|
Emilio Spedicato
Emilio Spedicato (born 1945) is full professor of operations research at the University of Bergamo in Italy. He attended the Liceo Classico Manzoni, obtaining (with Enrico Camporesi, now medical professor in Florida) the highest score in northern Italy at the final exams. He graduated in physics at Milan University and was the first non-Chinese to receive a PhD in a mathematical discipline in China, at Dalian University of Technology. Starting in 1969,ABS projection algorithms: mathematical techniques for linear and nonlinear equations p. 227 (1989) (biographical sketch accompanying article) he worked for seven years at CISE, a nuclear research center near Milano. He also spent two years in the United Kingdom, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city has 3.26 million inhabitants. Its continuously built-up urban area (whose outer suburbs extend well beyond the boundaries of the administrative metropolitan city and even stretch into the nearby country of Switzerland) is the fourth largest in the EU with 5.27 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan), is estimated between 8.2 million and 12.5 million making it by far the largest metropolitan area in Italy and one of the largest in the EU.* * * * Milan is considered a leading alpha global city, with strengths in the fields of art, chemicals, commerce, design, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplex Algorithm
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm (or simplex method) is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The name of the algorithm is derived from the concept of a simplex and was suggested by T. S. Motzkin. Simplices are not actually used in the method, but one interpretation of it is that it operates on simplicial ''cones'', and these become proper simplices with an additional constraint. The simplicial cones in question are the corners (i.e., the neighborhoods of the vertices) of a geometric object called a polytope. The shape of this polytope is defined by the constraints applied to the objective function. History George Dantzig worked on planning methods for the US Army Air Force during World War II using a desk calculator. During 1946 his colleague challenged him to mechanize the planning process to distract him from taking another job. Dantzig formulated the problem as linear inequalities inspired by the work of Wassily Leontief, however, at that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian language, Sumerian poems about Bilgamesh (Sumerian for "Gilgamesh"), king of Uruk, dating from the Third Dynasty of Ur (). These independent stories were later used as source material for a combined epic in Akkadian language, Akkadian. The first surviving version of this combined epic, known as the "Old Babylonian" version, dates back to the 18th century BC and is titled after its incipit, ''Shūtur eli sharrī'' ("Surpassing All Other Kings"). Only a few clay tablet, tablets of it have survived. The later Standard Babylonian version compiled by Sîn-lēqi-unninni dates from the 13th to the 10th centuries BC and bears the incipit ''Sha naqba īmuru'' ("He who Saw the Abyss", in unmetaphoric terms: "He who Sees the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deucalion
In Greek mythology, Deucalion (; grc-gre, Δευκαλίων) was the son of Prometheus; ancient sources name his mother as Clymene, Hesione, or Pronoia.A scholium to ''Odyssey'' 10.2 (='' Catalogue'' fr. 4) reports that Hesiod called Deucalion's mother "Pryneie" or "Prynoe", corrupt forms which Dindorf believed to conceal Pronoea's name. The emendation is considered to have "undeniable merit" by A. Casanova (1979) ''La famiglia di Pandora: analisi filologica dei miti di Pandora e Prometeo nella tradizione esiodea''. Florence, p. 145. He is closely connected with the flood myth in Greek mythology. Etymology According to folk etymology, Deucalion's name comes from , ''deukos'', a variant of , ''gleucos'', i.e. "sweet new wine, must, sweetness" and from , ''haliéus'', i.e. "sailor, seaman, fisher". His wife Pyrrha's name derives from the adjective , -ά, -όν, ''pyrrhós, -á, -ón'', i.e. "flame-colored, orange". Family Of Deucalion's birth, the ''Argonautica'' (from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from grc, Ἔξοδος, translit=Éxodos; he, שְׁמוֹת ''Šəmōṯ'', "Names") is the second book of the Bible. It narrates the story of the Exodus, in which the Israelites leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of Yahweh, who has chosen them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the prophet Moses to Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the 10 commandments and they enter into a covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them their laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to possess the land of Canaan (the "Promised Land"), which had earlier, according to the story of Genesis, been promised to the seed of Abraham. Traditionally ascribed to Moses himself, modern scholars see its initial composition as a product of the Babylonian exile (6th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
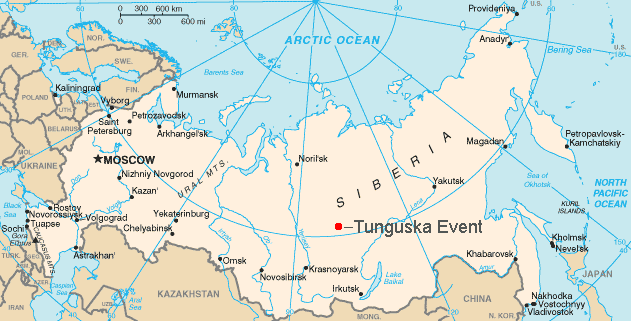
Tunguska Event
The Tunguska event (occasionally also called the Tunguska incident) was an approximately 12-megaton explosion that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of June 30, 1908. The explosion over the sparsely populated Eastern Siberian Taiga flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of of forest, and eyewitness reports suggest that at least three people may have died in the event. The explosion is generally attributed to a meteor air burst: the atmospheric explosion of a stony asteroid about in size. The supposed asteroid approached from the east-southeast, and likely with a relatively high speed of about (~ Ma 80). It is classified as an impact event, even though no impact crater has been found; the object is thought to have disintegrated at an altitude of rather than having hit the surface of the Earth. The Tunguska event is the largest impact event on Earth in recorded history, thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest Roman geographer. He was born in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45. His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less than one hundred pages of ordinary print, and is described by the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (1911) as "dry in style and deficient in method, but of pure Latinity, and occasionally relieved by pleasing word-pictures." Except for the geographical parts of Pliny's ''Historia naturalis'' (where Mela is cited as an important authority), the ''De situ orbis'' is the only formal treatise on the subject in Classical Latin. Biography Little is known of the author except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera in southern Spain, on Algeciras Bay (Mela ii. 6, § 96; but the text is here corrupt). The date of his writing may be approximately fixed by his allusion (iii. 6 § 49) to a proposed British expedition of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Mechanics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, to produce ephemeris data. History Modern analytic celestial mechanics started with Isaac Newton's Principia of 1687. The name "celestial mechanics" is more recent than that. Newton wrote that the field should be called "rational mechanics." The term "dynamics" came in a little later with Gottfried Leibniz, and over a century after Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace introduced the term "celestial mechanics." Prior to Kepler there was little connection between exact, quantitative prediction of planetary positions, using geometrical or arithmetical techniques, and contemporary discussions of the physical causes of the planets' motion. Johannes Kepler Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) was the first to closely integrate the predictive geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert's Tenth Problem
Hilbert's tenth problem is the tenth on the list of mathematical problems that the German mathematician David Hilbert posed in 1900. It is the challenge to provide a general algorithm which, for any given Diophantine equation (a polynomial equation with integer coefficients and a finite number of unknowns), can decide whether the equation has a solution with all unknowns taking integer values. For example, the Diophantine equation 3x^2-2xy-y^2z-7=0 has an integer solution: x=1,\ y=2,\ z=-2. By contrast, the Diophantine equation x^2+y^2+1=0 has no such solution. Hilbert's tenth problem has been solved, and it has a negative answer: such a general algorithm does not exist. This is the result of combined work of Martin Davis, Yuri Matiyasevich, Hilary Putnam and Julia Robinson which spans 21 years, with Matiyasevich completing the theorem in 1970. The theorem is now known as Matiyasevich's theorem or the MRDP theorem (an initialism for the surnames of the four principal contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diophantine Equations
In mathematics, a Diophantine equation is an equation, typically a polynomial equation in two or more unknowns with integer coefficients, such that the only solutions of interest are the integer ones. A linear Diophantine equation equates to a constant the sum of two or more monomials, each of degree one. An exponential Diophantine equation is one in which unknowns can appear in exponents. Diophantine problems have fewer equations than unknowns and involve finding integers that solve simultaneously all equations. As such systems of equations define algebraic curves, algebraic surfaces, or, more generally, algebraic sets, their study is a part of algebraic geometry that is called ''Diophantine geometry''. The word ''Diophantine'' refers to the Hellenistic mathematician of the 3rd century, Diophantus of Alexandria, who made a study of such equations and was one of the first mathematicians to introduce symbolism into algebra. The mathematical study of Diophantine problems that Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobian Matrix And Determinant
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix (, ) of a vector-valued function of several variables is the matrix of all its first-order partial derivatives. When this matrix is square, that is, when the function takes the same number of variables as input as the number of vector components of its output, its determinant is referred to as the Jacobian determinant. Both the matrix and (if applicable) the determinant are often referred to simply as the Jacobian in literature. Suppose is a function such that each of its first-order partial derivatives exist on . This function takes a point as input and produces the vector as output. Then the Jacobian matrix of is defined to be an matrix, denoted by , whose th entry is \mathbf J_ = \frac, or explicitly :\mathbf J = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac \end = \begin \nabla^ f_1 \\ \vdots \\ \nabla^ f_m \end = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ \dfrac & \cdots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |