|
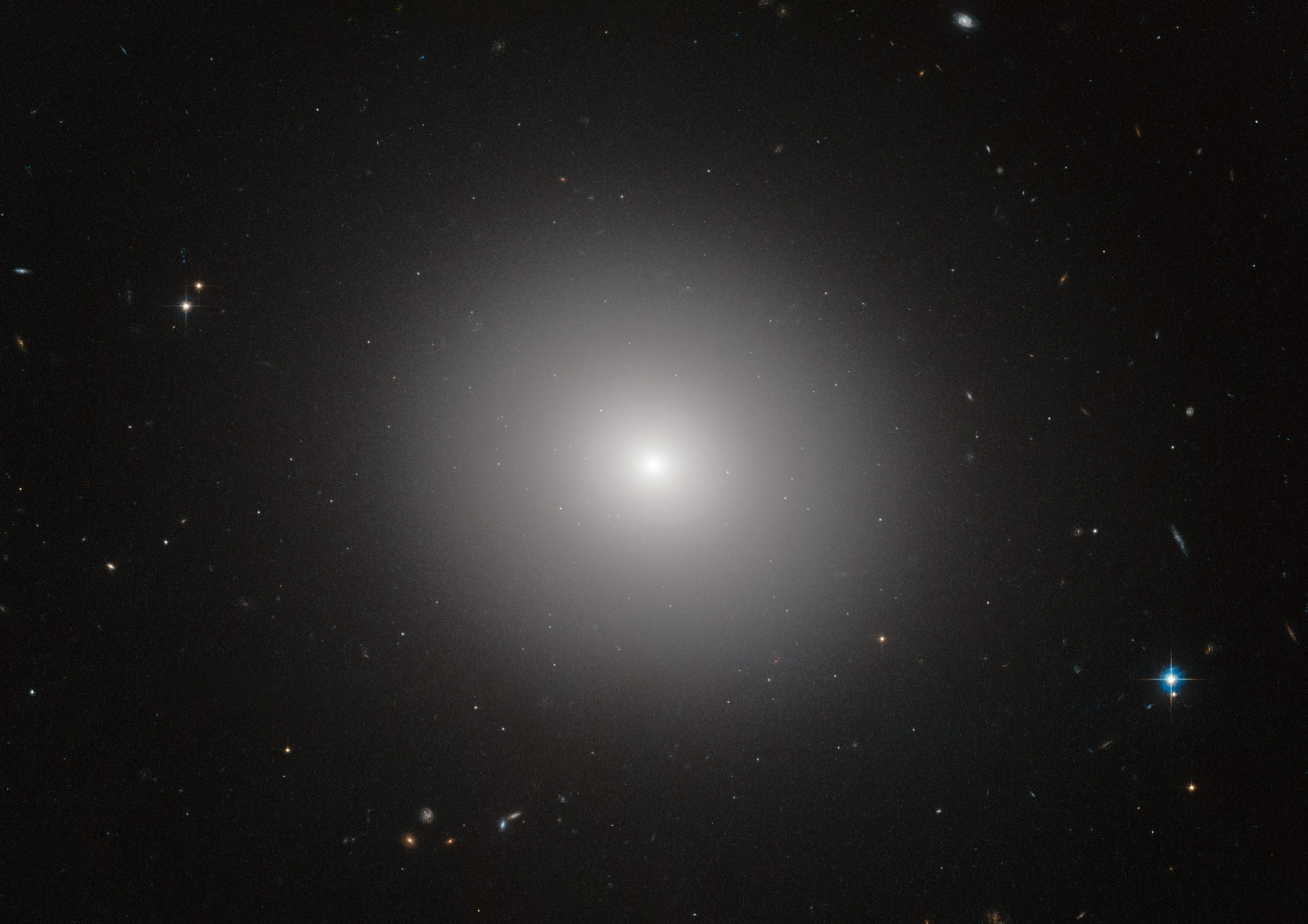
Elliptical Galaxies
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae'', with their intermediate scale disks, a subset of the "early-type" galaxy population. Most elliptical galaxies are composed of older, low-mass stars, with a sparse interstellar medium, and they tend to be surrounded by large numbers of globular clusters. Star formation activity in elliptical galaxies is typically minimal; they may, however, undergo brief periods of star formation when merging with other galaxies. Elliptical galaxies are believed to make up approximately 10–15% of galaxies in the Virgo Supercluster, and they are not the dominant type of galaxy in the universe overall. They are preferentially found close to the centers of galaxy clusters. Elliptical galaxies range in size from dwarf ellipticals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell S740, Cropped To ESO 325-G004
Abell may refer to: People *Abell (surname) *George O. Abell, of the astronomical catalogues fame Places ;United States * Abell, Maryland, a location in St. Mary's County, Maryland * Abell, Baltimore, Abell, a neighborhood in Baltimore, Maryland * Abells Corners, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community Astronomy *Abell catalogue of rich clusters of galaxies (ACO) *Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae (A) Bibliographical database *ABELL, the ''Annual Bibliography of English Language and Literature'' See also *Abel (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type-cD Galaxy
The type-cD galaxy (also cD-type galaxy, cD galaxy) is a galaxy morphology classification, a subtype of type-D galaxy, type-D Elliptical galaxy#Sizes and shapes, giant elliptical galaxy. Characterized by a large galactic halo, halo of stars, they can be found near the centres of some rich galaxy clusters. They are also known as supergiant ellipticals or central dominant galaxies. Characteristics The cD-type is a classification in the Galaxy morphological classification, Yerkes galaxy classification scheme, one of two Yerkes classifications still in common use, along with D-type. The "c" in "cD" refers to the fact that the galaxies are very large, hence the adjective supergiant, while the "D" refers to the fact that the galaxies appear diffuse. A backformation of "cD" is frequently used to indicate "central Dominant galaxy"."Uncertainties on Clusters of Galaxies Distances", C. Adami, M.P. Ulmer, 18 July 2000, (accessed 14 April 2010) cDs are also frequently considered the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESO 383-76
ESO 383-76 (ESO 383-G 076) is an elongated, X-ray luminous supergiant elliptical galaxy, residing as the dominant, brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) of the Abell 3571 galaxy cluster, the sixth-brightest in the sky at X-ray wavelengths. It is located at the distance of from Earth, and is possibly a member of the large Shapley Supercluster. With a diameter of about , it is one of the largest galaxies known. It also contains a supermassive black hole, one of the most massive known with mass estimates varying from to . Observation history The first known observation of the galaxy was during the creation of the Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies by Boris Vorontsov-Velyaminov and V.P. Harkipova in 1974, with the catalogue entry MCG-05-33-002. The galaxy was also observed around this time by the ESO Sky Survey Atlas, a large-scale survey of the Southern Sky conducted using the 1-metre Schmidt telescope in La Silla Observatory. In 1982, the ESO/Uppsala Catalogue then lists the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 4697 Group
The Virgo II Groups, also known as the Virgo II Cloud, Virgo Southern Extension, or the Virgo S Cloud, are a series of at least 100 Galaxy cluster, galactic clusters and individual galaxy, galaxies stretching approximately off the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. It is located approximately to from the Solar System, at a right ascension of to . These clusters include: *M61 Group: **IC 3474 **Messier 61, M61 (NGC 4303) **NGC 4255 **NGC 4420 **NGC 4496A **NGC 4517A **NGC 4527 **NGC 4533 **NGC 4536 **NGC 4581 **NGC 4599 **NGC 4632 **PGC 40951 **UGC 7387 **UGC 7522 **UGC 7612 **UGC 7780 *NGC 4030 Group: **NGC 4030 **UGC 6970 **UGC 7000 *NGC 4179 Group: **NGC 4116 **NGC 4123 **NGC 4179 **UGC 7035 *NGC 4697 Group: **IC 3908 **MCG-1-33-1 **MCG-1-33-3 **MCG-1-33-11 **MCG-1-33-33 **MCG-1-33-59 **MCG-1-33-61 **MCG-1-33-82 **NGC 4697 **NGC 4731 **NGC 4775 **NGC 4941 **NGC 4948 **NGC 4948A **NGC 4951 **NGC 4958 **UGCA 310 *NGC 4699 Group: **MCG-2-33-15 **MCG-2-33-47 **MCG-1-33-60 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 4697
NGC 4697 (also known as Caldwell 52) is an elliptical galaxy some 40 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It is a member of the NGC 4697 Group, a group of galaxies also containing NGC 4731 and several generally much smaller galaxies. This group is about 55 million light-years away; it is one of the many Virgo II Groups, which form a southern extension of the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies. The distance to NGC 4697 is not known with high precision: measurements vary from 28 to 76 million light-years. According to the NASA Extra-galactic Database, the average is about 38 million light-years; according to SIMBAD, about 50 million light-years. The supermassive black hole at the core of NGC 4697 has a mass of as measured from Atacama Large Millimeter Array observations of the rotation of the central gas disk. One supernova has been observed in NGC 4697: SN 2018imd ( type Ia, mag. 15.5). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 105
Messier 105 or M105, also known as NGC 3379, is an elliptical galaxy 36.6 million light-years away in the equatorial constellation of Leo. It is the biggest elliptical galaxy in the Messier catalogue that is not in the Virgo cluster. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781, just a few days after he discovered the nearby galaxies Messier 95 and Messier 96. This galaxy is one of a few not object-verified by Messier so omitted in the editions of his Catalogue of his era. It was appended when Helen S. Hogg found a letter by Méchain locating and describing this object which matched those aspects under its first-published name, NGC 3379. It has a morphological classification of E1, indicating a standard elliptical galaxy with a flattening of 10%. The major axis is aligned along a position angle of 71°. Isophotes of the galaxy are near perfect ellipses, twisting no more than 5° out of alignment, with changes in ellipticity of no more than 0.06. There is no fine st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 89
Messier 89 (M89 for short, also known as NGC 4552) is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by Charles Messier on March 18, 1781. M89 is a member of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. Features Current observations allow the possibility that M89 may be nearly perfectly spherical. Distinct flattening as ellipsoids is found in all easily measurable comparators up to a few times of its distance. The alternative explanation is that it is an ellipsoid oriented so that it appears spherical to an observer on Earth. The galaxy features a surrounding structure of gas and dust, extending up to 150,000 light-years and jets of heated particles up to two-thirds of that. This indicates that it may have once been an active quasar or radio galaxy. M89 has an extensive and complex system of surrounding shells and plumes, indicating that it has seen one or several notable mergers. Chandra studies in the wavelength of the X-Rays show two ring-like structures of hot gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time (magazine)
''Time'' (stylized in all caps as ''TIME'') is an American news magazine based in New York City. It was published Weekly newspaper, weekly for nearly a century. Starting in March 2020, it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on March 3, 1923, and for many years it was run by its influential co-founder, Henry Luce. A European edition (''Time Europe'', formerly known as ''Time Atlantic'') is published in London and also covers the Middle East, Africa, and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition (''Time Asia'') is based in Hong Kong. The South Pacific edition, which covers Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands, is based in Sydney. Since 2018, ''Time'' has been owned by Salesforce founder Marc Benioff, who acquired it from Meredith Corporation. Benioff currently publishes the magazine through the company Time USA, LLC. History 20th century ''Time'' has been based in New York City since its first issue published on March 3, 1923 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
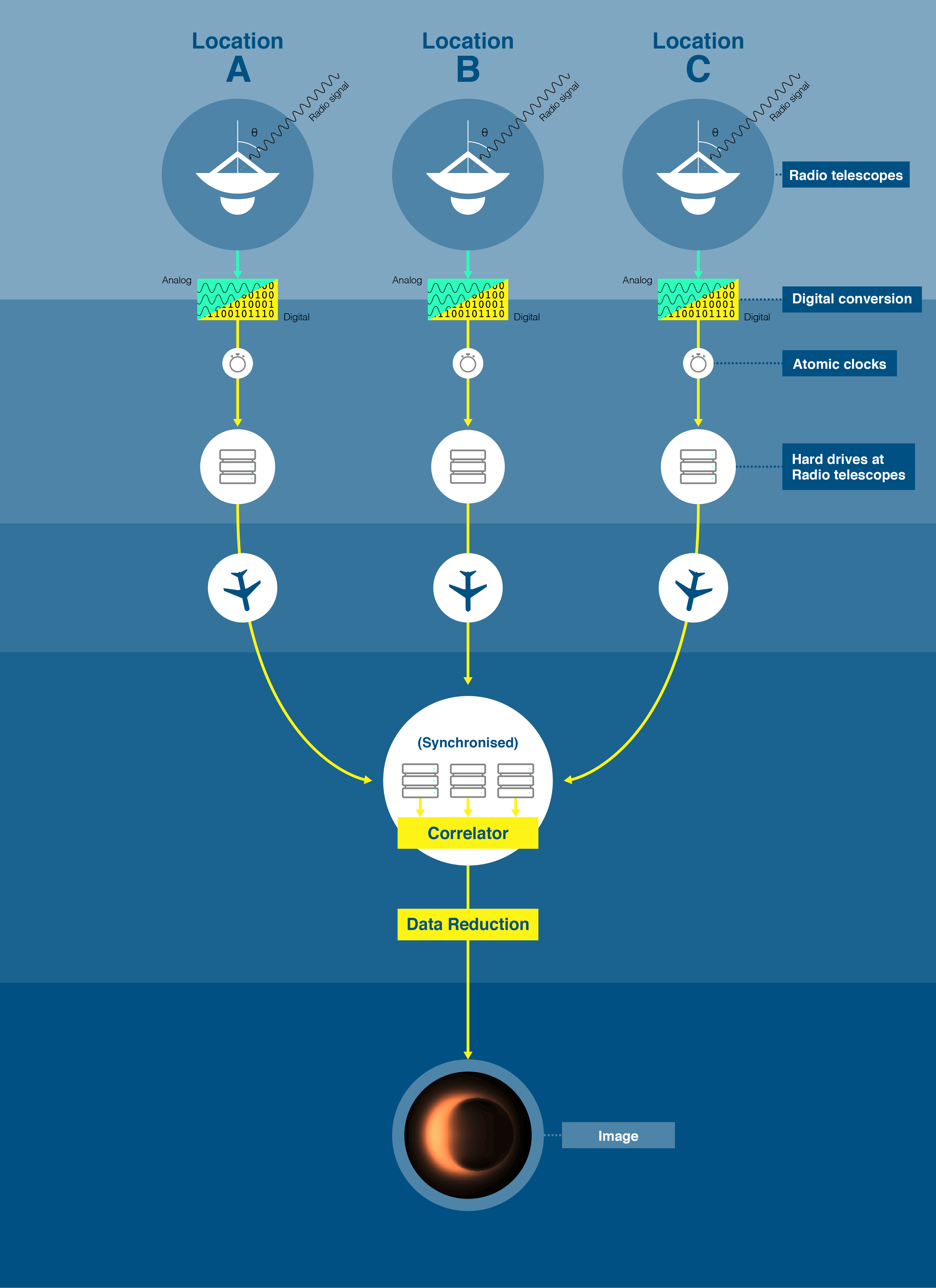
Event Horizon Telescope
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a Astronomical interferometer, telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A*, at Galactic Center, the center of the Milky Way. The Event Horizon Telescope project is an international collaboration that was launched in 2009 after a long period of theoretical and technical developments. On the theory side, work on the photon orbit and first simulations of what a black hole would look like progressed to predictions of VLBI imaging for the Galactic Cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy, elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo that contains several trillion stars. One of the List of largest galaxies, largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters—about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way—and a jet of energetic plasma (physics), plasma that originates at the core and extends at least , traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers. The French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, and cataloged it as a nebula. M87 is about from Earth and is the second-brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, having many satellite galaxies. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 60
Messier 60 or M60, also known as NGC 4649, is an elliptical galaxy approximately 57 million light-years away in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. Together with NGC 4647, it forms a pair known as Arp 116. Messier 60 and nearby elliptical galaxy Messier 59 were discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler in April 1779, observing a comet in the same part of the sky. Charles Messier added both to his catalogue about three days after this. Characteristics This is an elliptical galaxy of type E (E1.5), although some sources class it as S0 – a lenticular galaxy. An E2 class indicates a flattening of 20%, which has a nearly round appearance. The isophotes of the galaxy are boxy in shape, rather than simple ellipses. The mass-to-light ratio is a near constant 9.5 in the V (visual) band of the UBV system. The galaxy has an effective radius of (translating, at its distance, to about 10 kpc), with an estimated mass of ~1012 within a threefold volume, of wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 59
Messier 59 or M59, also known as NGC 4621, is an elliptical galaxy in the celestial equator, equatorial constellation of Virgo (constellation), Virgo. It is a member of the Virgo Cluster, with the nearest fellow member away and around 5 magnitudes fainter. The nearest cluster member of comparable brightness is the lenticular galaxy NGC 4638, which is around away. It and the angularly nearby elliptical galaxy Messier 60 were both discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler in April 1779 when observing comet seeming close by. Charles Messier listed both in the Messier Catalogue about three days after Koehler's discovery. This is an elliptical galaxy of type E5 with a position angle of 163.3°, indicating the overall shape shows a flattening of 50%. However, isophotes for this galaxy deviate from a perfect ellipticity, showing pointed shapes instead. These can be decomposed mathematically into a three component model, with each part having a different eccentricity. The main elliptical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |