|
Eduard Reichenow
Johann Eduard Reichenow (7 July 1883 – 23 March 1960) was a German protozoologist. He was the son of ornithologist Anton Reichenow. Biography Reichenow was born in Berlin. He studied natural sciences in Heidelberg, Berlin and Munich, and received his doctorate in 1908. After graduation he conducted research of protozoans at the Imperial Health Ministry in Berlin. From 1913 onward, he served as a government zoologist in Kamerun, where he did studies on the biology of the malaria pathogen. From 1916 to 1919 he conducted research at the ''Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales'' in Madrid, and in 1921 was appointed director of the protozoology department at the '' Schiffs- und Tropenkrankheiten'' in Hamburg. During the same year, he received his habilitation from the University of Hamburg and in 1925 obtained the title of professor. He was an editor of the journals: ''Zeitschrift für Tropenmedizin'', the ''Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie'' and the ''Zeitschrift für Parasitenk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zentralblatt Für Bakteriologie
The ''International Journal of Medical Microbiology'', formerly the ''Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie'', is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering research on microbiology published by Elsevier. It was established in 1887 by Friedrich Loeffler. The current editor-in-chief is Sebastian Suerbaum (Max von Pettenkofer-Institut). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.298. References External links * {{Official website, http://www.elsevier.com/wps/find/journaldescription.cws_home/701772/description#description Microbiology journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1887 English-language journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1960 Deaths
Year 196 ( CXCVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Dexter and Messalla (or, less frequently, year 949 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 196 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus attempts to assassinate Clodius Albinus but fails, causing Albinus to retaliate militarily. * Emperor Septimius Severus captures and sacks Byzantium; the city is rebuilt and regains its previous prosperity. * In order to assure the support of the Roman legion in Germany on his march to Rome, Clodius Albinus is declared Augustus by his army while crossing Gaul. * Hadrian's wall in Britain is partially destroyed. China * First year of the '' Jian'an era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * Emperor Xian o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1883 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – ''Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States. * January 10 – A fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people. * January 16 – The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act, establishing the United States civil service, is passed. * January 19 – The first electric lighting system employing overhead wires begins service in Roselle, New Jersey, United States, installed by Thomas Edison. * February – ''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' by Carlo Collodi is first published complete in book form, in Italy. * February 15 – Tokyo Electrical Lightning Grid, predecessor of Tokyo Electrical Power (TEPCO), one of the largest electrical grids in Asia and the world, is founded in Japan. * February 16 – The '' Ladies' Home Journal'' is published for the first time, in the United States. * February 23 – Alabama becomes the first U.S. stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosoma
''Trypanosoma'' is a genus of kinetoplastids (class Trypanosomatidae), a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. Trypanosoma is part of the phylum Sarcomastigophora. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano-'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of their corkscrew-like motion. Most trypanosomes are heteroxenous (requiring more than one obligatory host to complete life cycle) and most are transmitted via a vector. The majority of species are transmitted by blood-feeding invertebrates, but there are different mechanisms among the varying species. Some, such as '' Trypanosoma equiperdum'', are spread by direct contact. In an invertebrate host they are generally found in the intestine, but normally occupy the bloodstream or an intracellular environment in the vertebrate host. Trypanosomes infect a variety of hosts and cause various diseases, including the fatal human diseases sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'', and Chagas disease, caused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa. Infection with these parasites is known as coccidiosis. Coccidia can infect all mammals, some birds, some fish, some reptiles, and some amphibians. Most species of coccidia are species-specific in their host. An exception is ''Toxoplasma gondii'', which can infect all mammals, although it can only undergo sexual reproduction in cats. Depending on the species of coccidia, infection can cause fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, and nervous system effects and changes to behavior, and may lead to death. Healthy adults may recover without medication—but those who are immunocompromised or young almost certainly requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Theodor Doflein
Franz Theodor Doflein (5 April 1873, in Paris – 24 August 1924, in Obernigk, near today's Wrocław) was a German zoologist known for his studies of animal ecology. Biography He studied medicine and zoology at the University of Munich, where he was influenced by Richard Hertwig. In 1895–96 he worked as an auxiliary assistant to Alexander Götte at the University of Strasbourg, followed by research of fish diseases at Munich as an assistant under Bruno Hofer. In 1898, on behalf of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences, he took part in a study trip to the West Indies, Mexico and California. After his return to Germany, he served as an assistant at the ''Zoologischen Staatssammlung'' (Zoological State Collections) in Munich.Doflein, Franz at Deutsche Biographie In 1904–05 he conducted zoological research in |
Plasmodium Relictum
''Plasmodium relictum'' is a species in the genus ''Plasmodium,'' subgenus '' Haemamoeba''. It is a parasite, and the most common cause of malaria in birds. Like all ''Plasmodium'' species, ''P. relictum'' has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are birds. Distribution ''P. relictum'' is geographically widespread, and is the most widespread malaria parasite of birds. Climate change is broadening its distribution further and is expected to continue to do so, including into higher elevations. Hosts Avian ''P. relictum'' infects a wide variety of birds including birds from various orders. Infections in numerous wild birds and experimental animals have been described including partridges, canaries, chickens, ducks, pigeons and '' Spheniscus magellanicus'' (Magellanic penguins). . . Experimental attempts to infect owls were not successful, suggesting owls may not be susceptible to ''P. relictum''. Vector ''Culex quinquefasciatus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; "''Wupper Dale''") is, with a population of approximately 355,000, the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia as well as the 17th-largest city of Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of the cities and towns of Elberfeld, Barmen, Ronsdorf, Cronenberg and Vohwinkel, and was initially "Barmen-Elberfeld" before adopting its present name in 1930. It is regarded as the capital and largest city of the Bergisches Land (historically this was Düsseldorf). The city straddles the densely populated banks of the River Wupper, a tributary of the Rhine called ''Wipper'' in its upper course. Wuppertal is located between the Ruhr (Essen) to the north, Düsseldorf to the west, and Cologne to the southwest, and over time has grown together with Solingen, Remscheid and Hagen. The stretching of the city in a long band along the narrow Wupper Valley leads to a spatial impression of Wuppertal being larger than it actually is. The city is known for its steep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
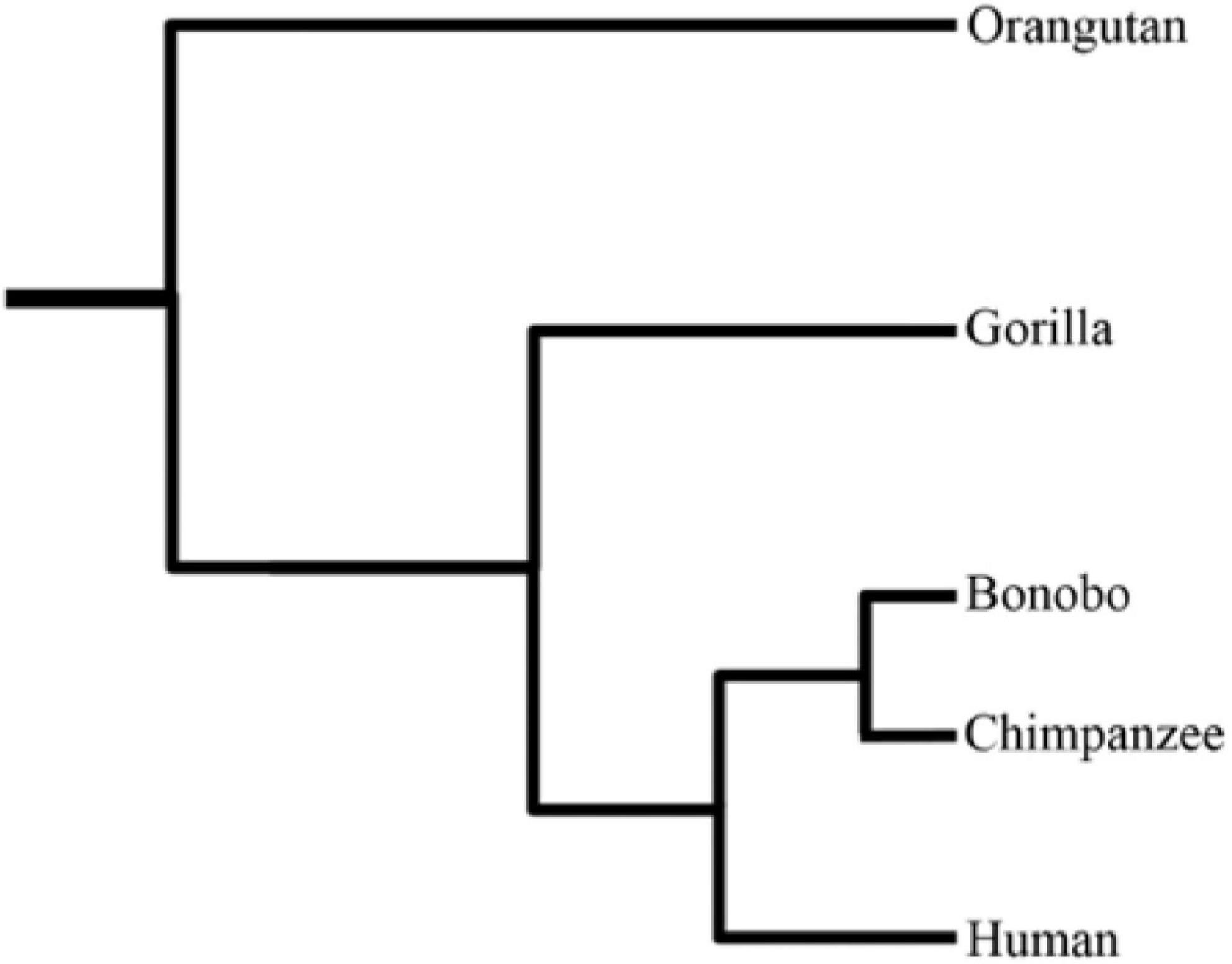
Gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five subspecies. The DNA of gorillas is highly similar to that of humans, from 95 to 99% depending on what is included, and they are the next closest living relatives to humans after chimpanzees and bonobos. Gorillas are the largest living primates, reaching heights between 1.25 and 1.8 metres, weights between 100 and 270 kg, and arm spans up to 2.6 metres, depending on species and sex. They tend to live in troops, with the leader being called a silverback. The Eastern gorilla is distinguished from the Western by darker fur colour and some other minor morphological differences. Gorillas tend to live 35–40 years in the wild. The oldest gorilla known is Fatou (b. 1957), who is still alive at the advanced age of 65 years. Gorillas' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus Pan (genus), ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the Human evolution, human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more Robustness (morphology), robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |