|
Electrocardiogram In Myocardial Infarction
Electrocardiography in suspected myocardial infarction has the main purpose of detecting ischemia or acute coronary injury in emergency department populations coming for symptoms of myocardial infarction (MI). Also, it can distinguish clinically different types of myocardial infarction. Technical issues The standard 12 lead electrocardiogram (ECG) has several limitations. An ECG represents a brief sample in time. Because unstable ischemic syndromes have rapidly changing supply versus demand characteristics, a single ECG may not accurately represent the entire picture.Cannon CP at al. ''Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes''. p. 175. New Jersey: Humana Press, 1999. . It is therefore desirable to obtain ''serial'' 12 lead ECGs, particularly if the first ECG is obtained during a pain-free episode. Alternatively, many emergency departments and chest pain centers use computers capable of continuous ST segment monitoring. The standard 12 lead ECG also does not directly examine the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Bundle Branch Block
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality in the heart that can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). In this condition, activation of the left ventricle of the heart is delayed, which causes the left ventricle to contract later than the right ventricle. Causes Among the causes of LBBB are: * Aortic stenosis * Dilated cardiomyopathy * Acute myocardial infarction * Extensive coronary artery disease * Primary disease of the cardiac electrical conduction system * Long standing hypertension leading to aortic root dilatation and subsequent aortic regurgitation * Lyme disease Mechanisms Slow or absent conduction through the left bundle branch means that it takes longer than normal for the left ventricle to fully depolarise. This can be due to a damaged bundle branch that is completely unable to conduct, but may represent intact conduction that is slower than normal. LBBB may be fixed, present at all times, but may be intermittent for example occurring only durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sgarbossa's Criteria
Sgarbossa's criteria are a set of electrocardiographic findings generally used to identify myocardial infarction (also called ''acute myocardial infarction or a "heart attack"'') in the presence of a left bundle branch block (LBBB) or a ventricular paced rhythm. Myocardial infarction (MI) is often difficult to detect when LBBB is present on ECG. A large clinical trial of thrombolytic therapy for MI (GUSTO-1) evaluated the electrocardiographic diagnosis of evolving MI in the presence of LBBB. The rule was defined by Dr. Elena Sgarbossa, Argentine- born American cardiologist. Among 26,003 North American patients who had a myocardial infarction confirmed by enzyme studies, 131 (0.5%) had LBBB. A scoring system, now commonly called Sgarbossa criteria, was developed from the coefficients assigned by a logistic model for each independent criterion, on a scale of 0 to 5. A minimal score of 3 was required for a specificity of 90%. Sgarbossa's criteria Three criteria are included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the ''relative refractory period'' or ''vulnerable period''. The T wave contains more information than the QT interval. The T wave can be described by its symmetry, skewness, slope of ascending and descending limbs, amplitude and subintervals like the Tpeak–Tend interval. In most leads, the T wave is positive. This is due to the repolarization of the membrane. During ventricle contraction (QRS complex), the heart depolarizes. Repolarization of the ventricle happens in the opposite direction of depolarization and is negative current, signifying the relaxation of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles. But this negative flow causes a positive T wave; although the cell becomes more negatively charged, the net effect is in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the heart and contraction of the large ventricular muscles. In adults, the QRS complex normally lasts ; in children it may be shorter. The Q, R, and S waves occur in rapid succession, do not all appear in all leads, and reflect a single event and thus are usually considered together. A Q wave is any downward deflection immediately following the P wave. An R wave follows as an upward deflection, and the S wave is any downward deflection after the R wave. The T wave follows the S wave, and in some cases, an additional U wave follows the T wave. To measure the QRS interval start at the end of the PR interval (or beginning of the Q wave) to the end of the S wave. Normally this interval is 0.08 to 0.10 seconds. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Flather
Marcus Denis Flather (born December 1957) is an American academic who is a clinical professor in medicine at Norwich Medical School. A specialist in cardiology, he is also a recognised expert in clinical trials. Education Flather was educated at Rugby School. He graduated from the UCL Medical School in 1982 and trained in general medicine and cardiology in London and Oxford. He completed an MBA at the University of East Anglia in 2016. Career Flather is a former director of the Clinical Trials and Evaluation Unit (CTEU) at the Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals. He has an h-index of 102 according to Google Scholar Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes p .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Flather, Marcus Denis 1957 births Living people People educated at Rugby Scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
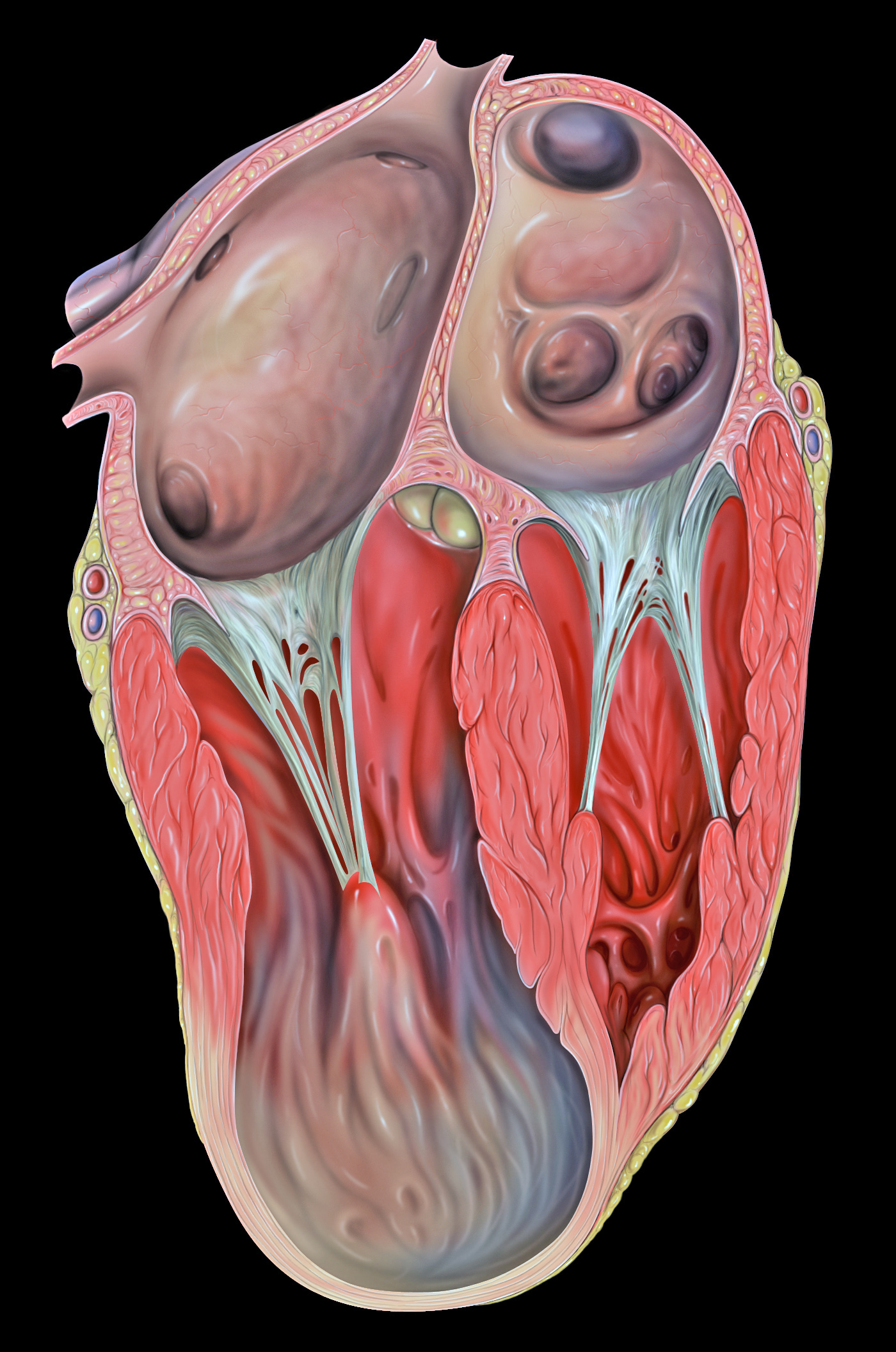
Ventricular Aneurysm
Ventricular aneurysms are one of the many complications that may occur after a heart attack. The word aneurysm refers to a bulge or 'pocketing' of the wall or lining of a vessel commonly occurring in the blood vessels at the base of the septum, or within the aorta. In the heart, they usually arise from a patch of weakened tissue in a ventricular wall, which swells into a bubble filled with blood. This, in turn, may block the passageways leading out of the heart, leading to severely constricted blood flow to the body. Ventricular aneurysms can be fatal. They are usually non-rupturing because they are lined by scar tissue. A left ventricular aneurysm can be associated with ST elevation. Signs and symptoms Ventricular aneurysms usually grow at a very slow pace, but can still pose problems. Usually, this type of aneurysm grows in the left ventricle. This bubble has the potential to block blood flow to the rest of the body, and thus limit the patient's stamina. In other cases, a sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death. Common causes of hyperkalemia include kidney failure, hypoaldosteronism, and rhabdomyolysis. A number of medications can also cause high blood potassium including spironolactone, NSAIDs, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. The severity is divided into mild (5.5–5.9mmol/L), moderate (6.0–6.4mmol/L), and severe (>6.5mmol/L). High levels can be detected on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Pseudohyperkalemia, due to breakdown of cells during or after taking the blood sample, should be ruled out. Initial treatment in those with ECG changes is salts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe when sitting up and more severe when lying down or breathing deeply. Other symptoms of pericarditis can include fever, weakness, palpitations, and shortness of breath. The onset of symptoms can occasionally be gradual rather than sudden. The cause of pericarditis often remains unknown but is believed to be most often due to a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infections such as tuberculosis, uremic pericarditis, heart attack, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chest trauma. Diagnosis is based on the presence of chest pain, a pericardial rub, specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, and fluid around the heart. A heart attack may produce similar symptoms to pericarditis. Treatment in most cases is with NSAIDs and possibly the ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Repolarization
Benign early repolarization also known as early repolarization (abbreviation, abbr.: BER) is found on ECG in about 1% of those with chest pain. It is diagnosed based on an elevated J-point / ST elevation with an end-QRS notch or end-QRS slur and where the ST segment concave up. It is believed to be a normal variant. Benign early repolarization that occurs as some patterns is associated with ventricular fibrillation. The association, revealed by research performed in the late 2000s, is very small. Types Benign early repolarization, very prevalent in younger people and healthy male athletes, can be divided into 3 subtypes: * Type 1 – BER pattern seen in lateral precordial leads. * Type 2 – BER pattern seen in inferior or inferolateral leads. * Type 3 – BER pattern seen globally (inferior, lateral, right precordial leads). Associations with serious conditions Research in the late 2000s has linked this finding when found as some patterns to ventricular fibrillation, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart either the upper atria, or lower ventricles to cause the targeted chambers to contract and pump blood. By doing so, the pacemaker regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because the heart's natural pacemaker is not fast enough, or because there is a block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist, to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Causes While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular disease, or high blood pressure. It is one aspect of ventricular remodeling. While LVH itself is not a disease, it is usually a marker for disease involving the heart. Disease processes that can cause LVH include any disease that increases the afterload that the heart has to contract against, and some primary diseases of the muscle of the heart. Causes of increased afterload that can cause LVH include aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency and hypertension. Primary disease of the muscle of the heart that cause LVH are known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, which can lead into heart failure. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |