|
Edward Prince
Edward Philip Prince (1846–1923) was a British engraver and punchcutter, a cutter of the punches used to stamp the matrices used to cast metal type. Working during the period of the Arts and Crafts movement, after William Morris's Kelmscott Press commissioned him to cut a typeface known as the Golden Type to Morris's design he became known for cutting private typefaces for fine book printing presses. Another client was the Doves Press The Doves Press was a private press based in Hammersmith, London. During nearly seventeen years of operation, the Doves Press produced notable examples of twentieth-century typography. A distinguishing feature of its books was a specially-devis ..., whose Doves Type he cut; it was famously thrown into the Thames following a business disagreement. He also worked with the Ashendene Press to cut the Subiaco and Ptolemy types. A somewhat retiring figure, only two photographs of him are known to exist. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Prince, Edward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doves Press Bible
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on seeds, fruits, and plants. The family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms. The family contains 344 species divided into 50 genera. Thirteen of the species are extinct. In English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves" and the larger ones "pigeons". However, the distinction is not consistent, and does not exist in most other languages. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the terms. The bird most commonly referred to as just "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, which is common in many cities as the feral pigeon. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests, often using sticks and other debris, which may be placed on b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelmscott Press Typefaces
Kelmscott is a village and civil parish on the River Thames in West Oxfordshire, about east of Lechlade in neighbouring Gloucestershire. Since 2001 it has absorbed Little Faringdon, which had been a separate civil parish. The 2011 Census recorded the merged parish's population as 198. Kelmscott Manor Kelmscott Manor is a Cotswold stone house, built in about 1570 during the Great Rebuilding of England and extended late in the 17th century. It was the country home of William Morris from 1871 until his death in 1896. He drew great inspiration from the unspoilt authenticity of the house's architecture and craftsmanship, and its organic relationship with its setting. Kelmscott Manor now belongs to the Society of Antiquaries of London. Morris renamed his London town house Kelmscott House after Kelmscott when he bought it in April 1879. He named his private press, which he started in 1891, Kelmscott Press. Parish church The nave of the Church of England parish church of Saint Geor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
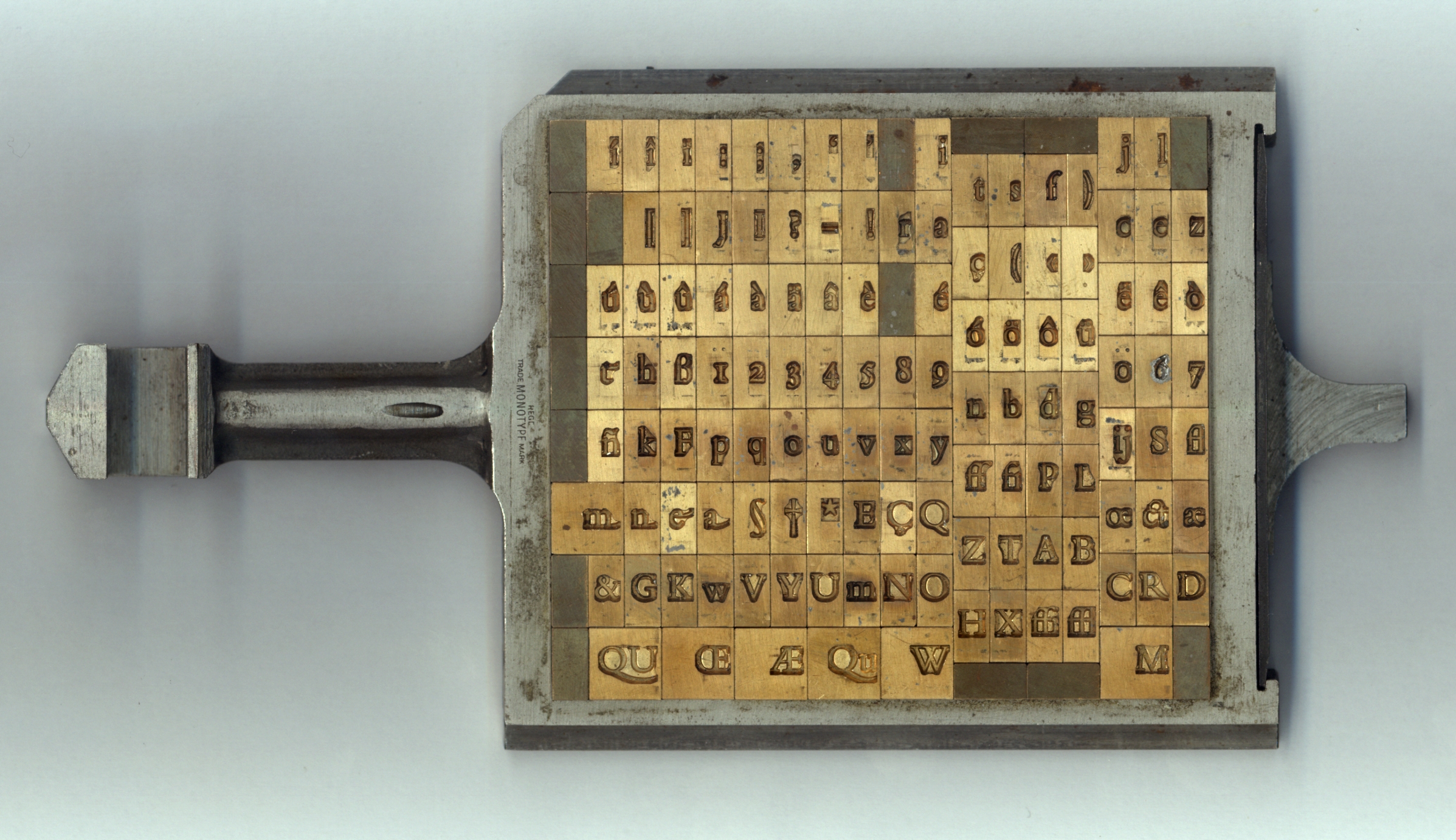
Punchcutting
Punchcutting is a craft used in traditional typography to cut letter punches in steel as the first stage of making metal type. Steel punches in the shape of the letter would be used to stamp matrices into copper, which were locked into a mould shape to cast type. Cutting punches and casting type was the first step of traditional typesetting. The cutting of letter punches was a highly skilled craft requiring much patience and practice. Often the designer of the type would not be personally involved in the cutting. The initial design for type would be two-dimensional, but a punch has depth, and the three-dimensional shape of the punch, as well as factors such as the angle and depth to which it was driven into the matrix, would affect the appearance of the type on the page. The angle of the side of the punch was particularly significant. Process The punchcutter begins by transferring the outline of a letter design to one end of a steel bar. The outer shape of the punch could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (printing)
In the manufacture of metal type used in letterpress printing, a matrix (from the Latin meaning ''womb'' or ''a female breeding animal'') is the mould used to cast a letter, known as a sort. Matrices for printing types were made of copper. However, in printmaking the matrix is whatever is used, with ink, to hold the image that makes up the print, whether a plate in etching and engraving or a woodblock in woodcut. Description In letterpress or "cold metal" typesetting, used from the beginning of printing to the late nineteenth century, the matrix of one letter is inserted into the bottom of an adjustable-width hand mould, the mould is locked and molten type metal is poured into a straight-sided vertical cavity above the matrix. When the metal has cooled and solidified the mould is unlocked and the newly cast metal sort is removed. The matrix can then be reused to produce more copies of the sort.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design.'' John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. (pp 58� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was a British textile designer, poet, artist, novelist, architectural conservationist, printer, translator and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He was a major contributor to the revival of traditional British textile arts and methods of production. His literary contributions helped to establish the modern fantasy genre, while he helped win acceptance of socialism in ''fin de siècle'' Great Britain. Morris was born in Walthamstow, Essex, to a wealthy middle-class family. He came under the strong influence of medievalism while studying Classics at Oxford University, there joining the Birmingham Set. After university, he married Jane Burden, and developed close friendships with Pre-Raphaelite artists Edward Burne-Jones and Dante Gabriel Rossetti and with Neo-Gothic architect Philip Webb. Webb and Morris designed Red House in Kent where Morris lived from 1859 to 1865, before moving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelmscott Press
The Kelmscott Press, founded by William Morris and Emery Walker, published fifty-three books in sixty-six volumes between 1891 and 1898. Each book was designed and ornamented by Morris and printed by hand in limited editions of around 300. Many books were illustrated by Edward Burne-Jones. Kelmscott Press books sought to replicate the style of 15th-century printing and were part of the Gothic revival movement. Kelmscott Press started the contemporary fine press movement, which focuses on the craft and design of bookmaking, often using hand presses. While their most famous books are richly decorated, most Kelmscott Press books did not have elaborate decoration, but were published simply. Morris was interested in medieval book design, visiting the Bodleian Library often with Burne-Jones to examine illuminated manuscripts. He designed and published several books before founding Kelmscott Press. Book dealers and designers complained about the poor quality of books published on the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Type
The Golden Type is a serif font designed by artist William Morris for his fine book printing project, the Kelmscott Press, in 1890. It is an "old-style" serif font, based on type designed by engraver and printer Nicolas Jenson in Venice around 1470. It is named for the ''Golden Legend'', which was intended to be the first book printed using it. The original design has neither an italic nor a bold weight, as neither of these existed in Jenson's time. Morris's aim in the Kelmscott Press was to revive the style of early printing and medieval manuscripts, and the design accordingly is a profound rejection of the harsh, industrial aesthetic of the contemporary Didone typefaces used at the time in general-purpose printing, and also of the relatively pallid "modernised old style" designs popular in books. Instead, the design has a relatively heavy "colour" on the page. The design is a loose revival, somewhat bolder than Jenson's original engraving, giving it something of the appearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Book Printing
Fine press printing and publishing comprises historical and contemporary printers and publishers publishing books and other printed matter of exceptional intrinsic quality and artistic taste, including both commercial and private presses. History of fine press As part of the Arts and Crafts movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Englishman William Morris wanted to counter the industrialization of culture through a revival of craft in printing, printmaking, and publishing. One of the books they published was the Kelmscott Chaucer. Soon, fine presses began to spring up in the United States as well. The most prominent was the Roycroft Press. Los Angeles was a center of the fine press movement, particularly centered on the Ward Ritchie press. In the 1920s, San Francisco became known for the elegant publications of John Henry Nash, and likewise became a fine press center on the west coast. List of fine presses United States * Alderbrink Press (1897 - 1928?) * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doves Press
The Doves Press was a private press based in Hammersmith, London. During nearly seventeen years of operation, the Doves Press produced notable examples of twentieth-century typography. A distinguishing feature of its books was a specially-devised typeface, known variously as the Doves Roman, the Doves Press Fount of Type, or simply the Doves type. The Doves Press business The Doves Press was founded by T. J. Cobden-Sanderson before 1900 when he asked Emery Walker to join him. The business was financed by Anne Cobden-Sanderson. Their partnership was dissolved in 1908 but Cobden-Sanderson continued to print. Cobden-Sanderson commissioned the press's type, which was drawn under Walker's supervision, and the Doves Bindery which he had set up in 1893 bound the books he and Walker printed. The Press produced all its books using a single size of this type, between 1900 and 1916, and is considered to have been a significant contributor to the Arts and Crafts movement. The founders we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashendene Press
The Ashendene Press was a small private press founded by St John Hornby (1867–1946). It operated from 1895 to 1915 in Chelsea, London and was revived after the war in 1920. The press closed in 1935. Its peers included the Kelmscott Press and the Doves Press. Hornby became friends with William Morris and Emery Walker, who helped inspire his work. These three presses were part of a "revival of fine printing" that focused on treating bookmaking as fine art. The Ashendene Press was famous for producing high-quality works by Dante. Ashendene books had excellent bindings and focused more on pleasure than reform than the other private presses of the time, though one review claims that the Ashendene Press was the most successful private press in recapturing the essence of fifteenth-century printing. Ashendene books were carefully printed with large margins, and despite their lack of extravagant decoration, they were considered spectacular works of art. Two original typefaces were create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Engravers
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
