|
Endpoint (chemistry)
The equivalence point, or stoichiometric point, of a chemical reaction is the point at which chemically equivalent quantities of reactants have been mixed. For an acid-base reaction the equivalence point is where the moles of acid and the moles of base would neutralize each other according to the chemical reaction. This does not necessarily imply a 1:1 molar ratio of acid:base, merely that the ratio is the same as in the chemical reaction. It can be found by means of an indicator, for example phenolphthalein or methyl orange. The endpoint (related to, but not the same as the equivalence point) refers to the point at which the indicator changes color in a colorimetric titration. Methods to determine the equivalence point Different methods to determine the equivalence point include: ;pH indicator: A pH indicator is a substance that changes color in response to a chemical change. An acid-base indicator (e.g., phenolphthalein) changes color depending on the pH. Redox indicators are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is: : Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amperometric Titration
Amperometric titration refers to a class of titrations in which the equivalence point is determined through measurement of the electric current produced by the titration reaction. It is a form of quantitative analysis. Background A solution containing the analyte, A, in the presence of some conductive buffer. If an electrolytic potential is applied to the solution through a working electrode, then the measured current depends (in part) on the concentration of the analyte. Measurement of this current can be used to determine the concentration of the analyte directly; this is a form of amperometry. However, the difficulty is that the measured current depends on several other variables, and it is not always possible to control all of them adequately. This limits the precision of direct amperometry. If the potential applied to the working electrode is sufficient to reduce the analyte, then the concentration of analyte close to the working electrode will decrease. More of the ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amperometry
Amperometry in chemistry is detection of ions in a solution based on electric current or changes in electric current. Amperometry is used in electrophysiology to study vesicle release events using a carbon fiber electrode. Unlike patch clamp techniques, the electrode used for amperometry is not inserted into or attached to the cell, but brought in close proximity of the cell. The measurements from the electrode originate from an oxidizing reaction of a vesicle cargo released into the medium. Another technique used to measure vesicle release is capacitive measurements. History Electrochemical or amperometric detection as it was first used in ion chromatography was single-potential or DC amperometry, useful for certain electrochemically active ions such as cyanide, sulfite, and iodide. The development of pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) for analytes that fouled electrode surfaces when detected eventually helped create a new category of ion chromatography for the deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum. Spectrum has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad range of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar caustic'' because silver was called ''luna'' by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon. In solid silver nitrate, the silver ions are three- coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement. Synthesis and structure Albertus Magnus, in the 13th century, documented the ability of nitric acid to separate gold and silver by dissolving the silver. Indeed silver nitrate can be prepared by dissolving silver in nitric acid followed by evaporation of the solution. The stoichiometry of the reaction depends upon the concentration of nitric acid used. :3 Ag + 4 HNO3 (cold and diluted) → 3 AgNO3 + 2 H2O + NO :Ag + 2 HNO3 (hot and concentrated) → AgNO3 + H2O + NO2 The structure of silver nitrate has been examined by X-ray crystallography sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheatstone Bridge
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of the circuit is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider). Its operation is similar to the original potentiometer. The Wheatstone bridge was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie (sometimes spelled "Christy") in 1833 and improved and popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1843. One of the Wheatstone bridge's initial uses was for soil analysis and comparison."The Genesis of the Wheatstone Bridge" by Stig Ekelof discusses Christie's and Wheatstone's contributions, and why the bridge carries Wheatstone's name. Published in "Engineering Science and Education Journal", volume 10, no 1, February 2001, pages 37–40. Operation In the figure, is the fixed, yet unknown, resistance to be measured. and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
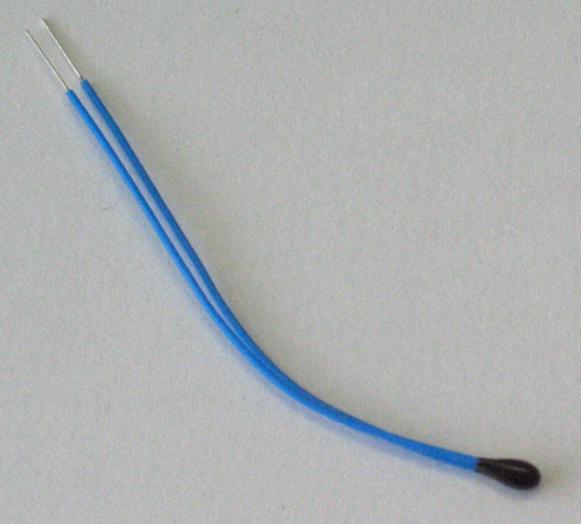
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their conduction model. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. Hence, a PTC thermistor's resistance is directly proportional to temperature. NTC thermistor are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, while PTC thermistors are used as self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. An operational temperature range of a thermistor is dependent on the probe type and is typically between −100 °C and 300 °C (−148 °F and 572 °F). Types Depending on materials used, thermistors are classified into two types: *With ''NTC'' th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the low level language, lowest programming level, executable code consists of Machine code, machine language instructions supported by an individual Microprocessor, processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of Binary number, binary values signifying Instruction set architecture, processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction System call, may also invoke one of many Input/output, input or output operations, for example displaying some text on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. p. 617. In such a process, a closed system usually absorbs thermal energy from its Environment (systems), surroundings, which is heat transfer into the system. Thus, an endothermic reaction generally leads to an increase in the temperature of the system and a decrease in that of the surroundings. It may be a chemical process, such as dissolving ammonium nitrate () in water (), or a physical process, such as the melting of ice cubes. The term was coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an endothermic process is an exothermic process, one that releases or "gives out" energy, usually in the form of heat and sometimes as electrical energy. Thus in each term (endothermic and exothermic) the prefix refers to whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |