|
Elżbieta Pleszczyńska
Elżbieta Pleszczyńska (born 20 March 1933) is a Polish full professor of statistics, activist of disability rights movement. Biography She gained an M.Sc. in mathematics at University of Warsaw, Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry in 1956. She held position at Institute of Mathematics PAS until 1972. She received her Ph.D. in 1965 in the area of discriminant analysis ("Power of Test, and Separability of Hypothesis in Statistical Design of Experiments"). Her habilitation thesis, titled "Trend Estimation Problems in Time Series Analysis", was accepted in 1973. In 1967/8 she was visiting researcher in University of Wales (Great Britain), and in 1971/2 in University of Montreal. In 1973 she moved to the Institute of Computer Science, PAS. In 1977, 1979 and 1989 she was awarded by the Polish Academy of Science. In 1981 she visited Italy invited by CNR. In the 1990s she started (together with her team) so called grade data analysis, a science of applying copula and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wola Wydrzyna
Wola Wydrzyna is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sulmierzyce, within Pajęczno County, Łódź Voivodeship, in central Poland. It lies approximately north-west of Sulmierzyce, north-east of Pajęczno, and south of the regional capital Łódź Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti .... References Villages in Pajęczno County {{Pajęczno-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined. For a unimodal distribution, negative skew commonly indicates that the ''tail'' is on the left side of the distribution, and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. In cases where one tail is long but the other tail is fat, skewness does not obey a simple rule. For example, a zero value means that the tails on both sides of the mean balance out overall; this is the case for a symmetric distribution, but can also be true for an asymmetric distribution where one tail is long and thin, and the other is short but fat. Introduction Consider the two distributions in the figure just below. Within each graph, the values on the right side of the distribution taper differently from the values on the left side. These tapering sides are called ''tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Density Function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a ''relative likelihood'' that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the ''absolute likelihood'' for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling ''within a particular range of values'', as opposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outliers
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
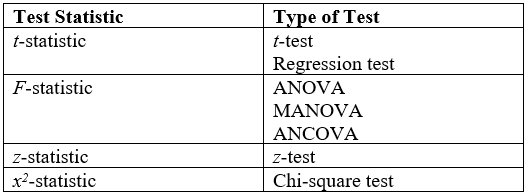
Statistical Test
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset (Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the multivariate normal distribution, multivariate Gaussian distribution, or joint normal distribution is a generalization of the one-dimensional (univariate) normal distribution to higher dimensions. One definition is that a random vector is said to be ''k''-variate normally distributed if every linear combination of its ''k'' components has a univariate normal distribution. Its importance derives mainly from the multivariate central limit theorem. The multivariate normal distribution is often used to describe, at least approximately, any set of (possibly) correlated real-valued random variables each of which clusters around a mean value. Definitions Notation and parameterization The multivariate normal distribution of a ''k''-dimensional random vector \mathbf = (X_1,\ldots,X_k)^ can be written in the following notation: : \mathbf\ \sim\ \mathcal(\boldsymbol\mu,\, \boldsymbol\Sigma), or to make it explicitly known that ''X'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Squares Method
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the residuals (a residual being the difference between an observed value and the fitted value provided by a model) made in the results of each individual equation. The most important application is in data fitting. When the problem has substantial uncertainties in the independent variable (the ''x'' variable), then simple regression and least-squares methods have problems; in such cases, the methodology required for fitting errors-in-variables models may be considered instead of that for least squares. Least squares problems fall into two categories: linear or ordinary least squares and nonlinear least squares, depending on whether or not the residuals are linear in all unknowns. The linear least-squares problem occurs in statistical regressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, pronounced ) ― also known as Pearson's ''r'', the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), the bivariate correlation, or colloquially simply as the correlation coefficient ― is a measure of linear correlation between two sets of data. It is the ratio between the covariance of two variables and the product of their standard deviations; thus, it is essentially a normalized measurement of the covariance, such that the result always has a value between −1 and 1. As with covariance itself, the measure can only reflect a linear correlation of variables, and ignores many other types of relationships or correlations. As a simple example, one would expect the age and height of a sample of teenagers from a high school to have a Pearson correlation coefficient significantly greater than 0, but less than 1 (as 1 would represent an unrealistically perfect correlation). Naming and history It was developed by Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametric Statistics
Parametric statistics is a branch of statistics which assumes that sample data comes from a population that can be adequately modeled by a probability distribution that has a fixed set of Statistical parameter, parameters. Conversely a non-parametric model does not assume an explicit (finite-parametric) mathematical form for the distribution when modeling the data. However, it may make some assumptions about that distribution, such as continuity or symmetry. Most well-known statistical methods are parametric. Regarding nonparametric (and semiparametric) models, David Cox (statistician), Sir David Cox has said, "These typically involve fewer assumptions of structure and distributional form but usually contain strong assumptions about independencies". Example The normal distribution, normal family of distributions all have the same general shape and are ''parameterized'' by mean and standard deviation. That means that if the mean and standard deviation are known and if the distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |