|
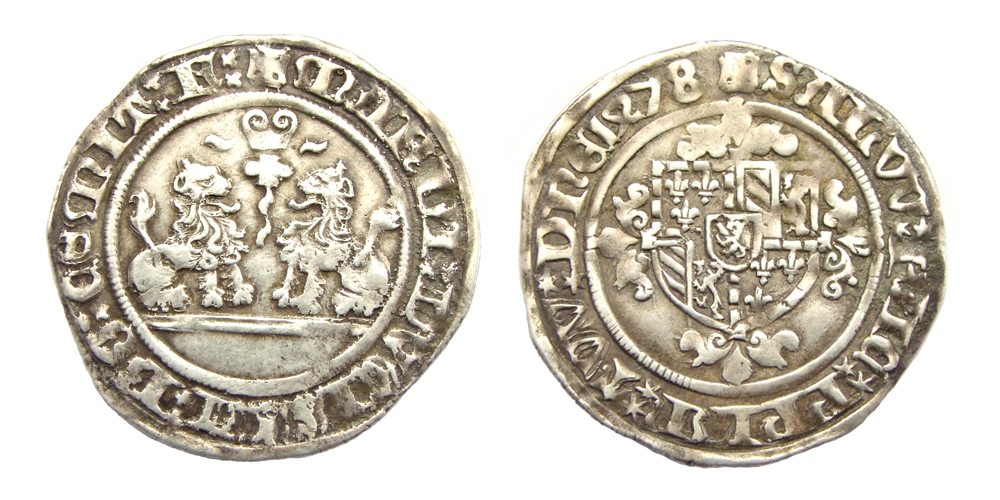
Engelbert II Of Nassau
Engelbert II of Nassau, ''Engelbrecht'' in Dutch (17 May 1451 – 31 May 1504), was count of Nassau and Vianden and lord of Breda, Lek, Diest, Roosendaal, Nispen and Wouw. He was a soldier and courtier, for some time leader of the Privy council of the Duchy of Burgundy and a significant patron of the arts. Biography Engelbert was born in Breda on 17 May 1451, the son of John IV of Nassau-Siegen and his wife Mary of Looz-Heinsberg.George Chastelain and the Shaping of Valois Burgundy: Political and Historical Culture at Court in the Fifteenth Century by Graeme Small (, 1997) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rijksmuseum Amsterdam
The Rijksmuseum () is the national museum of the Netherlands dedicated to Dutch arts and history and is located in Amsterdam. The museum is located at the Museumplein, Museum Square in the stadsdeel, borough of Amsterdam-Zuid, Amsterdam South, close to the Van Gogh Museum, the Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam, and the Concertgebouw, Amsterdam, Concertgebouw. The Rijksmuseum was founded in The Hague on 19 November 1798 and moved to Amsterdam in 1808, where it was first located in the Royal Palace (Amsterdam), Royal Palace and later in the Trippenhuis. The current main building was designed by Pierre Cuypers and first opened in 1885.The renovation Rijksmuseum. Retrieved on 4 April 2013. On 13 April 2013, after a ten-year renovation which cost euro, €375 million, the main building was reopened by Beatrix of the Netherla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
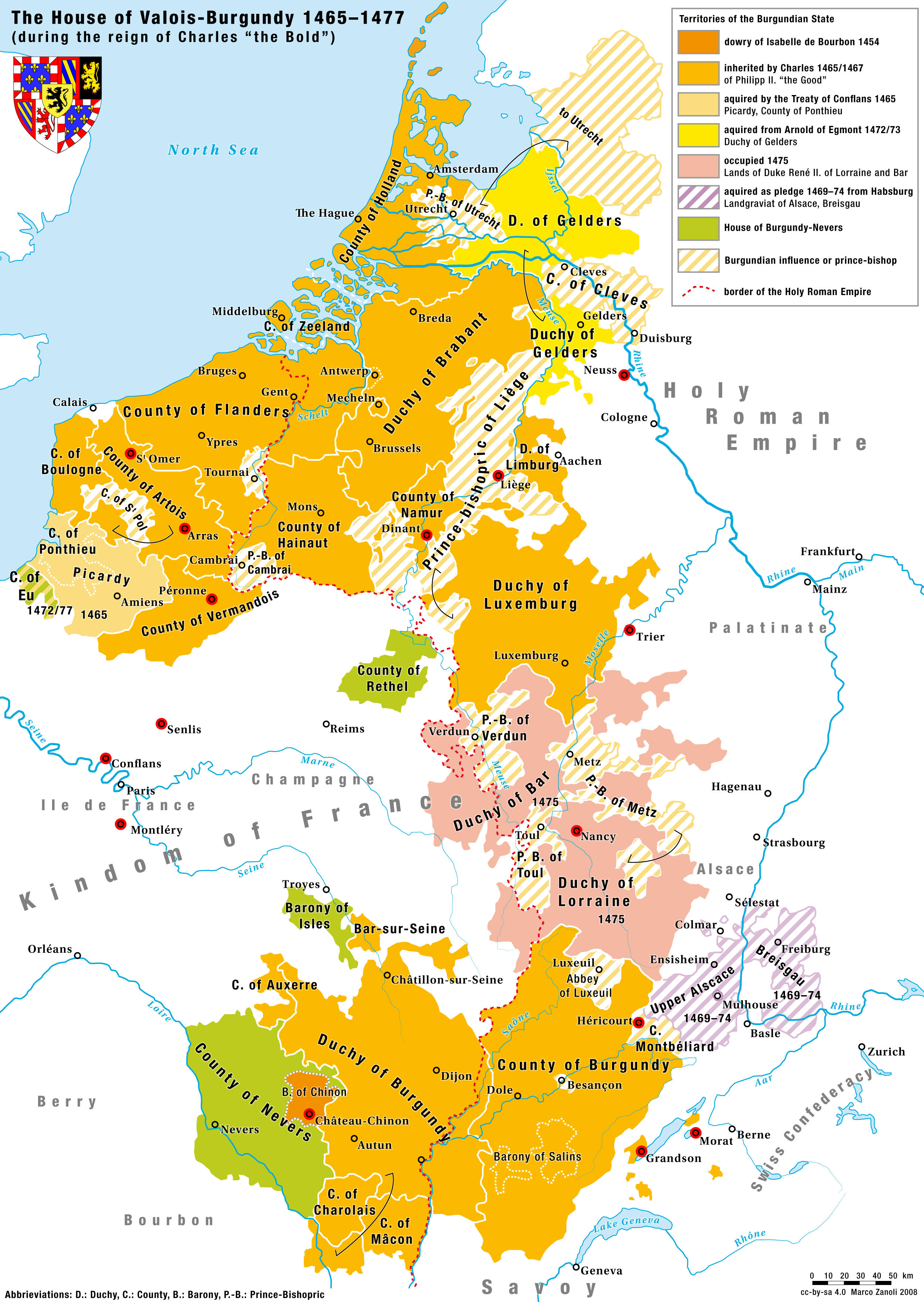
Duchy Of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; ; ) was a medieval and early modern feudal polity in north-western regions of historical Burgundy. It was a duchy, ruled by dukes of Burgundy. The Duchy belonged to the Kingdom of France, and was initially bordering the Kingdom of Burgundy to the east and south, thus being distinct from the neighboring Free County of Burgundy (modern region of Franche-Comté). The first duke of Burgundy (), attested in sources by that title, was Richard the Justiciar in 918. In 1004, prince Henry of France, a son of king Robert II of France, inherited the Duchy, but later ceded it to his younger brother Robert in 1032. Robert became the ancestor of the ducal House of Burgundy, a cadet branch of the royal Capet dynasty, ruling over a territory that roughly conformed to the borders and territories of the modern region of Burgundy (Bourgogne). Upon the extinction of the Burgundian male line with the death of Duke Philip I in 1361, the duchy reverted to King John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Béthune
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bruges
Bruges ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country. The area of the whole city amounts to more than 14,099 hectares (140.99 km2; 54.44 sq. miles), including 1,075 hectares off the coast, at Zeebrugge (from , meaning 'Bruges by the Sea'). The historic city center is a prominent World Heritage Site of UNESCO. It is oval and about 430 hectares in size. The city's total population is 117,073 (1 January 2008),Statistics Belgium; ''Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008'' (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 19 October 2008. of who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Guinegate (1479)
The First Battle of Guinegate took place on 7 August 1479. King Louis XI's French troops, led by Philippe de Crèvecœur d'Esquerdes (who had been a commander under Charles the Bold but defected to the French side after the latter's death in 1477), were defeated by the Burgundians, led by Archduke (later Emperor) Maximilian of Habsburg. The battle was the first in which the innovative Swiss pike square formation was used by a power that was not natively Swiss. Background Charles the Bold, the last Duke of Burgundy, had been killed at the Battle of Nancy on 5 January 1477. King Louis XI immediately adjudicated his territories to be recovered fiefs of the French Kingdom and campaigned in the Counties of Artois, Flanders and Hainaut and the Duchy of Burgundy. Nevertheless, Charles' only heir, Mary of Burgundy, on 19 August had married Archduke Maximilian, who, determined to protect the Burgundian inheritance, organised troops in the Burgundian Netherlands and marched against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mary Of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy (; ; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled the Burgundian lands, comprising the Duchy of Burgundy, Duchy and Free County of Burgundy, County of Burgundy and the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1477 to her death. As the only child of Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, and his wife Isabella of Bourbon, Mary inherited the Burgundian lands at the age of 19 upon the death of her father in the Battle of Nancy on 5 January 1477. In order to counter the appetite of the French king Louis XI for her lands, she married Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian of Austria, with whom she had two children. The marriage kept large parts of the Burgundian lands from disintegration, but also changed the dynasty from Valois to Habsburg (the Duchy of Burgundy itself soon became a French possession). This was a turning point in European politics, leading to a French–Habsburg rivalry that would endure for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death in 1519. He was never crowned by the Pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself elected emperor in 1508 at Trent, with Pope Julius II later recognizing it. This broke the tradition of requiring a papal coronation for the adoption of the Imperial title. Maximilian was the only surviving son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, and Eleanor of Portugal. From his coronation as King of the Romans in 1486, he ran a double government, or ''Doppelregierung'' with his father until Frederick's death in 1493. Maximilian expanded the influence of the House of Habsburg through war and his marriage in 1477 to Mary, Duchess of Burgundy. However, he also lost his family's lands in Switzerland to the Swiss Confederacy. Through the marriage of his son Philip the Handsome to eventual queen Joanna of Castile in 1496, Maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Order Of The Golden Fleece
The Distinguished Order of the Golden Fleece (, ) is a Catholic order of chivalry founded in 1430 in Brugge by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, to celebrate his marriage to Isabella of Portugal, Duchess of Burgundy, Isabella of Portugal. Today, two branches of the order exist, namely the Spanish Fleece and the Austrian Fleece; the current grand masters are Felipe VI, King Felipe VI of Spain and Karl von Habsburg, head of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, respectively. The Grand Chaplain of the Austrian branch is Cardinal Christoph Schönborn, Archbishop of Vienna. The separation of the two existing branches took place as a result of the War of the Spanish Succession of 1701–1714. The grand master of the order, Charles II of Spain (a House of Habsburg , Habsburg), had died childless in 1700, and so the right to succeed to the throne of Spain (and thus to become the Sovereign of the Order of the Golden Fleece) initiated a global conflict. On one hand, Charles VI, Holy Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles The Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, Isabella of Portugal. As heir and as ruler, Charles vied for power and influence with rivals such as his overlord, King Louis XI of France. In 1465 Charles led a successful revolt of Louis's vassals in the War of the Public Weal. After becoming the Duke of Burgundy in 1467, Charles pursued his ambitions for a kingdom, independent from France, that would stretch contiguously from the North Sea in the north to the borders of Savoy in the south. For this purpose, he acquired Guelders and Upper Alsace; sought the title King of the Romans; and gradually became an enemy of the Germans. Charles married Margaret of York for an English alliance. He arranged the betrothal between his sole child, Mary, with Maximilian of Austria. A passiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Switzerland border, Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Constance downstream, it forms part of the Germany-Switzerland border, Swiss-German border. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border. It then flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally, the Rhine turns to flow predominantly west to enter the Netherlands, eventually emptying into the North Sea. It drains an area of 185,000 km2. Its name derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish ''Rēnos''. There are two States of Germany, German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, in addition to several districts of Germany, districts (e.g. Rhein-Sieg-Kreis, Rhein-Sieg). The departments of France, department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John V, Count Of Nassau-Siegen
Count John V of Nassau-SiegenIn many sources he is called John V of Nassau(-Dillenburg). His official titles were Count of Nassau, Vianden and Diez, Lord of Breda. It is incorrect to refer to him as the only reigning Count of Nassau, because the County of Nassau was divided into Nassau-Beilstein, Nassau-Idstein, Nassau-Siegen, Nassau-Weilburg and Nassau-Wiesbaden. Furthermore, there was the cadet branch of Nassau-Saarbrücken, which ruled the County of Saarbrücken. John ruled the County of Nassau-Siegen, which is erroneously called Nassau-Dillenburg in many sources. See note 2. (9 November 1455 – 30 July 1516), , official titles: ''Graf zu Nassau, Vianden und Diez, Herr zu Breda'', was since 1475 Count of Nassau-SiegenThe County of Nassau-Siegen is erroneously called Nassau-Dillenburg in many sources. The county was not named after the small, unimportant city of Dillenburg, which did not even have a church until 1491, but after the, for that time, large cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles I, Margrave Of Baden-Baden
Charles I of Baden (1427 – 24 February 1475, Pforzheim Pforzheim () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city of over 125,000 inhabitants in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg, in the southwest of Germany. It is known for its jewelry and watch-making industry, and as such has gained the ...) was a Margrave of Baden-Baden during 1454–1475. Charles was the elder son of Jacob, Margrave of Baden-Baden, and his wife Catherine, daughter of Charles II, Duke of Lorraine. In 1462 he became involved in the Bavarian War (1459–63) against Frederick I, Elector Palatine. This war finished in the same year with Charles's defeat and capture at the Battle of Seckenheim in 1462. Family and children On 1 July 1447, Charles married Catherine of Austria (1423 – 11 September 1493), daughter of Archduke Ernest the Iron. They had: # Katharina (15 January 1449 – before 8 May 1484), married on 19 May 1464 to Count George III of Werdenberg-Sargans # Zimburg (15 May 1450 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |