|
Einstellung Effect
Einstellung () is the development of a mechanized state of mind. Often called a problem solving set, Einstellung refers to a person's predisposition to solve a given problem in a specific manner even though better or more appropriate methods of solving the problem exist. The Einstellung effect is the negative effect of previous experience when solving new problems. The Einstellung effect has been tested experimentally in many different contexts. The most famous example (which led to the coining of the term by Abraham S. Luchins and Edith Hirsch, Edith Hirsch Luchins) is the Luchins water jar experiment, in which subjects were asked to solve a series of water pouring puzzle, water jar problems. After solving many problems which had the same solution, subjects applied the same solution to later problems even though a simpler solution existed (Luchins, 1942).. Other experiments on the Einstellung effect can be found in ''The Effect of Einstellung on Compositional Processes'' and ''Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problem Solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices. Solutions require sufficient resources and knowledge to attain the goal. Professionals such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term ''Intelligenzquotient'', his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book. Historically, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction (quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern IQ tests, the raw score is transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2.5 percent each above 130 and below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XY Problem
The XY problem is a communication problem encountered in help desk, technical support, software engineering, or customer service situations where the question is about an end user's attempted solution (''Y'') rather than the root problem itself (''X''). The XY problem obscures the real issues and may even introduce secondary problems that lead to miscommunication, resource mismanagement, and sub-par solutions. The solution for the support personnel is to ask probing questions as to why the information is needed in order to identify the root problem ''X'' and redirect the end user away from an unproductive path of inquiry. Terminology The term ''XY problem'' was implicitly coined by Eric S. Raymond in ''How To Ask Questions The Smart Way'' when he wrote "How can I use X to do Y?" in the "Questions Not To Ask" section (note that in this original version ''X'' and ''Y'' are swapped): Q: How can I use X to do Y? A: If what you want is to do Y, you should ask that question without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinking Outside The Box
Thinking outside the box (also thinking out of the box or thinking beyond the box and, especially in Australia, thinking outside the square) is a metaphor that means to think differently, unconventionally, or from a new perspective. The phrase also often refers to novel or creative thinking. History The origin of the phrase is unclear. "Think beyond the boundary"-metaphors, that is, metaphors that allude to think differently or with less constraints, seem to have an old history. For example, in 1888, The Annual Register records the phrase ''think outside the lines''. Since at least 1954, the nine dots puzzle has been used as a metaphor of the type "think beyond the boundary". Early phrasings include ''go outside the dots'' (1954), ''breakthrough thinking that gets outside the nine-dot square'' (1959), and ''what are the actual boundaries of the problem?'' (1963). In 1969, Norman Vincent Peale writes this in an article for the Chicago Tribune, quote: In 1970, the phrase ''th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
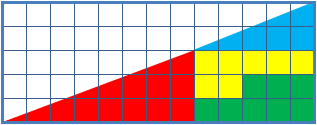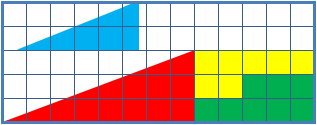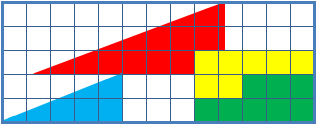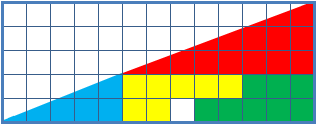
Missing Square Puzzle
The missing square puzzle is an optical illusion used in mathematics classes to help students reason about geometrical figures; or rather to teach them not to reason using figures, but to use only textual descriptions and the axioms of geometry. It depicts two arrangements made of similar shapes in slightly different configurations. Each apparently forms a 13×5 right-angled triangle, but one has a 1×1 hole in it. Solution The key to the puzzle is the fact that neither of the 13×5 "triangles" is truly a triangle, nor would either truly be 13x5 if it were, because what appears to be the hypotenuse is bent. In other words, the "hypotenuse" does not maintain a consistent slope, even though it may appear that way to the human eye. A true 13×5 triangle cannot be created from the given component parts. The four figures (the yellow, red, blue and green shapes) total 32 units of area. The apparent triangles formed from the figures are 13 units wide and 5 units tall, so it appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of The Instrument
The law of the instrument, law of the hammer, Maslow's hammer (or gavel), or golden hammer is a cognitive bias that involves an over-reliance on a familiar tool. Abraham Maslow wrote in 1966, "If the only tool you have is a hammer, it is tempting to treat everything as if it were a nail." The concept is attributed both to Maslow and to Abraham Kaplan, although the hammer and nail line may not be original to either of them. History The English expression "a Birmingham screwdriver", meaning a hammer, refers to the practice of using the one tool for all purposes, and predates both Kaplan and Maslow by at least a century. In 1868, a London periodical, '' Once a Week'', contained this observation: "Give a boy a hammer and chisel; show him how to use them; at once he begins to hack the doorposts, to take off the corners of shutter and window frames, until you teach him a better use for them, and how to keep his activity within bounds." The first recorded statement of the concept wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candle Problem
The candle problem or candle task, also known as Duncker's candle problem, is a cognitive performance test, measuring the influence of functional fixedness on a participant's problem solving capabilities. The test was created by Gestalt psychologist Karl Duncker and published posthumously in 1945. Duncker originally presented this test in his thesis on problem-solving tasks at Clark University. Problem The test presents the participant with the following task: how to fix and light a candle on a wall (a cork board) in a way so the candle wax won't drip onto the table below. To do so, one may only use the following along with the candle: *a book of matches *a box of thumbtacks Solution The most efficient solution is to empty the box of thumbtacks, use the thumbtacks to nail the box to the wall, put the candle into the box, and light the candle with the match. The concept of functional fixedness predicts that the participant will only see the box as a device to hold the thumbtac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Fixedness
Functional fixedness is a cognitive bias that limits a person to use an object only in the way it is traditionally used. The concept of functional fixedness originated in Gestalt psychology, a movement in psychology that emphasizes holistic processing. Karl Duncker defined functional fixedness as being a mental block against using an object in a new way that is required to solve a problem.Duncker, K. (1945). "On problem solving". '' Psychological Monographs'', 58:5 (Whole No. 270). This "block" limits the ability of an individual to use components given to them to complete a task, as they cannot move past the original purpose of those components. For example, if someone needs a paperweight, but they only have a hammer, they may not see how the hammer can be used as a paperweight. Functional fixedness is this inability to see a hammer's use as anything other than for pounding nails; the person couldn't think to use the hammer in a way other than in its conventional function. When tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Hypothesis
A working hypothesis is a hypothesis that is provisionally accepted as a basis for further ongoing research in the hope that a tenable theory will be produced, even if the hypothesis ultimately fails.See in "hypothesis", ''Century Dictionary Supplement'', v. 1, 1909, New York: The Century Company. Reprintedv. 11, p. 616(via ''Internet Archive''] of the ''Century Dictionary and Cyclopedia'', 1911. Like all hypotheses, a working hypothesis is constructed as a statement of expectations, which can be linked to deductive, exploratory research Shields, Patricia and Rangarjan, N. (2013). ''A Playbook for Research Methods: Integrating Conceptual Frameworks and Project Management''. Stillwater, OK: New Forums Press. See Chapter 5. in empirical investigation and is often used as a conceptual framework in qualitative research. The term "working" indicates that the hypothesis is subject to change. History Use of the phrase "working hypothesis" goes back to at least the 1850s. Charles Sander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshin
''Shoshin'' ( ja, text=初心) is a concept from Zen Buddhism meaning beginner's mind. It refers to having an attitude of openness, eagerness, and lack of preconceptions when studying, even at an advanced level, just as a beginner would. The term is especially used in the study of Zen Buddhism and Japanese martial arts, and was popularized outside of Japan by Shunryū Suzuki's 1970 book ''Zen Mind, Beginner's Mind''. The practice of ''shoshin'' acts as a counter to the hubris and closed-mindedness often associated with thinking of oneself as an expert. This includes the Einstellung effect, where a person becomes so accustomed to a certain way of doing things that they do not consider or acknowledge new ideas or approaches. The word ''shoshin'' is a combination of ''sho'' ( ja, text=初, links=no), meaning "beginner" or "initial", and ''shin'' ( ja, text=心, links=no), meaning "mind". History The concept was taught in the thirteenth century by Dōgen Zenji, the founder of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigidity (psychology)
In psychology, rigidity or mental rigidity refers to an obstinate inability to yield or a refusal to appreciate another person's viewpoint or emotions characterized by a lack of empathy. It can also refer to the tendency to perseverate, which is the inability to change habits and the inability to modify concepts and attitudes once developed. A specific example of rigidity is functional fixedness, which is a difficulty conceiving new uses for familiar objects. History Rigidity is an ancient part of our human cognition. Systematic research on rigidity can be found tracing back to Gestalt psychologists, going as far back as the late 19th to early 20th century with Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka in Germany. With more than 100 years of research on the matter there is some established and clear data. Nonetheless, there is still much controversy surrounding several of the fundamental aspects of rigidity. In the early stages of approaching the idea of rigidity, it is tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Inertia
Cognitive inertia is the tendency for a particular orientation in how an individual thinks about an issue, belief or strategy to resist change. In clinical and neuroscientific literature it is often defined as a lack of motivation to generate distinct cognitive processes needed to attend to a problem or issue. The physics term inertia is to emphasize the rigidity and resistance to change in the method of cognitive processing that has been in use for a significant amount of time. Commonly confused with belief perseverance, cognitive inertia is the perseverance of how one interprets information, not the perseverance of the belief itself. Cognitive inertia has been causally implicated in disregard of impending threat to one's health or environment, enduring political values and deficits in task switching. Interest in the phenomenon was largely taken up by economic and industrial psychologists to explain resistance to change in brand loyalty, group brainstorming and business strategi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |