|
Egyptian Museum (Milan)
The Museo Egizio is a museum sited in the Sforza Castle of Milan, Italy. The Castle is one of the most famous monuments in Milan and is home to several museums including the Egyptian Section of the Milan Archaeological Museum, the Museum of Ancient Art, the Pinacoteca and the Museum of Musical Instruments. The Egyptian Museum, situated in the underground level of the ducal courtyard, is divided into seven different sections: * ABOUT ANCIENT EGYPTIAN WRITING * ABOUT PHARAOHS * ABOUT DEITIES AND CULTS * ABOUT EVERYDAY LIFE FOR THE EGYPTIANS * ABOUT FUNERARY CULT * EXCAVATIONS CONDUCTED BY ACHILLE VOGLIANO * MUMMIES, SARCOPHAGI AND FUNERARY MASKS A mummy dating from the Greco-Roman period, from Thebes, and ancient Egyptian sarcophagi are exposed in the "mummies, sarcophagi and funerary mask" section, while some papyri of the ''Book of the Dead'' are exposed in the Funerary Cult section. Gallery File:1901 - Milano - Museo egizio - Libro dei morti (età tolemaica) - Foto Giovanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city has 3.26 million inhabitants. Its continuously built-up urban area (whose outer suburbs extend well beyond the boundaries of the administrative metropolitan city and even stretch into the nearby country of Switzerland) is the fourth largest in the EU with 5.27 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan), is estimated between 8.2 million and 12.5 million making it by far the largest metropolitan area in Italy and one of the largest in the EU.* * * * Milan is considered a leading alpha global city, with strengths in the fields of art, chemicals, commerce, design, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sforza Castle
The Castello Sforzesco (Italian for "Sforza's Castle") is a medieval fortification located in Milan, northern Italy. It was built in the 15th century by Francesco Sforza, Duke of Milan, on the remnants of a 14th-century fortification. Later renovated and enlarged, in the 16th and 17th centuries it was one of the largest citadels in Europe. Extensively rebuilt by Luca Beltrami in 1891–1905, it now houses several of the city's museums and art collections. History The original construction was ordered by Galeazzo II Visconti, a local nobleman, in 1358 – c. 1370; this castle was known as the ''Castello di Porta Giova'' (or ''Porta Zubia''), from the name of a gate in walls located nearby. It was built in the same area of the ancient Roman fortification of ''Castrum Portae Jovis'', which served as '' castra pretoria'' when the city was the capital of the Roman Empire. It was enlarged by Galeazzo's successors, Gian Galeazzo, Giovanni Maria and Filippo Maria Visconti, until it beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Museum (Milan)
The Archaeological Museum of Milan (''Civico Museo Archeologico di Milano'' in Italian) is located in the ex-convent of the Monastero Maggiore, alongside the ancient church of San Maurizio al Monastero Maggiore, with entrance on Corso Magenta. The first part of the museum, sited in the original site of Corso Magenta, is dedicated to the history of Mediolanum (ancient Milan) founded in the 4th century BC and conquered by the ancient Romans in 222 BC. In the basement floor there is also a small section about Gandhara's arts. The inner cloister, where Roman remains (1st-3rd century AD) and two medieval towers are visible, connects the first part of the museum with the new building sited in via Nirone. In this part of the Archaeological Museum of Milan are sited, on four floors, the ''Early Middle Ages'' section, the ''Etruscan'' section, the ''Ancient Greek'' section and the temporary exhibition room. In the Middle Ages polygonal tower sited in the inner cloister are exposed a Domen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Museum Of Ancient Art
The Museo d'Arte Antica ('Museum of Ancient Art') is an art museum in the Castello Sforzesco in Milan, in Lombardy in northern Italy. It has a large collection of sculpture from late antiquity and the medieval and Renaissance periods. The various frescoed rooms of the museum house an armoury, a tapestry room, some funerary monuments, Michelangelo's '' Rondanini Pietà'' and two medieval portals. The Sala Verde ('green room') displays 15th- and 16th-century sculptures, the collection of arms of the Castello Sforzesco and the Portale del Banco Mediceo, a gate removed from Via Bossi. The collection of arms, in the second part of the room, displays sculptures, armour, swords and firearms in chronological sequence from the Middle Ages to the 18th century. The Sala delle Asse, designed and frescoed by Leonardo da Vinci at the request of Lodovico il Moro, represents the Sforza The House of Sforza () was a ruling family of Renaissance Italy, based in Milan. They acquired the Duc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sforza Castle Pinacoteca
The Pinacoteca del Castello Sforzesco is an art gallery in the museum complex of the Castello Sforzesco in Milan, northern Italy. History Inaugurated in 1878, the gallery displays over 230 artworks, which include masterpieces by Titian, Andrea Mantegna, Canaletto, Antonello da Messina, Pisanello, Vincenzo Foppa, Giovanni Bellini, Correggio, Bernardino Luini, Lorenzo Lotto, Tintoretto and others. The complete collection of the museum, enriched in the last two centuries by donations of illustrious citizens and collectors, now has more than 1,500 artworks. The first rooms of the Pinacoteca are dedicated to religious paintings of the 15th and 16th centuries, with artworks by Vincenzo Foppa, Bergognone, Bramantino, Carlo Crivelli, Bernardino Luini and other Lombard and Italian Renaissance painters. This part of the museum includes the '' Trivulzio Madonna'' by Andrea Mantegna, dating from 1497. (Another ''Trivulzio Madonna'' by Filippo Lippi is also in the museum.) The second half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Of Musical Instruments (Milan)
The Museum of Musical Instruments of Milan exhibits over 700 musical instruments from the fifteenth to twentieth centuries with particular attention to Lombard instruments. The collection contains plucked instruments, Lombard and Cremonese violins, hunting horns, numerous wood instruments (e.g. flutes, oboes, clarinets, English horns), bassoons, pianos and some ancient organs. In particular the Cremonese lutherie (from Cremona in low Lombardy) is appreciated all over the world for the high quality of its musical instruments. The museum also displays the equipment of the former Studio di fonologia musicale di Radio Milano. In 2000 a donation by the added 79 musical instruments, made between the 18th and 20th century, to the civic collection; they had been collected by the Monzino family. These musical instruments represent the strong tradition of Lombard lutherie. The museum is situated in the Sforza Castle complex that also includes The Museum of Ancient Art, the Pinacothec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
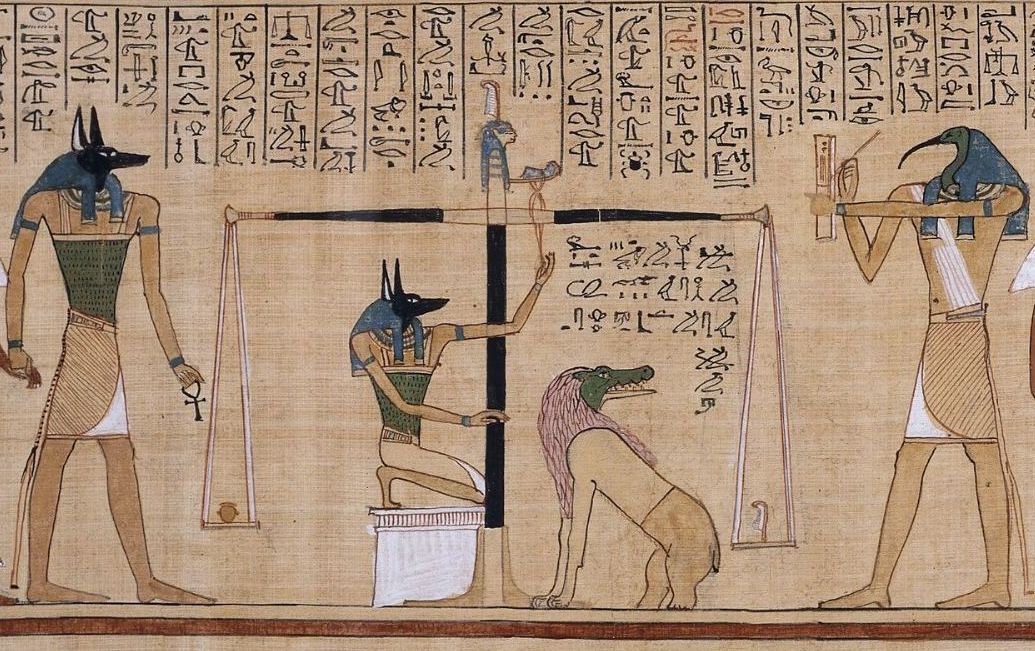
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay further if kept in cool and dry conditions. Some authorities restrict the use of the term to bodies deliberately embalmed with chemicals, but the use of the word to cover accidentally desiccated bodies goes back to at least 1615 AD (see the section Etymology and meaning). Mummies of humans and animals have been found on every continent, both as a result of natural preservation through unusual conditions, and as cultural artifacts. Over one million animal mummies have been found in Egypt, many of which are cats. Many of the Egyptian animal mummies are sacred ibis, and radiocarbon dating suggests the Egyptian Ibis mummies that have been analyzed were from time frame that falls between approximately 450 and 250 BC. In addition to the mummies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
, image = Decorated pillars of the temple at Karnac, Thebes, Egypt. Co Wellcome V0049316.jpg , alt = , caption = Pillars of the Great Hypostyle Hall, in ''The Holy Land, Syria, Idumea, Arabia, Egypt, and Nubia'' , map_type = Egypt , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = yes , coordinates = , location = Luxor, Luxor Governorate, Egypt , region = Upper Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = , ownership = , management = , public_access = , website = , notes = , designation1 = WHS , designation1_offname = Ancient Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhat III
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat III ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet III, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the sixth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was elevated to throne as co-regent by his father Senusret III, with whom he shared the throne as the active king for twenty years. During his reign, Egypt attained its cultural and economic zenith of the Middle Kingdom. The aggressive military and domestic policies of Senusret III, which re-subjugated Nubia and wrested power from the nomarchs, allowed Amenemhat III to inherit a stable and peaceful Egypt. He directed his efforts towards an extensive building program with particular focus on Faiyum. Here he dedicated a temple to Sobek, a chapel to Renenutet, erected two colossal statues of himself in Biahmu, and contributed to excavation of Lake Moeris. He built for himself two pyramids at Dahshur and Hawar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
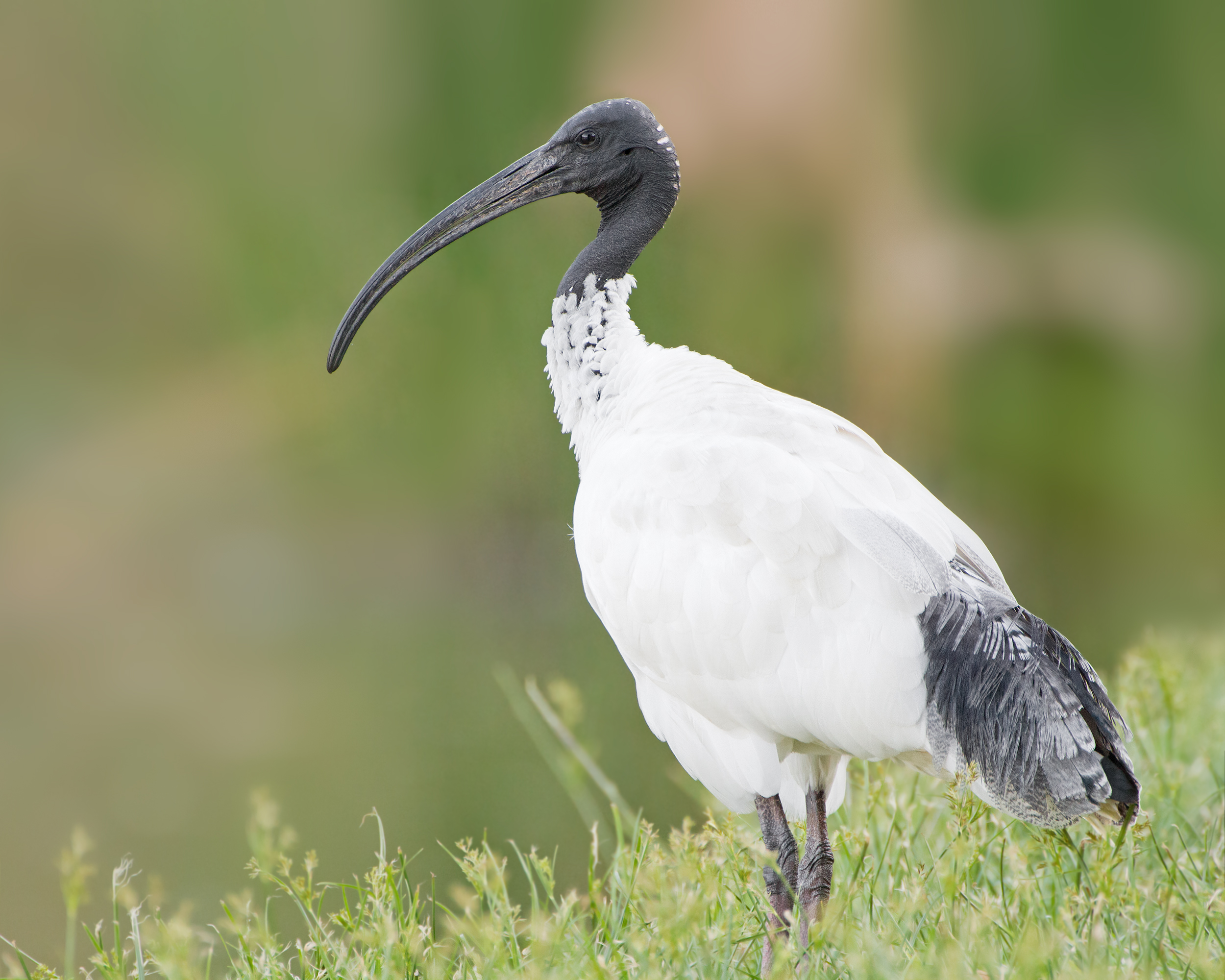
Ibis
The ibises () (collective plural ibis; classical plurals ibides and ibes) are a group of long-legged wading birds in the family Threskiornithidae, that inhabit wetlands, forests and plains. "Ibis" derives from the Latin and Ancient Greek word for this group of birds. It also occurs in the scientific name of the cattle egret (''Bubulcus ibis'') mistakenly identified in 1757 as being the sacred ibis. Description Ibises all have long, downcurved bills, and usually feed as a group, probing mud for food items, usually crustaceans. They are monogamous and highly territorial while nesting and feeding. Most nest in trees, often with spoonbills or herons. All extant species are capable of flight, but two extinct genera were flightless, namely the kiwi-like ''Apteribis'' in the Hawaiian Islands, and the peculiar '' Xenicibis'' in Jamaica. The word ''ibis'' comes from Latin ''ibis'' from Greek ἶβις ''ibis'' from Egyptian ''hb'', ''hīb''. Beekes, R. S. P. (2009) ''Etymological Dicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
