|
Emile Henry Lacombe
Emile Henry Lacombe (January 29, 1846 – November 28, 1924) was a United States circuit judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit and of the United States Circuit Courts for the Second Circuit. Education and career Born on January 29, 1846, in New York City, New York, Lacombe received an Artium Baccalaureus degree in 1863 from Columbia University and a Bachelor of Laws in 1865 from Columbia Law School. He served in the United States Army from 1862 to 1863 during the American Civil War. He entered private practice in New York City from 1865 to 1875. He was assistant corporation counsel for New York City from 1875 to 1884. He was Corporation Counsel for New York City from 1884 to 1887. Federal judicial service Lacombe received a recess appointment from President Grover Cleveland on May 26, 1887, to the United States Circuit Courts for the Second Circuit, to a new seat authorized by 24 Stat. 492. He was nominated to the same position by President Clevel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Court Of Appeals For The Second Circuit
The United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit (in case citations, 2d Cir.) is one of the thirteen United States Courts of Appeals. Its territory comprises the states of Connecticut, New York and Vermont. The court has appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts: * District of Connecticut * Eastern District of New York * Northern District of New York * Southern District of New York * Western District of New York * District of Vermont The Second Circuit has its clerk's office and hears oral arguments at the Thurgood Marshall United States Courthouse at 40 Foley Square in Lower Manhattan. Due to renovations at that building, from 2006 until early 2013, the court temporarily relocated to the Daniel Patrick Moynihan United States Courthouse across Pearl Street from Foley Square; certain court offices temporarily relocated to the Woolworth Building at 233 Broadway. Because the Second Circuit includes New York City, it has long b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City Law Department
The New York City Law Department, also known as the Office of the Corporation Counsel,http://www.nyc.gov/html/law/downloads/pdf/NYLD%20History%20Card.pdf is the department of the government of New York City responsible for most of the city's legal affairs. The department is headed by the Corporation Counsel, currently Sylvia Hinds-Radix, the 81st official to hold this position. The Law Department represents the mayor, city agencies, and city officials in all civil litigation, in juvenile delinquency proceedings in Family Court, and in prosecutions in the New York City Criminal Court under the New York City Administrative Code. Among the department's other duties are drafting contracts, leases, municipal bond issues, and other legal documents for the city; reviewing local and state legislation; and providing legal advice to city officials on a wide variety of issues. The '' New York City Charter'', the '' New York City Administrative Code'', and the '' Rules of the City of New Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindoos
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry from there. Afghanistan is made up of various ethnicities, of which the Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras and Uzbeks are the largest; the pre-nation state, historical ethnonym Afghan was used to refer to a member of the Pashtun ethnic group. Due to the changing political nature of the state, such as the British-drawn border with Pakistan (then British India) the meaning has changed, and term has shifted to be the national identity of people from Afghanistan from all ethnicities. The two main languages spoken by Afghans are Pashto and Dari (the Afghan dialect of Persian language), and many are bilingual. Background The earliest mention of the name ''Afghan'' (''Abgân'') is by Shapur I of the Sassanid Empire during the 3rd century CE, In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryan
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ''ā́rya'' was used by the Indo-Aryan speakers of the Vedic period as an endonym (self-designation) and in reference to the geographic region known as '' Āryāvarta'' ('abode of the Aryas'), where the Indo-Aryan culture emerged. In the '' Avesta'' scriptures, ancient Iranian peoples similarly used the term ''airya'' to designate themselves as an ethnic group, and in reference to their mythical homeland, '' Airyanem Waēǰō'' ('stretch of the Aryas'). The root also forms the etymological source of place names such as ''Iran'' (*''Aryānām'') and ''Alania'' (*''Aryāna-''). Although the root ''*arya-'' may be of Proto-Indo-European (PIE) origin, its use as an ethnocultural self-designation is only attested among Indo-Iranian peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
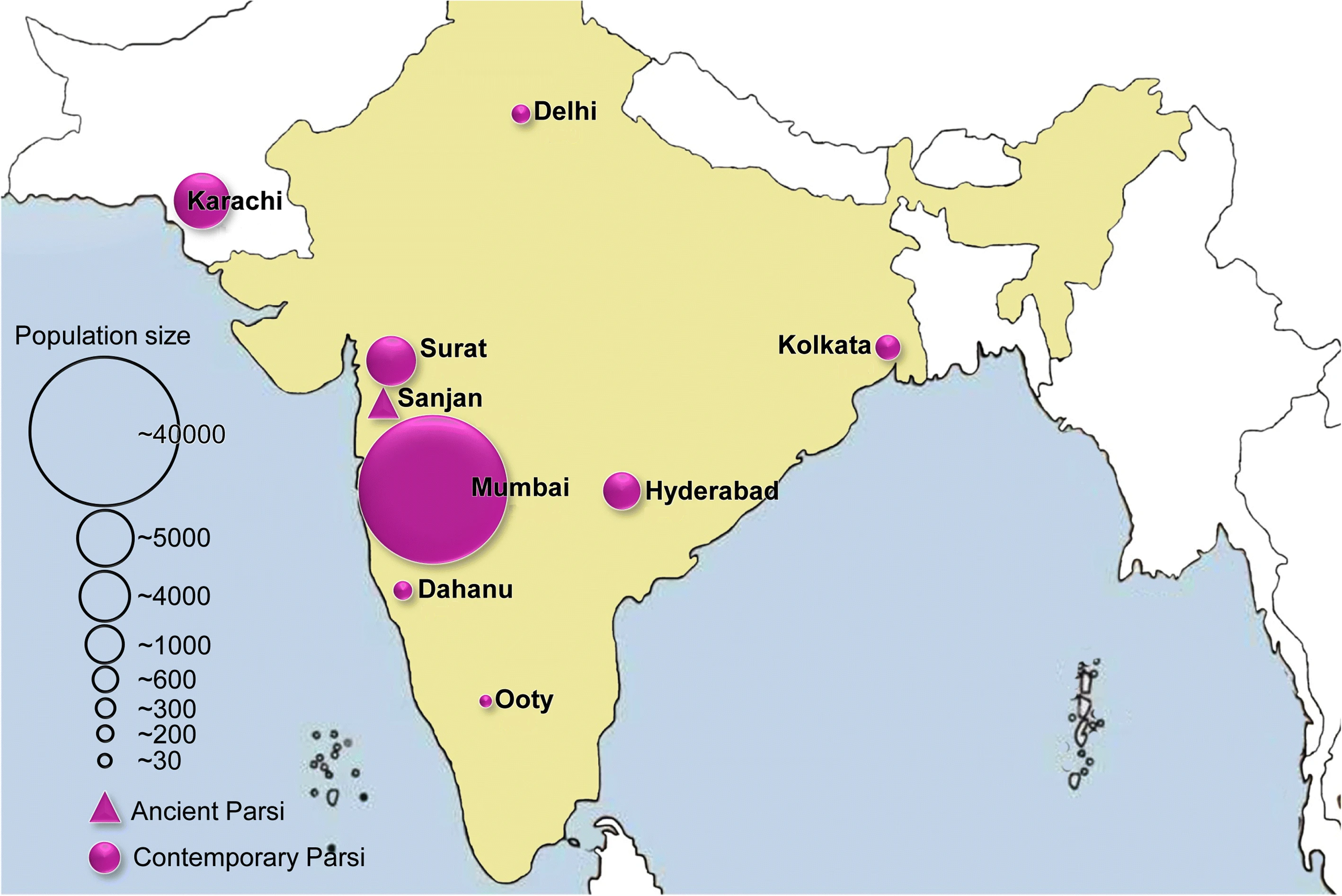
Parsee
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Attorney
United States attorneys are officials of the U.S. Department of Justice who serve as the chief federal law enforcement officers in each of the 94 U.S. federal judicial districts. Each U.S. attorney serves as the United States' chief federal criminal prosecutor in their judicial district and represents the U.S. federal government in civil litigation in federal and state court within their geographic jurisdiction. U.S. attorneys must be nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate, after which they serve four-year terms. Currently, there are 93 U.S. attorneys in 94 district offices located throughout the United States, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands. One U.S. attorney is assigned to each of the judicial districts, with the exception of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, where a single U.S. attorney serves both districts. Each U.S. attorney is the chief federal law enforcement officer within a specified jurisdicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsi
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, '' Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhicaji Balsara
Bhicaji Framji Balsara (often misrendered as Bhicaji Franyi Balsara) (May 30, 1872 – 1962) was an Indian immigrant to the United States, notable for being amongst the first Indians to become a naturalized U.S. citizen. Balsara was a Parsi Zoroastrian from Bombay. He arrived in the United States in 1900, as a cotton buyer for the Tata Group and both settled and married in New York. He applied for citizenship in 1906 but was granted the status only in 1909 after he fought his case before two courts, the Circuit Court in New York and the Federal Court of Appeal. This is as the initial presiding judge, Emile Henry Lacombe in the Circuit Court only reluctantly conferred American citizenship on Balsara, as he reasoned that there "was much force in the argument that the Congress which framed the original act for naturalization of aliens... intended it to include only white persons belonging to the races whose emigrants had contributed to the building up on this continent of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geary Act
The Geary Act was a United States law that extended the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 by adding onerous new requirements. It was written by California Representative Thomas J. Geary and was passed by Congress on . The law required all Chinese residents of the United States to carry a resident permit, a sort of internal passport. Failure to carry the permit at all times was punishable by deportation or a year of hard labor. In addition, Chinese were not allowed to bear witness in court, and could not receive bail in '' habeas corpus'' proceedings. The Geary Act was challenged in the courts but was upheld by the United States Supreme Court in an opinion by Justice Horace Gray, ''Fong Yue Ting v. United States'', 149 U.S. 698, 13 S. Ct. 1016. 37 L.Ed. 905 (1893), Justices David Josiah Brewer, Stephen J. Field, and Chief Justice Melville Fuller dissenting. The Chinese Exclusion Acts remained in force until partly modified by the Magnuson Act in 1943, which slightly ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evarts Act
The Judiciary Act of 1891 ({{USStat, 26, 826), also known as the Evarts Act after its primary sponsor, Senator William M. Evarts, created the United States courts of appeals and reassigned the jurisdiction of most routine appeals from the district and circuit courts to these appellate courts. Therefore, it is also called the Circuit Courts of Appeals Act. The Act created nine new courts that were originally known as the "United States circuit courts of appeals;" the name was changed to its current form in 1948. Each court was composed of two circuit judges and one district judge. The new courts had jurisdiction over most appeals of lower court decisions. The Supreme Court could review either legal issues that a court of appeals certified or decisions of court of appeals by writ of certiorari. The change resulted in an immediate reduction in the Supreme Court's workload (from 623 cases filed in 1890 to 379 in 1891 and 275 in 1892). The Act also eliminated the requirement of "circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)