|
Embryonal Fyn-associated Substrate
Embryonal fyn-associated substrate is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFS gene. It is also known as CASS3. History and discovery EFS (Embryonal Fyn-associated Substrate), also known as SIN (Src INteracting or Signal Integrating protein) was originally identified using cDNA library screening of mouse embryonal libraries for proteins containing SH3-interacting domains, or interacting with the SRC SH3 domain, in two independent studies by Ishino et al. in 1995 and Alexandropoulos et al. in 1996. In humans, the 561 amino acid EFS protein acts as a scaffolding protein for cell signaling based on interactions with SRC, FAK, and other proteins, and has been linked to roles in the function of the immune system, and the development of cancer. Gene The chromosomal location of the EFS gene is 14q11.2 and its genomic coordinates are 14:23356400-23365633 on the reverse strand in GRChB38p2 (Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 38 patch release 2). According to the Human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeasts
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CASS4
Cas scaffolding protein family member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASS4 gene. History and discovery CASS4 (Crk associated substrate 4) is the fourth and last described member of the CAS/CSE protein family, CAS protein family. CASS4 was detected by Singh et al. in 2008 following ''in silico'' screening of databases describing expressed sequence tags from an evolutionarily diverse group of organisms, using the CAS-related proteins (BCAR1, p130Cas, NEDD9, NEDD9/HEF1 and Embryonal fyn-associated substrate, EFS) mRNAs as templates. Singh et al. subsequently cloned and characterized the CASS4 gene, originally assigning the name HEPL (HEF1-EFS-p130Cas-like) for similarity to the other three defined CAS genes. The official name was subsequently changed to CASS4 by the Human Genome Organization (Human Genome Organisation, HUGO) Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). Gene The chromosomal location of the CASS4 gene is 20q13.31, with genomic coordinates of 20: 56411548-564 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEDD9
Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 9 (NEDD-9) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NEDD9'' gene. NEDD-9 is also known as enhancer of filamentation 1 (EF1), CRK-associated substrate-related protein (CAS-L), and Cas scaffolding protein family member 2 (CASS2). An important paralog of this gene is BCAR1. Discovery In 1992, Kumar, ''et al.,'' first described a sequence tag corresponding to the NEDD9 3′ untranslated region based on the cloning of a group of genes predominantly expressed in the brain of embryonic, but not adult mice, a group of genes designated neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated. In 1996, two groups independently described the complete sequence of the NEDD9 gene, and provided initial functional analysis of NEDD9 protein. Law ''et al.'' overexpressed a human cDNA library in ''S. cerevisiae'', and screened for genes that simultaneously affected cell cycle and cell polarity controls, inducing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCAR1
Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCAR1'' gene. Gene BCAR1 is localized on chromosome 16 on region q, on the negative strand and it consists of seven exons. Eight different gene isoforms have been identified that share the same sequence starting from the second exon onwards but are characterized by different starting sites. The longest isoform is called BCAR1-iso1 (RefSeq NM_001170714.1) and is 916 amino acids long, the other shorter isoforms start with an alternative first exon. Function BCAR1 is a ubiquitously expressed adaptor molecule originally identified as the major substrate of v-Src and v-Crk . p130Cas/BCAR1 belongs to the Cas family of adaptor proteins and can act as a docking protein for several signalling partners. Due to its ability to associate with multiple signaling partners, p130Cas/BCAR1 contributes to the regulation to a variety of signaling pathways leading to cell adhesion, migration, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adapter Molecule Crk
Adapter molecule crk also known as proto-oncogene c-Crk is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRK'' gene. The CRK protein participates in the Reelin signaling cascade downstream of DAB1. Function Adapter molecule crk is a member of an adapter protein family that binds to several tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. This protein has several SH2 and SH3 domains (src-homology domains) and is involved in several signaling pathways, recruiting cytoplasmic proteins in the vicinity of tyrosine kinase through SH2-phosphotyrosine interaction. The N-terminal SH2 domain of this protein functions as a positive regulator of transformation whereas the C-terminal SH3 domain functions as a negative regulator of transformation. Two alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms with distinct biological activity have been described. Crk together with CrkL participates in the Reelin signaling cascade downstream of DAB1. v-Crk, a transforming oncoprotein from avian sarcoma viruse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
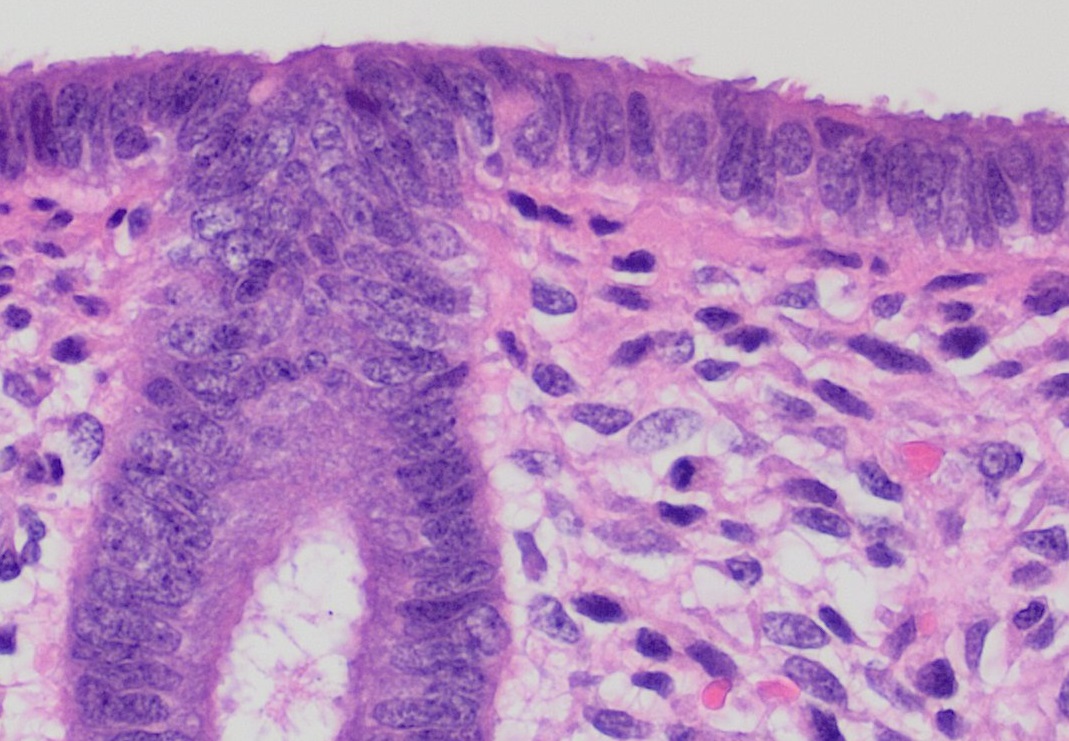
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17β-estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as the breasts, widening of the hips and a female-associated pattern of fat distribution. It is also important in the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the mammary glands, uterus and vagina during puberty, adulthood and pregnancy. It also has important effects in many other tissues including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain. Though estradiol levels in males are much lower than in females, estradiol has important roles in males as well. Apart from humans and other mammals, estradiol is also found in most vertebrates and crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species. Estradiol is produced especially within the follicles of the ovaries, but also in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy. It was first prescribed in 1934. Biological activity Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the nuclear progesterone receptor (nPR) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |