|
El Cóporo
El Cóporo is a prehispanic archaeological site at the northern frontiers of the Mesoamerican cultural area, located at an elevation of 150 meters on the western slopes of the Santa Bárbara range (Sierra de Santa Bárbara), near the San José del Torreón community, INAH and lies some due south of its municipal seat and largest township, on the northwestern corner of Guanajuato state, Mexico. The site is considered as one of the four most important archaeological sites in the state. ''Cóporo'' is a Purépecha word meaning 'over the big road'. The site is named after the Cóporo hill, where it is located and the site is located at its peak, 156 meters high. The ceremonial and government center has been completed about 80 percent; around the center 29 smaller settlements were established on the slopes, the main occupation period occurred between 500-900 CE. The site's main occupation dates to the Late Classic and Early Postclassic eras of Mesoamerican chronology, and shows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato, Guanajuato, Guanajuato. It is located in central Mexico and is bordered by the states of Jalisco to the west, Zacatecas to the northwest, San Luis Potosí to the north, Querétaro to the east, and Michoacán to the south. It covers an area of . The state is home to several historically important cities, especially those along the "Bicentennial Route", which retraces the path of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla's insurgent army at the beginning of the Mexican War of Independence. This route begins at Dolores Hidalgo, and passes through the Sanctuary of Atotonilco, San Miguel de Allende, Celaya, and the capital of Guanajuato City, Guanajuato. Other important cities in the state include León, Guanajuato, León, the state' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
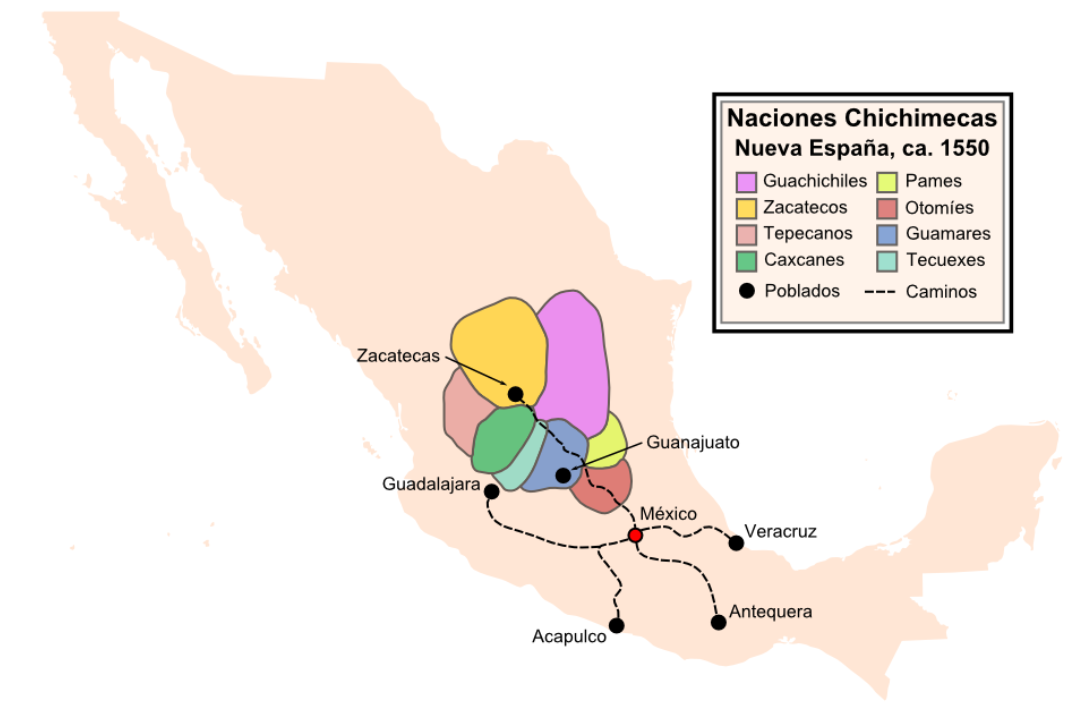
Otomi People
The Otomi (; ) are an Indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region. The Otomi are an Indigenous people of the Americas who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguistically related to the rest of the Oto-Manguean languages, Otomanguean-speaking peoples, whose ancestors have occupied the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt for several thousand years. Currently, the Otomi inhabit a fragmented territory ranging from northern Guanajuato, to eastern Michoacán and southeastern Tlaxcala. However, most of them are concentrated in the states of Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico and Querétaro City, Querétaro. According to the National Institute of Indigenous Peoples of Mexico, the Otomi ethnic group totaled 667,038 people in the Mexican Republic in 2015, making them the fifth largest Indigenous people in the country. Of these, only a little more than half spoke Otomi. In this regard, the Otomi language presents a high degree of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altavista (Zacatecas)
Altavista, or Chalchihuites, is an archaeological site near the municipality of Chalchihuites in the Mexican state of Zacatecas, in the northwest of Mexico. It is believed that the site was a cultural oasis that was occupied more or less continuously from AD 100 to AD 1400. The site is within the "Sierra de Chalchihuites" – from the Nahuatl word ''chalchíhuitl'', the name means "precious stone" – where the Chalchihuites-Chichimec culture was established. The Altavista name is due to a ranch that existed in the vicinity at the time when archaeologist Manuel Gamio visited the area. There are opinions that this ceremonial center was developed by the Súchil branch of the Chalchihuites culture. The site is related to the Chalchihuites culture that flourished during the Mesoamerican classical period, which had a social and political structure; had a hieroglyphical writing system; and constructed formal cities and ceremonial centers, as they had urbanization techniques, a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Quemada
La Quemada is an archeological site. It is located in the Villanueva Municipality, in the state of Zacatecas, about 56 km south of the city of Zacatecas on Fed 54 Zacatecas–Guadalajara, in Mexico. History Given the distance between La Quemada and the centre of Mesoamerica, this archeological zone has been subject of different interpretations on the part of historians and archeologists, who have attempted to associate it with different cultures. It has been proposed that this place could be either the legendary Chicomostoc, a Caxcan site, a Teotihuacán fortress, a Purépecha centre, a fort against Chichimeca intruders, a Toltec trading post, or simply consequence of independent development and a city of all the native groups established north of the Río Grande de Santiago. In 1615, Fray Juan de Torquemada identified La Quemada as one of the places visited by the Aztecs during their migration from the north to the Mexico central plateau, and where older people and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area are Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson, Arizona, Tucson. Before 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of New Mexico's pueblos and Santa Fe de Nuevo México#Regions and municipalities, Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahua Peoples
The Nahuas ( ) are a Uto-Nahuan ethnicity and one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest Indigenous group in Mexico, as well as the largest population out of any North American Indigenous people group who are native speakers of their respective Indigenous language. Amongst the Nahua, this is Nahuatl. When ranked amongst all Indigenous languages across the Americas, Nahuas list third after speakers of Guaraní and Quechua. The Mexica (Aztecs) are of Nahua ethnicity, as are their historical enemies and allies of the Spaniards: the Tlaxcallans (Tlaxcaltecs). The Toltecs which predated both groups are often thought to have been Nahua as well. However, in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity. Their Nahuan languages, or Nahuatl, consist of many variants, several of which are mutually uninte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: ; singular ) are a Nahuatl-speaking people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of the Triple Alliance, more commonly referred to as the Aztec Empire. The Mexica established Tenochtitlan, a settlement on an island in Lake Texcoco, in 1325. A dissident group in Tenochtitlan separated and founded the settlement of Tlatelolco with its own dynastic lineage. In 1521, their empire was overthrown by an alliance of Spanish conquistadors and rival indigenous nations, most prominently the Tlaxcaltecs. The Mexica were subjugated under the Spanish Empire for 300 years, until the Mexican War of Independence overthrew Spanish dominion in 1821. Today, descendants of the Mexica and other Aztecs are among the Nahua people of Mexico. Since 1810, the broader term ''Aztec'' is often used to describe the Mexica. When a distinction is made, Mexica are one (dominant) group within the Aztecs. Names The ''Mexica'' are eponymous of the place name Mexico (''Mēxihco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caxcan
The Caxcan are an ethnic group who are Indigenous to western and north-central Mexico, particularly the regions corresponding to modern-day Zacatecas, southern Durango, Jalisco, Colima, Aguascalientes, Nayarit. The Caxcan language is most often documented as an ancient variant of Nahuatl and is a member of the Uto-Aztecan language family. The last generation of natively fluent Caxcan language speakers came to an end in the 1890s. Despite this having long been conflated by anthropologists with an extinction of the Caxcan people themselves, much of Caxcan culture has persisted via oral tradition. There is currently an ongoing revitalization of Caxcan language, scholarship, and culture. History Pre-1550 The Caxcan were a partly nomadic, partly sedentary people. Under their leader, Tenamaztle, the Caxcan were allied with the Zacatecos against the Spaniards during the Mixtón Rebellion in 1540-42. During the rebellion, they were described as "the heart and the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tecuexe
The Tecuexe were an Indigenous peoples of Mexico, who lived in the eastern part of present-day Guadalajara. History It is believed that the Tecuexe derived from the dispersion of Zacateco groups from La Quemada. Like the Zacatecos, the Tecuexe were a tribe belonging to the generic "Chichimeca" peoples. It is known that they settled next to rivers which they used to their advantage to grow beans and corn. They were also expert artisans, carpenters and musicians. Toribio de Benavente Motolinia wrote "in any place… all know to work a stone, to make a house simple, to twist a cord and a rope, and the other subtle offices that do not require instruments or much art." The Tecuexe were known for their fierceness and cruelty towards their enemy. They were known to be so brave, it is said, that once, when the Mexica (Aztecs) came from Chicomostoc, Zacatecas to take control of Xolotl, (and course on to the lagoon where they found an eagle devouring a serpent) they attacked the settlers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guachichiles
The Guachichil, Cuauchichil, or Quauhchichitl are an exonym for an Indigenous people of Mexico. Prior to European contact, they occupied the most extensive territory of all the Indigenous Chichimeca tribes in pre-Columbian central Mexico. The Guachichiles settled a large region of Zacatecas; as well as portions of San Luis Potosí, Guanajuato, and northeastern Jalisco; south to the northern corners of Michoacán; and north to Saltillo in Coahuila. History Considered both warlike and brave, the Guachichiles played a major role in provoking the other Chichimeca tribes to resist the Spanish settlement. The historian Philip Wayne Powell wrote: :::" ''Their strategic position in relation to Spanish mines and highways, made them especially effective in raiding and in escape from Spanish reprisal''." These warriors were known to fight fiercely even if mortally wounded and were a key component in the Spanish defeat during the Chichimeca Wars. The children learned to use the bow at w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacateco
The Zacatecos (or Zacatecas) are an indigenous group, one of the peoples called Chichimecas by the Aztecs. They lived in most of what is now the state of Zacatecas and the northeastern part of Durango. They have many direct descendants, but most of their culture and traditions have disappeared with time. Large concentrations of modern-day descendants may reside in Zacatecas and Durango, as well as other large cities of Mexico. Name "Zacateco" is a Mexican Spanish derivation from the original Nahuatl ''Zacatecatl'', pluralized in early Mexican Spanish as ''Zacatecas'', the name given to the state and city. The name was given by the Aztecs to the people inhabiting a region in which a grass they called the ''zacatl'' was abundant. The region was thus called ''Zacatlan'' by the Aztecs. ( Mexica) Language The Zacateco language is extinct and poorly attested. It has been suspected to be a Nahuan language, or be close to Huichol. History The Chichimeca War The Zacateco u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |