|
Elstergebirge
The Elster Mountains (german: Elstergebirge, cs, Halštrovské hory) is a small range of mountains, in Saxony and the Czech Republic, to the west of the Ore Mountains. They lie in a region known as Vogtland, and take their name from the River Elster, or more precisely the White Elster which has its source in these hills, near the Czech town of Aš. The valley of the Zwota marks the northeastern border of the Ore Mountains, while to the southwest the valley of the Eger between Selb and Libá separates them from the Fichtelgebirge. The highest points ''Hoher Brand'' with an elevation of 805m, Vysoký kámen (''Hoher Stein'') at 773 m, ''Háj u Aše'' (''Hainberg'') at 758 m and the Kapellenberg at 757 m. The Elster Mountains have many mineral-rich springs on which the spa towns of Bad Brambach and Bad Elster in Vogtlandkreis were founded; and the Czech spa of Františkovy Lázně (''Franzenbad'') was founded. See also * List of regions of Saxony A classification of the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vysoký Kámen
:''Vysoký kámen, is the name of at least nine hills in Slovakia and the Czech Republic, they are distinguished by their height. This article is on the 773 m summit, in Vogtland'' The stony summit Vysoký kámen (German ''Hoher Stein'') lies 8 km west of Kraslice in okres Sokolov (Czech Republic) and 1 km from the German border in the Elstergebirge, part of the Erzgebirge. To the east of the hill is Počátky originally Kámen u Kraslic (German: Stein am Hohen Stein) and Kostelní (German: Kirchberg am Hohen Stein), and to the west lies Erlbach with it hamlet Eubabrunn. The ridge of rocks at the summit resemble a ruined castle. It is the western rocks that are used by climbers Climber may refer to: *Climber, a participant in the activity of climbing *Climber, general name for a vine *Climber, or climbing specialist, a road bicycle racer who can ride especially well on highly inclined roads * Climber (BEAM), a robot that .... They are ideal for beginners, with som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Ore Mountains
The Western Ore Mountains (german: Westerzgebirge) is a natural region that forms the westernmost part of the Ore Mountains in the German state of Saxony. It is also part of the major landscape unit known as the Saxon Highlands and Uplands. It extends eastwards to include the valley of the Schwarzwasser, and, below its mouth, that of the Zwickauer Mulde, and incorporates the western parts of the former major units known as the Lower and Upper Western Ore Mountains (''Unteres und Oberes Westerzgebirge''), no. 423, as well as the Southern Slopes of the Ore Mountains (''Südabdachung des Erzgebirges''), no. 420. In the current classification system of natural regions, the Western Ore Mountains only covers the western part of the region that bore the same name in the preceding system, whilst the eastern part of that region is now part of the Central Ore Mountains. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
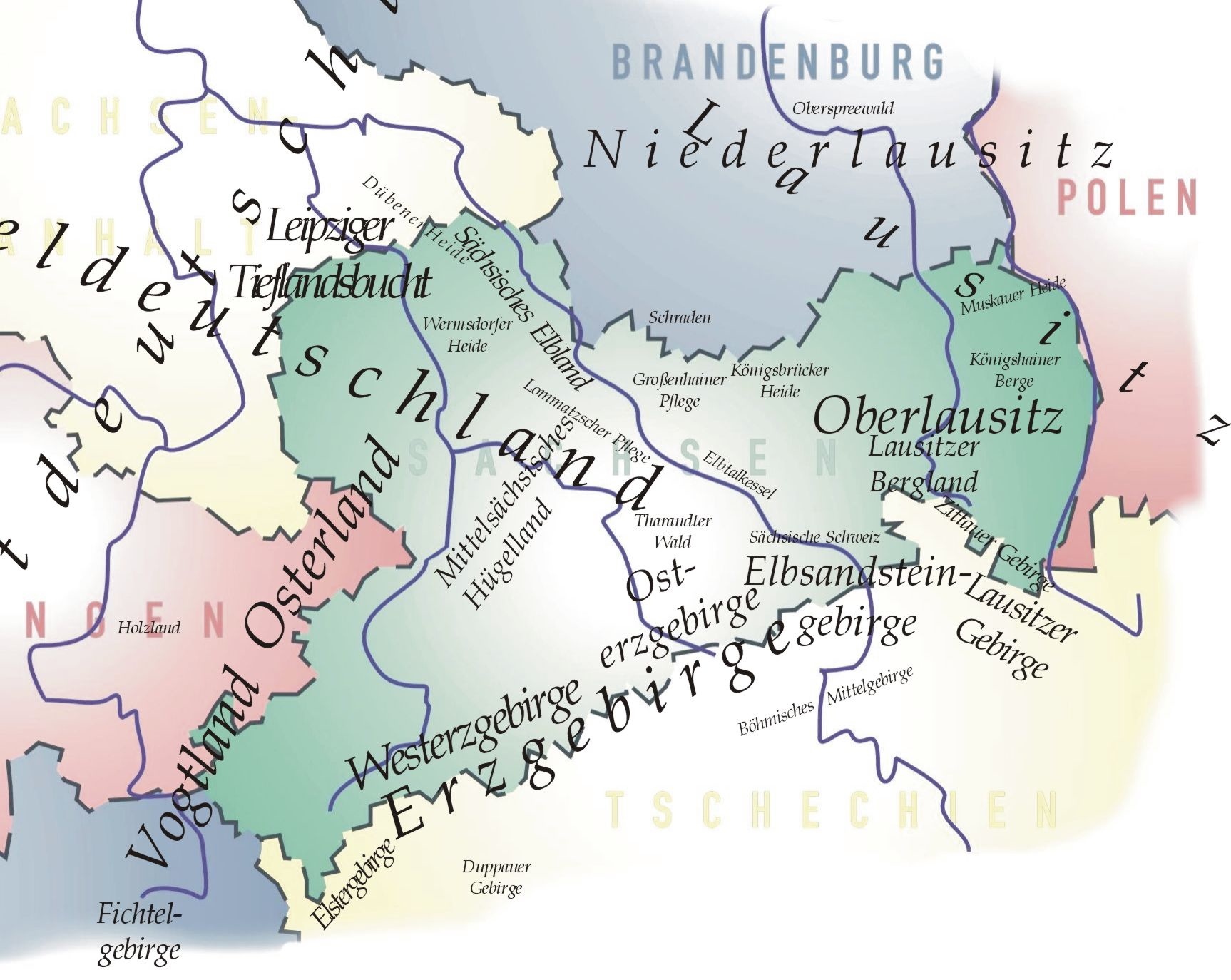
Natural Regions Of Saxony
The classification of natural regions of Saxony shown here was produced between 1994 and 2001 by a working group called "Ecosystem and Regional Character" (''Naturhaushalt und Gebietscharakter'') at the Saxonian Academy of Sciences in Leipzig as part of the research and development project "Natural Regions and Natural Region Potential of the Free State of Saxony" (''Naturräume und Naturraumpotentiale des Freistaates'') at a scale of 1:50,000 as the basis for the rural development and regional planning. This was also supported by the Saxon State Ministry of the Environment and Agriculture and the Saxon Ministry of the Interior. The basis of the structure was a comprehensive, statewide compilation of the smallest physical geographic landscape units (physiotopes). These were aggregated into larger units ( nano-geochores and micro-geochores) in an orderly way using the method of "natural region categories". For each of the micro-geochores that resulted from this, a 9-page document wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of Saxony
A classification of the various regions of Saxony cannot be achieved in any uniform or standard way, as the commonly used names usually represent a mixture of historical regions and geographical features. Many well-known names of regions, such as Lusatia, comprise a mixture of natural habitats and geological zones, while other, scientifically assigned, names are only known in university departments. The following list contains, in alphabetical order, both those names that are commonly used, as well as those only known regionally or used in the scientific field. They are listed by their English names with their German names in brackets. Names of settlements or other geographic features are omitted here. Overall, across much of the area, Saxony belongs both to Eastern Germany and Central Germany. However, on a smaller scale there are many regions and landscapes that overlap the boundaries of the Free State and extend beyond it: * Bahra Valley (''Bahratal'') * Biela Valley (''Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogtland
Vogtland (; cz, Fojtsko) is a region spanning the German states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and north-western Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the former leadership by the Vögte ("advocates" or "lords protector") of Weida, Gera and Plauen. Geography Natural geography The landscape of the Vogtland is sometimes referred to as idyllic, bearing in mind its fields, meadows and wooded hilltops. In the south and southeast, Vogtland rises to a low or mid-height mountain range also called ''Oberes Vogtland'', or Upper Vogtland. Here, monocultural coniferous forest is the predominant form of vegetation. The Vogtland's highest mountain is Schneehübel, reaching 974 metres; another remarkable landmark is the Schneckenstein, 883 m above sea level, which gained some renown for its (falsely) alleged unique abundance of topaz crystals. Its mountains spread from Ore Mountains in the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spa Town
A spa town is a resort town based on a mineral spa (a developed mineral spring). Patrons visit spas to "take the waters" for their purported health benefits. Thomas Guidott set up a medical practice in the English town of Bath in 1668. He became interested in the curative properties of the hot mineral waters there and in 1676 wrote ''A discourse of Bathe, and the hot waters there. Also, Some Enquiries into the Nature of the water''. This brought the purported health-giving properties of the waters to the attention of the aristocracy, who started to partake in them soon after. The term ''spa'' is used for towns or resorts offering hydrotherapy, which can include cold water or mineral water treatments and geothermal baths. Argentina *Termas de Rio Hondo *Presidencia Roque Sáenz Peña Australia There are mineral springs in the Central Highlands of Victoria. Most are in and around Daylesford and Hepburn Springs. Daylesford and Hepburn Springs call themselves 'Spa Countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills In Germany
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills In Europe
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Ranges Of Germany
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film '' The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Františkovy Lázně
Františkovy Lázně (; german: Franzensbad) is a spa town in Cheb District in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 5,200 inhabitants. Together with neighbouring Karlovy Vary and Mariánské Lázně, it is part of the West Bohemian Spa Triangle. The town centre is well preserved and since 1992 has been protected as an urban monument reservation. In 2021, the town became part of the transnational UNESCO World Heritage Site under the name "Great Spa Towns of Europe" because of its natural springs and its architectural testimony to the popularity of spa towns across Europe in the 18th through 20th centuries. Administrative parts Villages of Aleje-Zátiší, Dlouhé Mosty, Dolní Lomany, Horní Lomany, Krapice, Slatina and Žírovice are administrative parts of Františkovy Lázně. Geography Františkovy Lázně is located about north of Cheb, in the historical Egerland region. It is situated in the westernmost part of the Cheb Basin. The Slatinný Stream, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogtlandkreis
The Vogtlandkreis () is a ''Landkreis'' (rural district) in the southwest of Saxony, Germany, at the borders to Thuringia, Bavaria, and the Czech Republic. Neighboring districts are (from south clockwise) Hof, Saale-Orla, Greiz, Zwickau and Erzgebirgskreis. Plauen is the administrative center and largest city of the district. Other major cities ''( Große Kreisstädte)'' are Reichenbach im Vogtland, Auerbach, and Oelsnitz im Vogtland. History The Vogtland became part of the Holy Roman Empire under king Conrad III in the 12th century. In 1209 the minister dynasty administrating the area was split into three areas, Weida, Greiz and Gera-Plauen. When centralized power over the area decreased, county leaders, local administrators, called in Latin ''advocatus'' or in German ''Vögte'', were appointed, giving the area its current name. The Vogtland war (1354-1357) ended this administration and the area changed ownership to Bohemia. In 1546 Henry IV, Burgrave of Plauen got the area f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |