|
Electro-hydraulic Actuator
Electro-Hydrostatic actuators (EHAs), replace hydraulic systems with self-contained actuators operated solely by electrical power. EHAs eliminate the need for separate hydraulic pumps and tubing, because they include their own pump, simplifying system architectures and improving safety and reliability. This technology originally was developed for the aerospace industry but has since expanded into many other industries where hydraulic power is commonly used. Conventional designs Aircraft were originally controlled by small aerodynamic surfaces operated by cables, attached to levers that magnified the pilot's input, using mechanical advantage. As aircraft grew in size and performance, the aerodynamic forces on these surfaces grew to the point where it was no longer possible for the pilot to manually control them across a wide range of speeds - controls with enough advantage to control the aircraft at high speed left the aircraft with significant overcontrol at lower speeds when the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
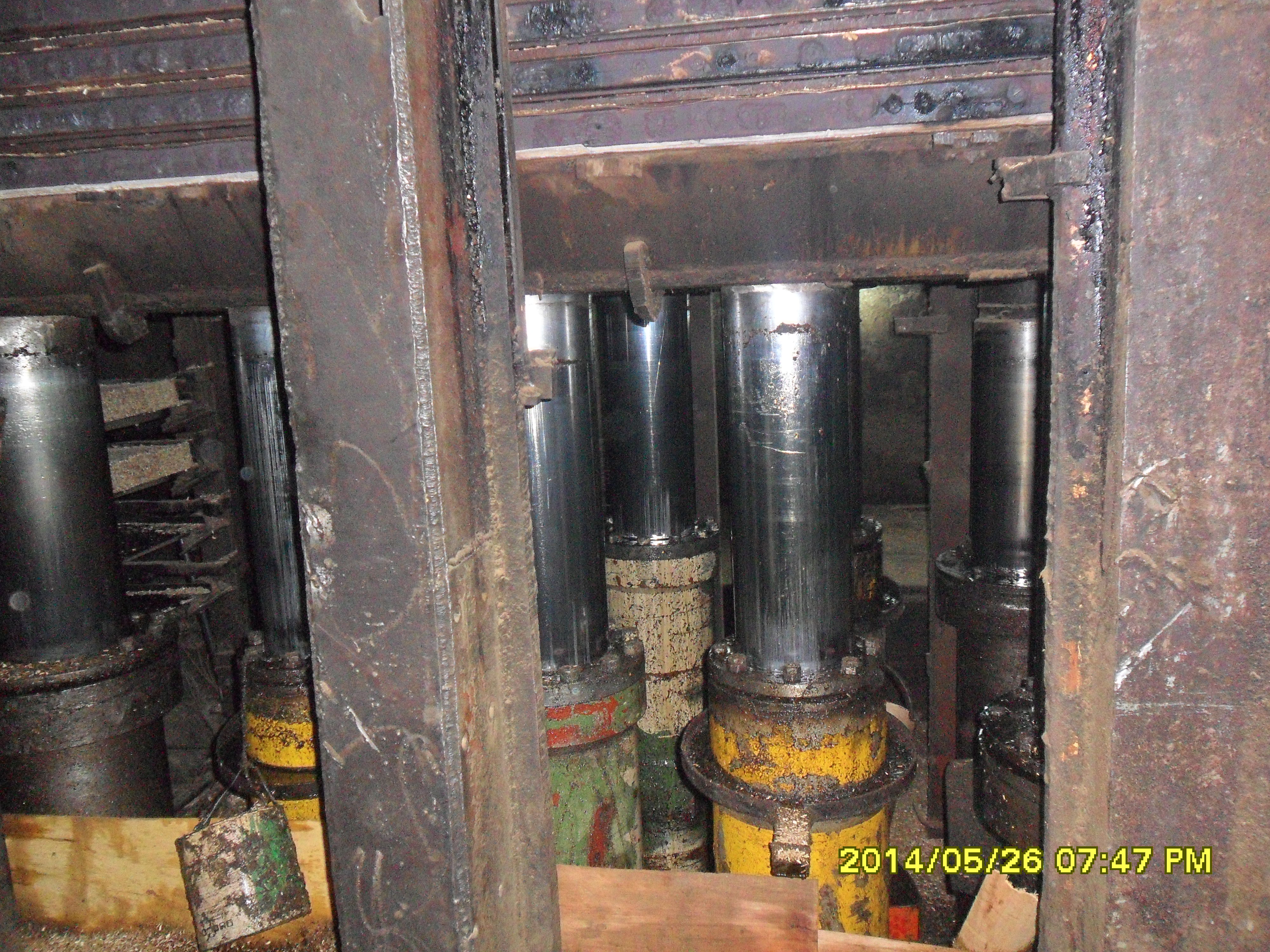
Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment (engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. Operation Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is incompressible. Typically oil is used as hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth. The barrel is closed on one end by the cylinder bottom (also called the cap) and the other end by the cylinder head (also called the gland) where the piston rod comes out of the cylinder. The piston has sliding rings and seals. The piston divides the inside of the cylinder into two chambers, the bottom chamber (cap end) and the piston rod side chamber (rod end/head-end). Flanges, trunnions, clevises, and lugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Actuator
A valve actuator is the mechanism for opening and closing a valve. Manually operated valves require someone in attendance to adjust them using a direct or geared mechanism attached to the valve stem. Power-operated actuators, using gas pressure, hydraulic pressure or electricity, allow a valve to be adjusted remotely, or allow rapid operation of large valves. Power-operated valve actuators may be the final elements of an automatic control loop which automatically regulates some flow, level or other process. Actuators may be only to open and close the valve, or may allow intermediate positioning; some valve actuators include switches or other ways to remotely indicate the position of the valve. Used for the automation of industrial valves, actuators can be found in all kinds of process plants. They are used in waste water treatment plants, power plants, refineries, mining and nuclear processes, food factories, and pipelines. Valve actuators play a major part in automating proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Pump
Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic. A hydraulic pump is a mechanical source of power that converts mechanical power into hydraulic energy ( hydrostatic energy i.e. flow, pressure). It generates flow with enough power to overcome pressure induced by the load at the pump outlet. When a hydraulic pump operates, it creates a vacuum at the pump inlet, which forces liquid from the reservoir into the inlet line to the pump and by mechanical action delivers this liquid to the pump outlet and forces it into the hydraulic system. Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement (flow through the pump per rotation of the pump) cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pumps, which have a more complicated construction that allows the displacement to be adjusted. Hydrodynamic pumps are more frequent in day-to-day life. Hydrostatic pumps of various types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the ''law of the lever.'' Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal. Lever The lever is a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to or positioned on or across a fixed point. The lever operates by applying forces at different distances from the fulcrum, or pivot. The location of the fulcrum determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi Zero
The Mitsubishi A6M "Zero" is a long-range carrier-based fighter aircraft formerly manufactured by Mitsubishi Aircraft Company, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and was operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1940 to 1945. The A6M was designated as the , or the Mitsubishi A6M Rei-sen. The A6M was usually referred to by its pilots as the ''Reisen'' (, zero fighter), "0" being the last digit of the imperial year 2600 (1940) when it entered service with the Imperial Navy. The official Allied reporting name was "Zeke", although the name "Zero" (from Type 0) was used colloquially as well. The Zero is considered to have been the most capable carrier-based fighter in the world when it was introduced early in World War II, combining excellent maneuverability and very long range.Hawks, Chuck"The Best Fighter Planes of World War II" chuckhawks.com. Retrieved: 18 January 2007. The Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS) also frequently used it as a land-based fighter. In ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twin-boom design with a central nacelle containing the cockpit and armament. Along with its use as a general fighter, the P-38 was used in various aerial combat roles, including as a highly effective fighter-bomber, a night fighter, and a long-range escort fighter when equipped with drop tanks. The P-38 was also used as a bomber-pathfinder, guiding streams of medium and heavy bombers, or even other P-38s equipped with bombs, to their targets."P-38 Lightning" National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved 21 Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fly-by-wire
Fly-by-wire (FBW) is a system that replaces the conventional manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface. The movements of flight controls are converted to electronic signals transmitted by wires, and flight control computers determine how to move the actuators at each control surface to provide the ordered response. It can use mechanical flight control backup systems (like the Boeing 777) or use fully fly-by-wire controls.Fly by Wire Flight Control Systems Sutherland Improved fully fly-by-wire systems interpret the pilot's control inputs as a desired outcome and calculate the control surface positions required to achieve that outcome; this results in various combinations of rudder, elevator, aileron, flaps and engine controls in different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fly-by-light
Fly-by-wire (FBW) is a system that replaces the conventional manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface. The movements of flight controls are converted to electronic signals transmitted by wires, and flight control computers determine how to move the actuators at each control surface to provide the ordered response. It can use mechanical flight control backup systems (like the Boeing 777) or use fully fly-by-wire controls.Fly by Wire Flight Control Systems Sutherland Improved fully fly-by-wire systems interpret the pilot's control inputs as a desired outcome and calculate the control surface positions required to achieve that outcome; this results in various combinations of rudder, elevator, aileron, flaps and engine controls in different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Vulcan
The Avro Vulcan (later Hawker Siddeley Vulcan from July 1963) is a jet-powered, tailless, delta-wing, high-altitude, strategic bomber, which was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1956 until 1984. Aircraft manufacturer A.V. Roe and Company ( Avro) designed the Vulcan in response to Specification B.35/46. Of the three V bombers produced, the Vulcan was considered the most technically advanced, hence the riskiest option. Several reduced-scale aircraft, designated Avro 707s, were produced to test and refine the delta-wing design principles. The Vulcan B.1 was first delivered to the RAF in 1956; deliveries of the improved Vulcan B.2 started in 1960. The B.2 featured more powerful engines, a larger wing, an improved electrical system, and electronic countermeasures, and many were modified to accept the Blue Steel missile. As a part of the V-force, the Vulcan was the backbone of the United Kingdom's airborne nuclear deterrent during much of the Cold War. Although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers VC10
The Vickers VC10 is a mid-sized, narrow-body long-range British jet airliner designed and built by Vickers-Armstrongs (Aircraft) Ltd and first flown at Brooklands, Surrey, in 1962. The airliner was designed to operate on long-distance routes from the shorter runways of the era and commanded excellent hot and high performance for operations from African airports. The performance of the VC10 was such that it achieved the fastest crossing of the Atlantic by a subsonic jet airliner of 5 hours and 1 minute, a record that was held for 41 years, until February 2020 when a British Airways Boeing 747 broke the record at 4 hours 56 minutes due to Storm Ciara. Only the supersonic Concorde was faster. The VC10 is often compared to the larger Soviet Ilyushin Il-62, the two types being the only airliners to use a rear-engined quad layout. The smaller business jet Lockheed JetStar also has this engine arrangement. Although only a relatively small number of VC10s were built, they provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)


