|
Early Repolarization
Benign early repolarization also known as early repolarization (abbreviation, abbr.: BER) is found on ECG in about 1% of those with chest pain. It is diagnosed based on an elevated J-point / ST elevation with an end-QRS notch or end-QRS slur and where the ST segment concave up. It is believed to be a normal variant. Benign early repolarization that occurs as some patterns is associated with ventricular fibrillation. The association, revealed by research performed in the late 2000s, is very small. Types Benign early repolarization, very prevalent in younger people and healthy male athletes, can be divided into 3 subtypes: * Type 1 – BER pattern seen in lateral precordial leads. * Type 2 – BER pattern seen in inferior or inferolateral leads. * Type 3 – BER pattern seen globally (inferior, lateral, right precordial leads). Associations with serious conditions Research in the late 2000s has linked this finding when found as some patterns to ventricular fibrillation, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNJ8
Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8, also known as KCNJ8, is a human gene encoding the Kir6.1 protein. A mutation in KCNJ8 has been associated with cardiac arrest in the early repolarization syndrome. Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. Kir6.1 is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. Kir6.1, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their ac .... See also * Inward-rectifier potassium ion channel References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodiagnosis
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts (that is, their natural electrophysiology) or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli (evoked potentials). The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing ( electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine (also EDX) is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular, and/or muscular systems. The provision of a quality electrodiagnostic medical evaluation requires exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCN10A
Nav1.8 is a sodium ion channel subtype that in humans is encoded by the ''SCN10A'' gene. Nav1.8-containing channels are tetrodotoxin (TTX)-resistant voltage-gated channels. Nav1.8 is expressed specifically in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG), in unmyelinated, small-diameter sensory neurons called C-fibres, and is involved in nociception. C-fibres can be activated by noxious thermal or mechanical stimuli and thus can carry pain messages. The specific location of Nav1.8 in sensory neurons of the DRG may make it a key therapeutic target for the development of new analgesics and the treatment of chronic pain. Function Voltage-gated sodium ion channels (VGSC) are essential in producing and propagating action potentials. Tetrodotoxin, a toxin found in pufferfish, is able to block some VGSCs and therefore is used to distinguish the different subtypes. There are three TTX-resistant VGSC: Nav1.5, Nav1.8 and Nav1.9. Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 are both expressed in nociceptors (damage-sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCN5A
Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha, also known as NaV1.5 is an integral membrane protein and tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel subunit. NaV1.5 is found primarily in cardiac muscle, where it mediates the fast influx of Na+-ions (INa) across the cell membrane, resulting in the fast depolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. As such, it plays a major role in impulse propagation through the heart. A vast number of cardiac diseases is associated with mutations in NaV1.5 (see paragraph genetics). ''SCN5A'' is the gene that encodes the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5. Gene structure SCN5A is a highly conserved gene located on human chromosome 3, where it spans more than 100 kb. The gene consists of 28 exons, of which exon 1 and in part exon 2 form the 5' untranslated region ( 5’UTR) and exon 28 the 3' untranslated region ( 3’UTR) of the RNA. SCN5A is part of a family of 10 genes that encode different types of sodium channels, i.e. brain-type ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e. either a voltage-change ("voltage-gated", "voltage-sensitive", or "voltage-dependent" sodium channel; also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") or a binding of a substance (a ligand) to the channel (ligand-gated sodium channels). In excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CACNA2D1
Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA2D1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the alpha-2/delta subunit family, a protein in the voltage-dependent calcium channel complex. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Research on a highly similar protein in rabbit suggests the protein described in this record is cleaved into alpha-2 and delta subunits. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed, but have not been thoroughly characterized. Gabapentinoids alpha2/delta proteins are believed to be the molecular target of the gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin, which are used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. See also * Voltage-dependent calcium channel Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
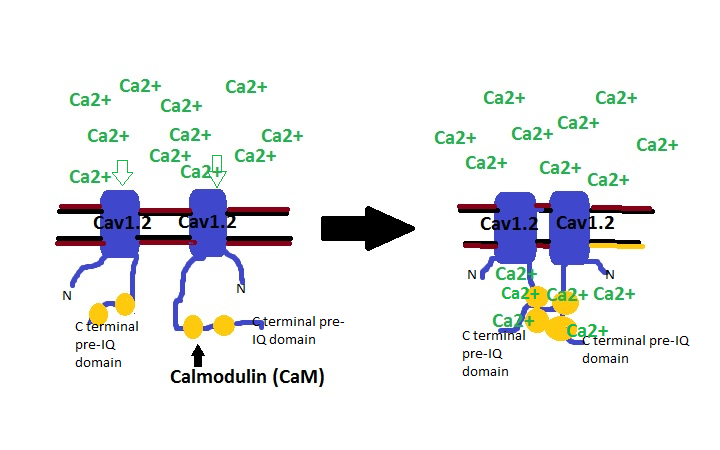
CACNA1c
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1C subunit (also known as Cav1.2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1C'' gene. Cav1.2 is a subunit of L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel. Structure and function This gene encodes an alpha-1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the cell upon membrane polarization (see membrane potential and calcium in biology). The alpha-1 subunit consists of 24 transmembrane segments and forms the pore through which ions pass into the cell. The calcium channel consists of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta and beta subunits in a 1:1:1 ratio. The S3-S4 linkers of Cav1.2 determine the gating phenotype and modulated gating kinetics of the channel. Cav1.2 is widely expressed in the smooth muscle, pancreatic cells, fibroblasts, and neurons. However, it is particularly important and well known for its expression in the heart where it mediates L-type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-type Voltage-gated Calcium Channel
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation- contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DPP10
Inactive dipeptidyl peptidase 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DPP10'' gene. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Function This gene encodes a single-pass type II membrane protein that is a member of the S9B family in clan SC of the serine proteases. This protein has no detectable protease activity, most likely due to the absence of the conserved serine residue normally present in the catalytic domain of serine proteases. However, it does bind specific voltage-gated potassium channels and alters their expression and biophysical properties. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been associated with asthma and autism spectrum disorders The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder, neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) .... R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNE5
KCNE1-like also known as KCNE1L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNE1L'' gene. Function Voltage-gated potassium ( Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. ''KCNE5'' encodes a membrane protein, KCNE5 (originally named KCNE1-L) that has sequence similarity to the KCNE1 gene product, a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, isk-related subfamily. The ''KCNE'' gene family comprises five genes in the human genome, each encoding a type I membrane protein. The KCNE subunits are potassium channel regulatory subunits that do not pass currents themselves but alter the properties of potassium channel pore-forming alpha subunits. KCNE5 is thus far the least-studied member of the KCNE f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Transient Outward Potassium Current
The cardiac transient outward potassium current (referred to as Ito1 or Ito ) is one of the ion currents across the cell membrane of heart muscle cells. It is the main contributing current during the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential. It is a result of the movement of positively charged potassium (K+) ions from the intracellular to the extracellular space. Ito1 is complemented with Ito2 resulting from Cl− ions to form the transient outward current Ito. Mechanism Ito1 is rapidly activated and deactivated. It is activated after the fast increase of the membrane potential following the phase 0 of the cardiac action potential. Once activated, (K+) ions from inside the cells flow to the extracellular space. This outward flow of positively charged ions constitutes the Ito1 and causes the transmembrane voltage to decrease. This decrease of the transmembrane potential is known as repolarization. Ito1 is then quickly deactivated, stopping the repolarization and endi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |