|
Engelbert Des Bois
Engelbert Des Bois (1578–1651) was the seventh bishop of Namur (1630–1651). Life Des Bois was born in Brussels on 9 July 1578 to parents from Burgundy. He studied Civil law (legal system), civil law and canon law, taking the degree of licentiate of laws, and became a canon and later archdeacon of Cambrai Cathedral. From 1618 to 1629 he was provost of the collegiate church of St Pierre in Lille. In 1629 he was named bishop of Namur, and he was installed in 1630. As bishop he was one of the representatives of the First Estate of the County of Namur in the Estates General of 1632. Urban VIII issued the papal bull ''In eminenti'' in 1641, condemning a number of propositions drawn from the writings of Cornelius Jansenius. In 1643 Des Bois was the first bishop in the Habsburg Netherlands to publish the bull, which he did without government permission. This led to a period of troubled relations with the civil authorities.E. H. J. Reusens, "Des Bois (Engelbert)", ''Biographie Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Namur
The Diocese of Namur is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Belgium. It is a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Mechelen-Brussels. The diocese is a suffragan in the ecclesiastical province in the metropolitan Archdiocese of Mechelen-Brussels. Its cathedra is found within St Aubin's Cathedral in the episcopal see of Namur. History The diocese was constituted as a suffragan see of the new metropolitan see of Cambrai by the papal bull of 12 May 1559 establishing the new bishoprics in the Low Countries. Its territory had previously belonged to the Diocese of Liège. After suppression in the French period the diocese was re-established by the Concordat of 1801, its extent matching that of the Department of Sambre-et-Meuse, and as suffragan of the Archdiocese of Mechelen. On 14 September 1823, the territory of the diocese was extended to include Luxembourg, which had previously been part of the Diocese of Metz. After the Belgian Revolution of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrai Cathedral
Cambrai Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Grâce de Cambrai) is a Catholic church located in Cambrai, Nord, France, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Cambrai. The cathedral was registered as a '' monument historique'' on 9 August 1906. It was built between 1696 and 1703, on the site of a former 11th-century building, as the church of the Abbey of Saint-Sépulcre. During the French Revolution the old cathedral of Cambrai was destroyed, but the abbey church survived because it was used instead as a Temple of Reason. When the ecclesiastical status of Cambrai was restored in 1802, albeit as a diocese rather than as an archdiocese, which it had previously been, the bishop's seat was established in the surviving abbey church, which became the cathedral of Cambrai. Cambrai was again constituted an archbishopric in 1841. The cathedral was severely damaged by fire in 1859, but at length restored, with advice from Viollet-le-Duc, and consecrated on 12 May 1894. It was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1578 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 1578 ( MDLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 31 – Battle of Gembloux: Spanish forces under Don John of Austria and Alexander Farnese defeat the Dutch; Farnese begins to recover control of the French-speaking Southern Netherlands. * April 27 – The Duel of the Mignons claims the lives of two favorites of Henry III of France, and two favourites of Henry I, Duke of Guise. * May 26 – The ''Alteratie'' in Amsterdam ends Catholic rule, and opens Catholic worship there. * May 31 – Martin Frobisher sails from Harwich, England to Frobisher Bay, Canada, on his third expedition. * June 11 – Humphrey Gilbert is granted letters patent from the English crown to establish a colony in North America. July–December * July – Martin Frobisher holds the first Thanksgiving celebration by Europeans in North America, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brogne Abbey
Brogne Abbey, also known as Saint-Gerard Abbey, was a Benedictine abbey founded in the early 10th century by Gerard of Brogne in the village of Brogne (now the Saint-Gérard subdivision of Mettet, Wallonia). Gerard founded the abbey on his own land, with the blessing of Stephen of Liège (died 920), and obtained a relic of St Eugenius from the abbot of Saint-Denis. A charter of 923 granted land in Hesbaye to the monastery. In 992 Otto III visited the abbey together with Notker of Liège and confirmed its independence and privileges. In 1183 Pope Lucius III confirmed the abbey in all its possessions. In 1566 the revenues of the abbacy were assigned to the recently founded Diocese of Namur by a bull of Pope Pius IV. Thereafter the monastery was governed by a prior on behalf of the bishop of Namur. In 1656 the monastery was incorporated into the Bursfelde Congregation. Just which revenues were due to the bishop remained subject to dispute, petitions and sometimes litigation unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographie Nationale De Belgique
The ''Biographie nationale de Belgique'' ( French; "National Biography of Belgium") is a biographical dictionary of Belgium. It was published by the Royal Academy of Belgium in 44 volumes between 1866 and 1986. A continuation series, entitled the ''Nouvelle Biographie Nationale'' ("New National Biography"), has been published by the Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium since 1988. Both the ''Biographie nationale'' and ''Nouvelle biographie nationale'' were digitised by the Fonds InBev-Baillet Latour and can be freely consulted at the Academy's website. A parallel biographical dictionary has been produced in Dutch since 1964, entitled the ''Nationaal Biografisch Woordenboek'' ("National Biographical Dictionary"). It places more emphasis on figures important to the history and culture of Flanders and is published by the Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium for Science and the Arts (with the co-operation of the Royal Academy of Dutch language and literature and the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
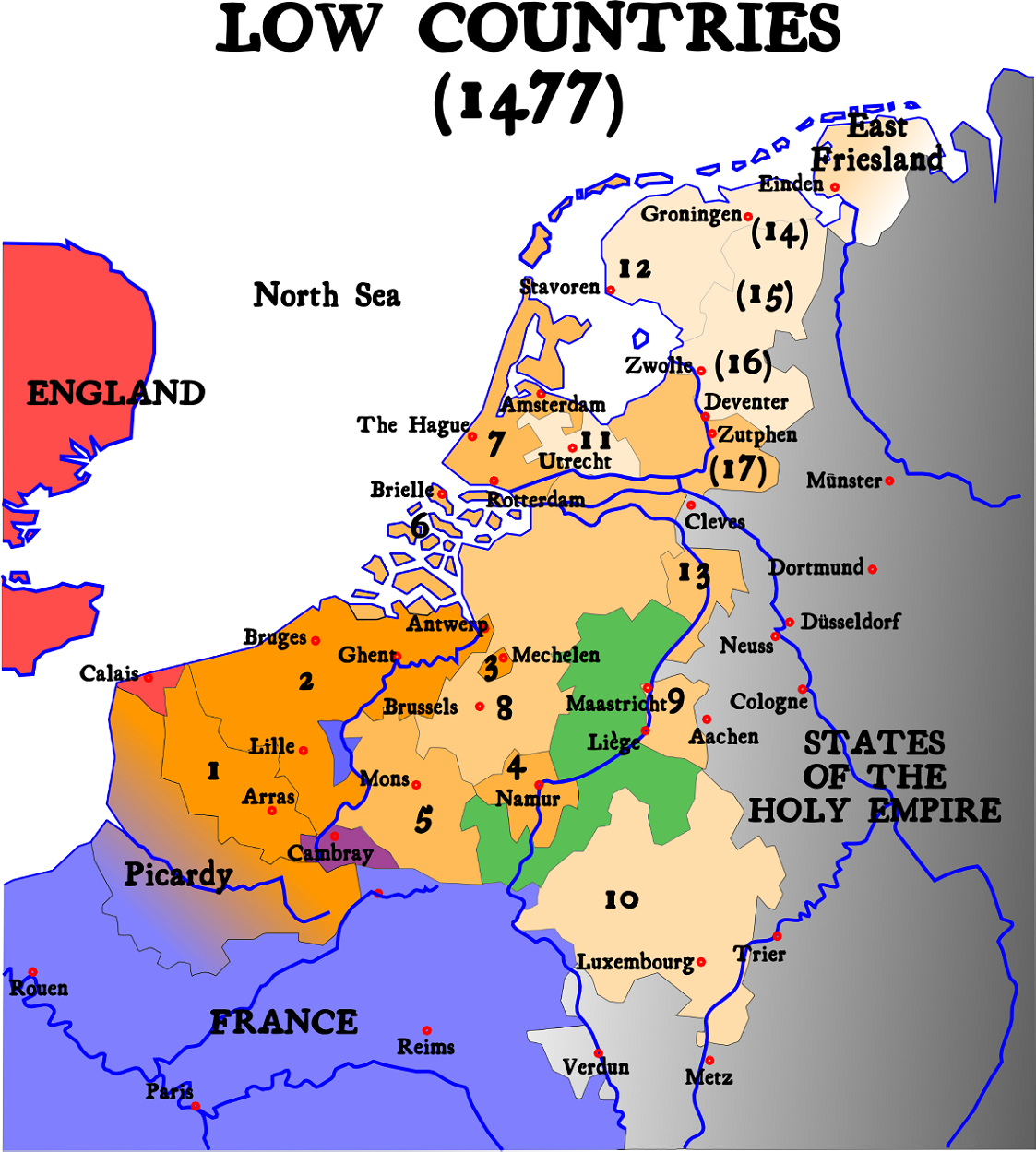
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last House of Valois-Burgundy, Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary of Burgundy, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austria, died. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. De facto Habsburg rule ended with the annexation by the revolutionary French First Republic in 1795. Austria, however, did not relinquish its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelius Jansenius
Cornelius Jansen (, ; Latinized name Cornelius Jansenius; also Corneille Jansen; 28 October 1585 – 6 May 1638) was the Dutch Catholic bishop of Ypres in Flanders and the father of a theological movement known as Jansenism. Biography He was born of humble Catholic parentage at Acquoy (then in the province of Holland, now in Gelderland), the Netherlands. In 1602 he entered the University of Leuven, then in the throes of an ideological conflict between the Jesuit – or scholastic – party and the followers of Michael Baius, who swore by St. Augustine. Jansen ended by attaching himself strongly to the latter "Augustinian" party, and presently made a momentous friendship with a like-minded fellow-student, Jean du Vergier de Hauranne, afterwards ''Abbé de Saint-Cyran''. After taking his degree he went to Paris, partly to improve his health by a change of scene, partly to study Greek. Eventually he joined Du Vergier at his country home near Bayonne, and spent some yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban VIII
Pope Urban VIII ( la, Urbanus VIII; it, Urbano VIII; baptised 5 April 1568 – 29 July 1644), born Maffeo Vincenzo Barberini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 August 1623 to his death in July 1644. As pope, he expanded the papal territory by force of arms and advantageous politicking, and was also a prominent patron of the arts and a reformer of Church missions. However, the massive debts incurred during his pontificate greatly weakened his successors, who were unable to maintain the papacy's longstanding political and military influence in Europe. He was also an opponent of Copernicanism and involved in the Galileo affair. He is the last pope to date to take the pontifical name "Urban". Biography Early life He was born Maffeo Vincenzo Barberini in April 1568 to Antonio Barberini, a Florentine nobleman, and Camilla Barbadoro. He was born at Barberino Val d'Elsa in "Tafania" house. His father died when he was only three years old and hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
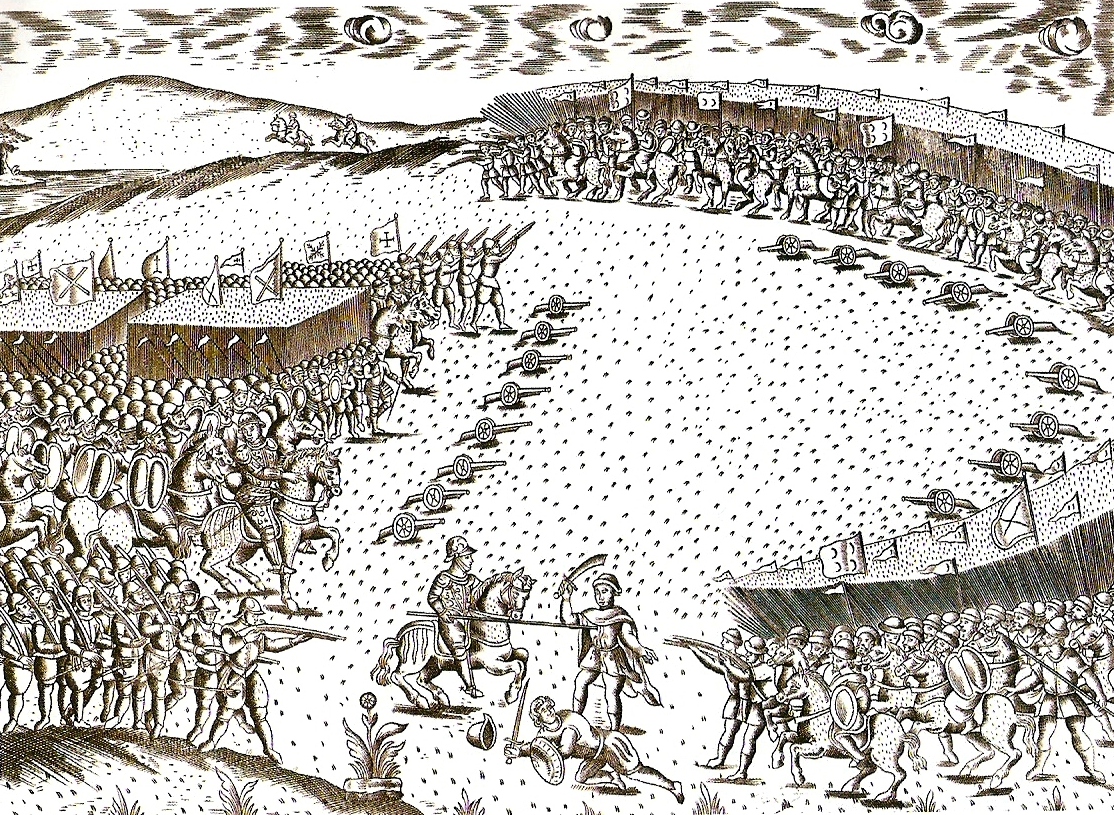
Estates General Of 1632
The Estates General of 1632 was a parliamentary assembly of representatives of the constituent provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands. It was the last such assembly. Crisis It had been over thirty years since a gathering of the Estates General had been convened by the Habsburg rulers in the Low Countries. In a situation of deep political crisis, the Governor-General, Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia, called the Estates General to rally the political elites to the Habsburg cause. The letters convoking the assembly were sent on 30 July, with the date for the opening set as 7 September. The assembly was dissolved on 5 July 1634. Delegates The delegates attending were as follows.Louis Prosper Gachard Louis Prosper Gachard (12 March 1800 – 24 December 1885), Belgian man of letters, was born in Paris. He entered the administration of the national archives in 1826, and was appointed director-general in 1831, a post which he held for fifty-fi ..., ''Actes des États Généraux de 1632 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Namur
Namur ( nl, Namen) was a county of the Carolingian and later Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, a region in northwestern Europe. Its territories largely correspond with the present-day Belgian arrondissement Namur plus the northwestern part of the arrondissement Dinant, both part of the modern province of Namur, and previously part of the French Republican department of Sambre-et-Meuse. Prehistory to the Roman period The city of Namur most likely arose around 'the Champeau', a rocky hill between the Sambre and Meuse rivers. Numerous prehistoric flint weapons have been found in the area. During Roman times, the region around Namur was first mentioned in Julius Caesar's ' in the second half of the 1st century BC. To the west of Namur were the Nervii, and to the east the Germani cisrhenani, but it has been suggested that Namur itself may have been home to the Aduatuci who Caesar described as descendants of the Cimbri and Teutons. (Today it is considered more likely to have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, and the main city of the Métropole Européenne de Lille, European Metropolis of Lille. The city of Lille proper had a population of 234,475 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its French suburbs and exurbs the Lille metropolitan area (French part only), which extends over , had a population of 1,510,079 that same year (Jan. 2019 census), the fourth most populated in France after Paris, Lyon, and Marseille. The city of Lille and 94 suburban French municipalities have formed since 2015 the Métropole Européenne de Lille, European Metropolis of Lille, an Indirect election, indirectly elected Métropole, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is the internal ecclesiastical law, or operational policy, governing the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and the Eastern Catholic Churches), the Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches, and the individual national churches within the Anglican Communion. The way that such church law is legislated, interpreted and at times adjudicated varies widely among these four bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon was originally a rule adopted by a church council; these canons formed the foundation of canon law. Etymology Greek / grc, κανών, Arabic / , Hebrew / , 'straight'; a rule, code, standard, or measure; the root meaning in all these languages is 'reed'; see also the Romance-language ancestors of the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |