|
Endurance And Trail Riding
Endurance (also related to sufferance, resilience, constitution, fortitude, and hardiness) is the ability of an organism to exert itself and remain active for a long period of time, as well as its ability to resist, withstand, recover from and have immunity to trauma, wounds or fatigue. It is usually used in aerobic or anaerobic exercise. The definition of 'long' varies according to the type of exertion – minutes for high intensity anaerobic exercise, hours or days for low intensity aerobic exercise. Training for endurance can reduce the ability to exert endurance strength unless an individual also undertakes resistance training to counteract this effect. When a person is able to accomplish or withstand a higher amount of effort than their original capabilities their endurance is increasing which to many personnel indicates progress. In looking to improve one's endurance they may slowly increase the amount of repetitions or time spent, if higher repetitions are taken rap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endurance Training For Mt Carstensz Pyramid
Endurance (also related to wikt:sufferance, sufferance, Psychological resilience, resilience, wikt:constitution, constitution, wikt:fortitude, fortitude, and Hardiness (psychology), hardiness) is the ability of an organism to exert itself and remain active for a long period of time, as well as its ability to resist, withstand, recover from and have immunity to Trauma (medicine), trauma, wounds or fatigue (medical), fatigue. It is usually used in aerobic exercise, aerobic or anaerobic exercise. The definition of 'long' varies according to the type of exertion – minutes for high intensity anaerobic exercise, hours or days for low intensity aerobic exercise. Training for endurance can reduce the ability to exert endurance physical strength, strength unless an individual also undertakes Strength training, resistance training to counteract this effect. When a person is able to accomplish or withstand a higher amount of effort than their original capabilities their endurance is incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athletic Training
Athletic training is an allied health care profession recognized by the American Medical Association (AMA)"What is an Athletic Trainer?". The Board of Certification Website. 2003. Athletic training is also recognized by the Health Resources Services Administration (HRSA) and the Department of Human and Health Services (HHS) as an allied health care profession. Athletic trainers (ATs) are health care professionals who render service or treatment under the direction of or in collaboration with a physician, in accordance with their education, training and the state's statutes, rules and regulations. The practice of athletic training encompasses health promotion and wellness and examination, diagnosis, immediate care, and rehabilitation of clients/patients with emergent, acute, and chronic health conditions. As defined by the Strategic Implementing Team of the National Athletic Trainers' Association (NATA) in August 2007. that "encompasses the prevention, examination, diagnosis, tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many individuals choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, the amount of recommended exercise depends upon the goal, the type of exercise, and the age of the person. Even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the human body: * Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that uses large muscle groups and causes the body to use more oxygen than it would while resting. The goal of aerobic exercise is to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grit (personality Trait)
In psychology, grit is a positive, non-cognitive trait based on an individual's perseverance of effort combined with the passion for a particular long-term goal or end state (a powerful motivation to achieve an objective). This perseverance of effort promotes the overcoming of obstacles or challenges that lie on the path to accomplishment and serves as a driving force in achievement realization. Distinct but commonly associated concepts within the field of psychology include "perseverance", " hardiness", " resilience", "ambition", "need for achievement" and "conscientiousness". These constructs can be conceptualized as individual differences related to the accomplishment of work rather than talent or ability. This distinction was brought into focus in 1907 when William James challenged the field to further investigate how certain individuals are capable of accessing richer trait reservoirs enabling them to accomplish more than the average person, but the construct dates back at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
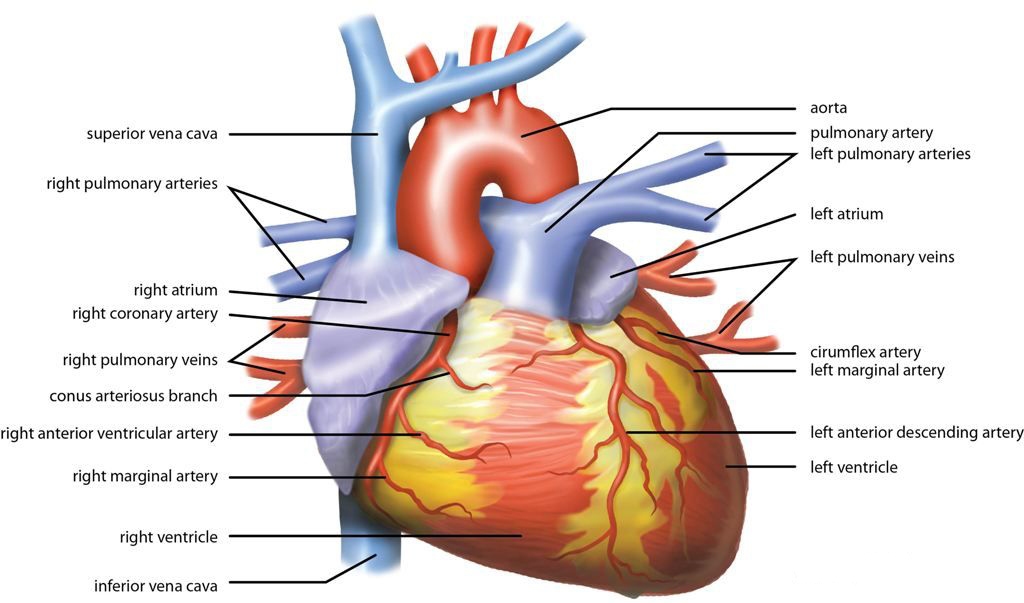
Cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Psychology (journal)
''Health Psychology'' is a monthly, Peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal published by the American Psychological Association. The journal is "devoted to understanding the scientific relations among psychological factors, behavior and physical health and illness." The editor-in-chief is Kenneth E. Freedland (Washington University in St. Louis). Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 5.556". See also * ''Journal of Health Psychology'' *Occupational health psychology References External links * APA Division 38, Health Psychology {{Authority control Health psychology journals American Psychological Association academic journals Bimonthly journals Publications established in 1982 English-language journals 1982 establishments in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Disease
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Lyme disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV which allow these individuals to live while managing symptoms. In medicine, ''chronic'' condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (biology)
Stress, either physiological, biological or psychological, is an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition. Stress is the body's method of reacting to a condition such as a threat, challenge or physical and psychological barrier. There are two hormones that an individual produces during a stressful situation, these are well known as adrenaline and cortisol. There are two kinds of stress hormone levels. Resting (basal) cortisol levels are normal everyday quantities that are essential for standard functioning. Reactive cortisol levels are increases in cortisol in response to stressors. Stimuli that alter an organism's environment are responded to by multiple systems in the body. In humans and most mammals, the autonomic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis are the two major systems that respond to stress. The sympathoadrenal medullary (SAM) axis may activate the fight-or-flight response through the sympathetic nervous system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental and behavioral disorder, the experience of depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, motivation, feelings, and sense of well-being. The core symptom of depression is said to be anhedonia, which refers to loss of interest or a loss of feeling of pleasure in certain activities that usually bring joy to people. Depressed mood is a symptom of some mood disorders such as major depressive disorder and dysthymia; it is a normal temporary reaction to life events, such as the loss of a loved one; and it is also a symptom of some physical diseases and a side effect of some drugs and medical treatments. It may feature sadness, difficulty in thinking and concentration and a significant increase or decrease in appetite and time spent sleeping. People experiencing depression may have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strength Training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training techniques such as bodyweight exercises, isometrics, and plyometrics. Training works by progressively increasing the force output of the muscles and uses a variety of exercises and types of equipment. Strength training is primarily an anaerobic activity, although circuit training also is a form of aerobic exercise. Strength training can increase muscle, tendon, and ligament strength as well as bone density, metabolism, and the lactate threshold; improve joint and cardiac function; and reduce the risk of injury in athletes and the elderly. For many sports and physical activities, strength training is central or is used as part of their training regimen. Principles and training methods The basic principles of strength training involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |