|
Elderly Care
Elderly care, or simply eldercare (also known in parts of the English-speaking world as aged care), serves the needs of old adults. It encompasses assisted living, adult daycare, long-term care, nursing homes (often called residential care), hospice care, and home care. Elderly care emphasizes the social and personal requirements of senior citizens who wish to age with dignity while needing assistance with daily activities and with healthcare. Much elderly care is unpaid. Elderly care includes a broad range of practices and institutions, as there is a wide variety of elderly care needs and cultural perspectives on the elderly throughout the world. Cultural and geographic differences The form of care provided for older adults varies greatly by country and even region, and is changing rapidly. Older people worldwide consume the most health spending of any age group. There is also an increasingly large proportion of older people worldwide, especially in developing nations wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing Home
A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of older people, senior citizens, or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as care homes, skilled nursing facilities (SNF), or long-term care facilities. Often, these terms have slightly different meanings to indicate whether the institutions are public or private, and whether they provide mostly assisted living, or nursing care and emergency medical care. Nursing homes are used by people who do not need to be in a hospital, but require care that is hard to provide in a home setting. The nursing home staff attends to the patients' medical and other needs. Most nursing homes have nursing aides and skilled nurses on hand 24 hours a day. In the United States, while nearly 1 in 10 residents aged 75 to 84 stays in a nursing home for five or more years, nearly 3 in 10 residents in that age group stay less than 100 days, the maximum duration covered by Medicare, according to the American Association for Long-Term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
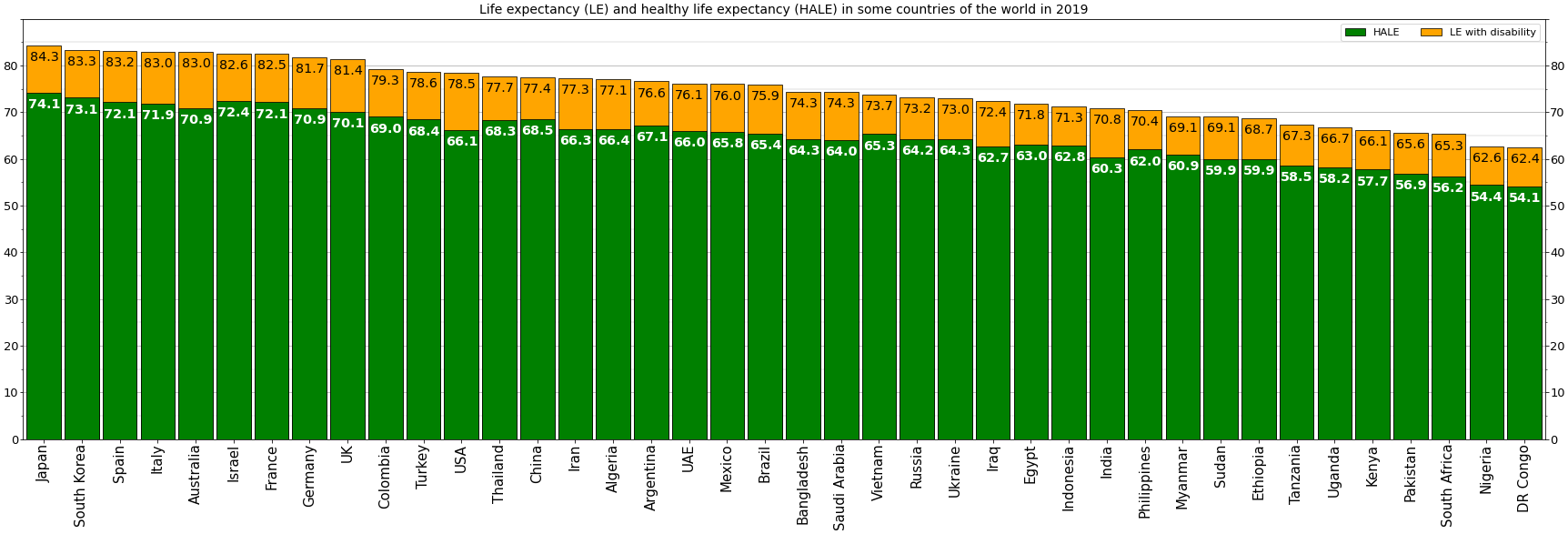
Life Expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth Cohort (statistics), cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Fund
The King's Fund is an independent think tank, which is involved with work relating to the health system in England. It organises conferences and other events. Since 1997, they have jointly funded a yearly award system with GlaxoSmithKline. They reward small to medium-sized health charities who are improving people's health. The Chief Executive is currently Sarah Woolnough, who was previously the Chief Executive of Asthma + Lung UK. She took up the position in December 2023. Before 1948 the body contributed significantly to London's voluntary hospitals. History Founded as the Prince of Wales's Hospital Fund for London in 1897, the fund changed its name in 1902 to King Edward's Hospital Fund after the accession to the throne of King Edward VII. In 1907, Parliament incorporated the fund as the King's Fund. George Stephen, 1st Baron Mount Stephen worked closely with the future George V in building the charity's endowment fund. Lord Mount Stephen was the charity's most import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity Commission
The Productivity Commission (PC) is the Australian Government's principal review and advisory body on microeconomic policy, regulation and a range of other social and environmental issues. The PC was created as an independent authority by the ''Productivity Commission Act 1998'', an Act of the Australian Parliament. PC reports often form the basis of government policy. However, the PC does not administer government programs or exercise executive power and governments are not required to act on its recommendations; although in practice, many recommendations are accepted. Functions The PC operates within the Treasury portfolio and its core function involves responding to references from the Treasurer, which can request a commissioned study or a public inquiry. References to the PC stipulate the length and terms of the project and may cover any sector of the Australian economy; address a particular industry or cut across industry boundaries; and involve wider social or environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statutory Authority
A statutory body or statutory authority is a body set up by law (statute) that is authorised to implement certain legislation on behalf of the relevant country or state, sometimes by being empowered or delegated to set rules (for example regulations or statutory instruments) in their field. They are typically found in countries which are governed by a British style of parliamentary democracy such as the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth countries like Australia, Canada, India and New Zealand. They are also found in Hong Kong, Israel and elsewhere. Statutory authorities may also be statutory corporations, if created as a body corporate. Australia Definitions Federal statutory authorities are established under the ''PGPA Act 2013''. "A statutory authority is a generic term for an authorisation by Parliament given to a person or group of people to exercise specific powers. A statutory authority can be established as a corporate Commonwealth entity or a non-corporate Common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aged Care In Australia
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing, or to the population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA oxidation) may cause biological systems to fail, or to the programmed ageing concept, whereby the internal processes (ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (such as mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funding
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm uses its internal reserves to satisfy its necessity for cash, while the term financing is used when the firm acquires capital from external sources. Sources of funding include credit, venture capital, donations, grants, savings, subsidies, and taxes. Funding methods such as donations, subsidies, and grants that have no direct requirement for return of investment are described as "soft funding" or "crowdfunding". Funding that facilitates the exchange of equity ownership in a company for capital investment via an online funding portal per the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (alternately, the "JOBS Act of 2012") (U.S.) is known as equity crowdfunding. Funds can be allocated for either short-term or long-term purposes. Economics I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filial Piety
Filial piety is the virtue of exhibiting love and respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors, particularly within the context of Confucian ethics, Confucian, Chinese Buddhism, Chinese Buddhist ethics, Buddhist, and Daoism, Daoist ethics. The Confucian ''Classic of Filial Piety'', thought to be written around the late Warring States-Qin dynasty, Qin-Han dynasty, Han period, has historically been the authoritative source on the Confucian tenet of filial piety. The book—a purported dialogue between Confucius and his student Zengzi—is about how to set up a good society using the principle of filial piety. Filial piety is central to Confucian role ethics. In more general terms, filial piety means to be good to one's parents; to take care of one's parents; to engage in good conduct, not just towards parents but also outside the home so as to bring a good name to one's parents and ancestors; to show love, respect, and support; to display courtesy; to ensure male heirs; to uph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The terms low-and middle-income country (LMIC) and newly emerging economy (NEE) are often used interchangeably but they refer only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high-, upper-middle-, lower-middle-, and low-income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries, and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over the terms' use, as some feel that it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |