|
Emanation
Emanation may refer to: * Emanation (chemistry), a dated name for the chemical element radon * Emanation From Below, a concept in Slavic religion * Emanation in the Eastern Orthodox Church, a belief found in Neoplatonism *Emanation of the state, a legal term for a public service body * Emanationism, an idea in the cosmology or cosmogony of certain religious or philosophical systems * "Emanations" (''Star Trek: Voyager''), a 1995 episode of ''Star Trek: Voyager'' * ''Emanations'' (Penderecki), a 1958 composition by Krzysztof Penderecki See also * Aeon (Gnosticism) In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("t ... *'' Emanate'', a 1999 album by Penumbra {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanationism
Emanationism is an idea in the cosmology or cosmogony of certain religious or philosophical systems. Emanation, from the Latin ''emanare'' meaning "to flow from" or "to pour forth or out of", is the mode by which all things are derived from the first reality, or principle. All things are derived from the first reality or perfect God by steps of degradation to lesser degrees of the first reality or God, and at every step the emanating beings are less pure, less perfect, less divine. Emanationism is a transcendent principle from which everything is derived, and is opposed to both creationism (wherein the universe is created by a sentient God who is separate from creation) and materialism (which posits no underlying subjective and/or ontological nature behind phenomena being immanent). Origins Emanationism is a cosmological theory which asserts that all things "flow" from an underlying principle or reality, usually called the Absolute or Godhead. Any teachings which involve emanati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanation (chemistry)
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into various short-lived radioactive elements and lead. Radon itself is the immediate decay product of radium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of only 3.8 days, making it one of the rarest elements. Since thorium and uranium are two of the most common radioactive elements on Earth, while also having three isotopes with half-lives on the order of several billion years, radon will be present on Earth long into the future despite its short half-life. The decay of radon produces many other short-lived nuclides, known as "radon daughters", ending at stable isotopes of lead.+ ion is believed to form by the following reaction: : Rn (g) + 2 (s) → (s) + 2 (g) For this reason, antimon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanation In The Eastern Orthodox Church
Emanation (literally "dripping") is a belief, found in Neoplatonism, that the cause of certain beings or states of being consists of an overflow from the essence of God or other higher spiritual beings, as opposed to a special act of creation. This overflow is usually conceived in a non-temporal way as a permanent relationship of causation rather than as an event causing an entity to come into existence at a given point in time. The word "emanation" can refer either to the process of emanation or to the thing emanated. Equivalent concepts are found in Gnosticism and in Kabbalah (Jewish mysticism). This article explores similar concepts in Eastern Orthodoxy and Eastern Catholicism. Concepts The Neoplatonic concept of ''emanation'' can be compared to the statements made by fourteenth-century Eastern Orthodox theologian Gregory Palamas. He drew a distinction between God's ''essence'' and ''energies'', affirming that God was unknowable in His essence, but knowable in His energie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanations (Penderecki)
''Emanations'', also referred to by its original German title ''Emanationen'' or by its Polish title ''Emanacje'', is a composition for two orchestras by Polish composer Krzysztof Penderecki. Composed in 1958, it is one of his early compositions. Composition and premiere The composition was conceived and written in 1958 and won the second prize at the Polish Composers Union Young Composers Competition, in April 1959. It would eventually be premiered on September 7, 1961, at the Darmstadt International Summer Courses for New Music. Michael Gielen conducted the Southwest German Radio Symphony Orchestra for its premiere. It was dedicated to Tadeusz Ochlewski and was published by the Polish Music Publishing House and the Moeck Musikinstrumente + Verlag. Analysis ''Emanations'' is scored for two string orchestras that are tuned a minor second A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanation Of The State
Emanation of the state is a term used in European law to describe any body which provides a public service under the control of government. The term was defined by the European Court of Justice (ECJ) in 1990, in the case of ''Foster, A and others v. British Gas plc''.Full text: The ECJ's ruling defines the term as: A body, whatever its legal form, which has been made responsible, pursuant to a measure adopted by the state, for providing a public service under the control of the state and has for that purpose special powers beyond that which result from the normal rules applicable in relations between individuals. The term is most obviously used to describe public sector employers, such as the police, fire service, local government bodies or schools. ''Foster, A and others v. British Gas plc'' This case was referred to the ECJ by the House of Lords in 1990. The issue to be decided was whether employees of a nationalised industry (in this case British Gas plc British Gas plc wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanation From Below
In the pre-Christian religion of Eastern and Southern Slavs, Rod (Slovenian, Croatian: Rod, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Macedonian, Russian, Serbian Cyrillic: Род, Ukrainian Cyrillic: Рід) is the god of the family, ancestors and fate, perhaps as the supreme god. Among Southern Slavs, he is also known as Sud ("(the) Judge"). He is usually mentioned together with Rozhanitsy deities (among Southern Slavs, the Sudzenitsy). One's first haircut (''postriziny'') was dedicated to him, in a celebration in which he and the rozhanitsy were given a meal and the cut hair. His cult lost its importance through time, and in the ninth or tenth century he was replaced by Perun, Svarog and/or Svetevid, which explains his absence in the pantheon of Vladimir the Great. Etymology Rod's name is confirmed in Old Church Slavonic and Old East Slavic sources about pre-Christian Slavic religion. The name is derived from the Proto-Slavic word *''rodъ'', meaning "family", "birth", "origin", "clan", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
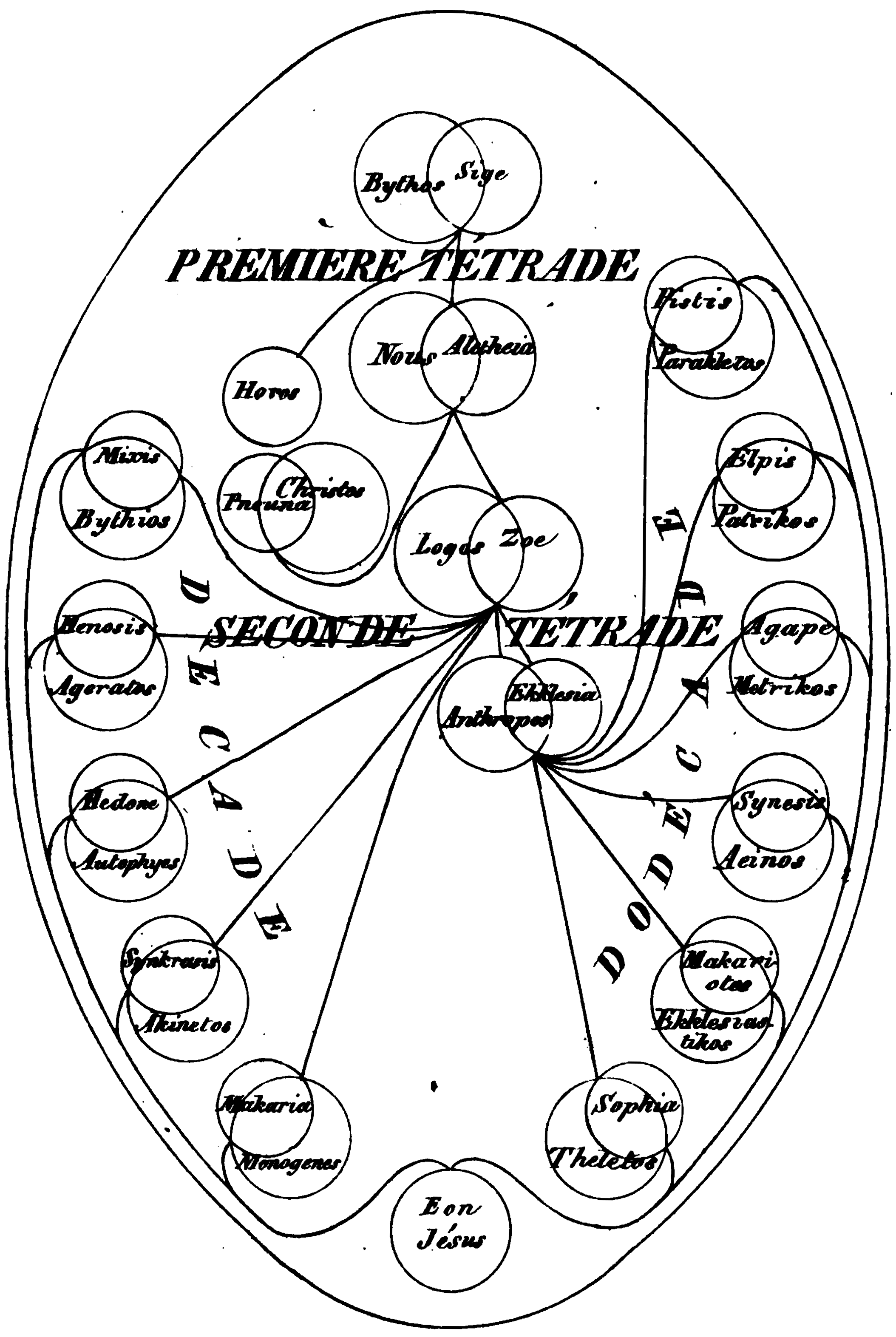
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the beginning", ), and Aeons. In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described, but emanation theory is common to all forms of Gnosticism. In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (Greek , from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'', lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' ("thought, intent", Greek ), ''Charis'' ("grace", Greek ), or ''Sige'' ("silence", Greek ). The split perfect being conceives the second Aeon, ''Nous'' ("mind", Greek Νους), within its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |