16th century. The name used for her by her captors is very similar to the Inuit word for "woman" (ᐊᕐᓇᖅ ''arnaq''), so her real name is unknown. She and her twelve-month old son, Nutaaq, were amongst four Inuit brought to England against their will by Frobisher. According to the 1578 account of George Best, who accompanied the 157 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalicho
Kalicho was the name assigned to an Inuk man from the Frobisher Bay area of Baffin Island, Nunavut Canada. He was brought back to England as a captive by Sir Martin Frobisher in 1577. He was taken along with an unrelated Inuk woman and her infant, who were named by the English as Arnaq and Nutaaq. The three were among the first Inuit and the first indigenous people from North America to be brought to England and among the best documented of the Tudor period. Life Kalicho was most likely born in or around Frobisher Bay on Baffin Island in the mid-16th century. He was part of a community of hunters and fishers in the area up to the time of his capture on 19 July 1577 by the English explorer, Sir Martin Frobisher. Kalicho's capture and experiences with the expedition in the bay were described by George Best in his 1578 account of Frobisher's three expeditions. Frobisher was leading an expedition organised by the English Cathay Company of London, which had been set up to locate a N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut. Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories, particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. With the exception of NunatuKavut, these areas are known, primarily by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
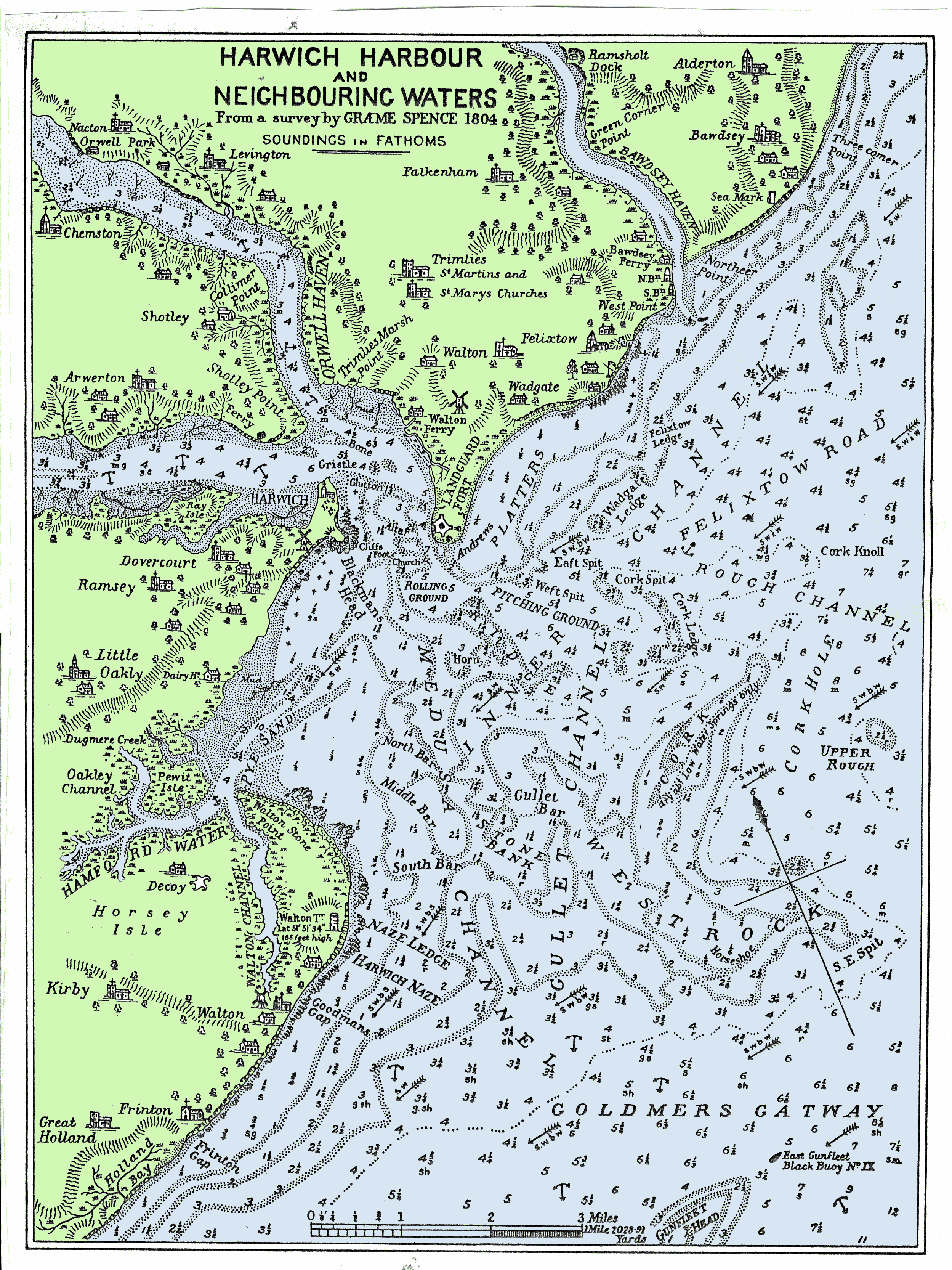
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the ''Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. History The tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Fenton
Edward Fenton (died 1603) was an English navigator, son of Henry Fenton and Cicely Beaumont and brother of Sir Geoffrey Fenton. He was also a publisher of diaries and journals. Biography He was a native of Sturton-le-Steeple, Nottinghamshire. His mother belonged to a prominent Leicestershire family whose seat was at Coleorton Hall. In 1577 he sailed, in command of the ''Gabriel'', with Sir Martin Frobisher's second expedition for the discovery of the Northwest Passage, and in the following year he took part as second in command in Frobisher's third expedition, his ship being the ''Judith''. He was then employed in Ireland for a time, but in 1582 he was put in charge of an expedition which was to sail round the Cape of Good Hope to the Moluccas and China, his instructions being to obtain any knowledge of the northwest passage that was possible without hindrance to his trade. For this voyage he was in charge of two warships, the ''Galleon Leicester'' and the ''Edward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel with three or more mast (sailing), masts having the fore- and mainmasts Square rig, rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) Fore-and-aft rig, rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, bearing a square-rigged sail above. Etymology The word "barque" entered English via the French term, which in turn came from the Latin language, Latin ''barca'' by way of Occitan language, Occitan, Catalan language, Catalan, Spanish, or Italian. The Latin ''barca'' may stem from Celtic language, Celtic ''barc'' (per Rudolf Thurneysen, Thurneysen) or Greek ''baris'' (per Friedrich Christian Diez, Diez), a term for an Egyptian boat. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'', however, considers the latter improbable. The word ''barc'' appears to have come from Celtic languages. The form adopted by English, perhaps from Irish language, Irish, was "bark", while that adopted by Latin as ''barca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)