|
Edoylerite
Edoylerite is a rare mercury containing mineral. Edoylerite was first discovered in 1961 by Edward H. Oyler, whom the mineral is named after, in a meter-sized boulder at the Clear Creek claim in San Benito County, California. The Clear Creek claim is located near the abandoned Clear Creek mercury mine. The material from the boulder underwent several analyses including, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), a single crystal study, and a preliminary electron microprobe analysis (EMA). Using these analyses it was determined that this was a new mineral but the nature of the material at the time prevented further investigation. It was not until 1986, with the discovery of crystals large enough for a crystal structure determination and a sufficient quantity for a full mineralogical characterization, that the study was renewed. The new edoylerite crystals were found in the same area at the Clear Creek claim but were situated in an outcrop of silica-carbonate rock. This silica-carbonate rock was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
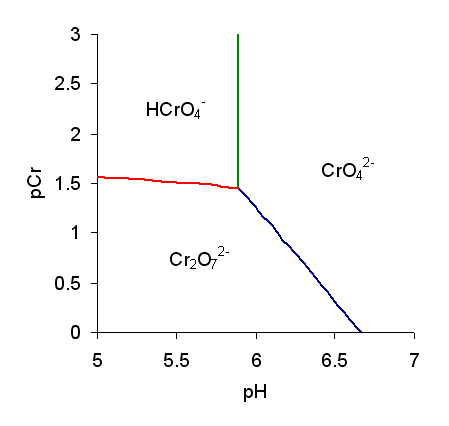
Monochromate
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, CrO(O2)2, is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex CrO(O2)2py. Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. :2 + 2 H+ + H2O The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystalline forms of silica, which are considered minerals. It is deposited at a relatively low temperature and may occur in the fissures of almost any kind of rock, being most commonly found with limonite, sandstone, rhyolite, marl, and basalt. The name ''opal'' is believed to be derived from the Sanskrit word (), which means 'jewel', and later the Greek derivative (), which means 'to see a change in color'. There are two broad classes of opal: precious and common. Precious opal displays play-of-color ( iridescence); common opal does not. Play-of-color is defined as "a pseudo chromatic optical effect resulting in flashes of colored light from certain minerals, as they are turned in white light." The internal structure of precious opal causes it to di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for lattice planes in crystal (Bravais) lattices. In particular, a family of lattice planes of a given (direct) Bravais lattice is determined by three integers ''h'', ''k'', and ''ℓ'', the ''Miller indices''. They are written (hkℓ), and denote the family of (parallel) lattice planes (of the given Bravais lattice) orthogonal to \mathbf_ = h\mathbf + k\mathbf + \ell\mathbf, where \mathbf are the basis or primitive translation vectors of the reciprocal lattice for the given Bravais lattice. (Note that the plane is not always orthogonal to the linear combination of direct or original lattice vectors h\mathbf + k\mathbf + \ell\mathbf because the direct lattice vectors need not be mutually orthogonal.) This is based on the fact that a reciprocal lattice vector \mathbf (the vector indicating a reciprocal lattice point from the reciprocal lattice origin) is the wavevector of a plane wave in the Fourier series of a spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for lattice planes in crystal (Bravais) lattices. In particular, a family of lattice planes of a given (direct) Bravais lattice is determined by three integers ''h'', ''k'', and ''ℓ'', the ''Miller indices''. They are written (hkℓ), and denote the family of (parallel) lattice planes (of the given Bravais lattice) orthogonal to \mathbf_ = h\mathbf + k\mathbf + \ell\mathbf, where \mathbf are the basis or primitive translation vectors of the reciprocal lattice for the given Bravais lattice. (Note that the plane is not always orthogonal to the linear combination of direct or original lattice vectors h\mathbf + k\mathbf + \ell\mathbf because the direct lattice vectors need not be mutually orthogonal.) This is based on the fact that a reciprocal lattice vector \mathbf (the vector indicating a reciprocal lattice point from the reciprocal lattice origin) is the wavevector of a plane wave in the Fourier series of a spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Habit
In mineralogy, crystal habit is the characteristic external shape of an individual crystal or aggregate of crystals. The habit of a crystal is dependent on its crystallographic form and growth conditions, which generally creates irregularities due to limited space in the Crystallization, crystallizing medium (commonly in Rock (geology), rocks).Klein, Cornelis, 2007, ''Minerals and Rocks: Exercises in Crystal and Mineral Chemistry, Crystallography, X-ray Powder Diffraction, Mineral and Rock Identification, and Ore Mineralogy,'' Wiley, third edition, Wenk, Hans-Rudolph and Andrei Bulakh, 2004, ''Minerals: Their Constitution and Origin,'' Cambridge, first edition, Crystal forms Recognizing the habit can aid in mineral identification and description, as the crystal habit is an external representation of the Crystal structure, internal ordered atomic arrangement. Most natural crystals, however, do not display ideal habits and are commonly malformed. Hence, it is also important to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lustre (mineralogy)
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhibit unus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous acid. Compounds The free acid, chlorous acid HClO2, is the least stable oxoacid of chlorine and has only been observed as an aqueous solution at low concentrations. Since it cannot be concentrated, it is not a commercial product. The alkali metal and alkaline earth metal compounds are all colorless or pale yellow, with sodium chlorite (NaClO2) being the only commercially important chlorite. Heavy metal chlorites (Ag+, Hg+, Tl+, Pb2+, and also Cu2+ and ) are unstable and decompose explosively with heat or shock. Sodium chlorite is derived indirectly from sodium chlorate, NaClO3. First, the explosively unstable gas chlorine dioxide, ClO2 is produced by reducing sodium chlorate with a suitable reducing agent such as methanol, hydrogen perox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient times for its use as a pigment (brown ochre). Evidence has been found of its use in paint pigment samples taken from the caves of Lascaux in France. It was first described in 1806 based on samples found in the Hollertszug Mine in Herdorf, Germany. The mineral was named after the German polymath and poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832). Composition Goethite is an iron oxyhydroxide containing ferric iron. It is the main component of rust and bog iron ore. Goethite's hardness ranges from 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs Scale, and its specific gravity varies from 3.3 to 4.3. The mineral forms prismatic needle-like crystals ("needle ironstone") but is more typically massive. Feroxyhyte and lepidocrocite are both polymorphs of the iron oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the mountains now known as the Dolomite Alps of northern Italy. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ions. Unless it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monoclinic. Chalcedony's standard chemical structure (based on the chemical structure of quartz) is SiO2 (silicon dioxide). Chalcedony has a waxy luster, and may be semitransparent or translucent. It can assume a wide range of colors, but those most commonly seen are white to gray, grayish-blue or a shade of brown ranging from pale to nearly black. The color of chalcedony sold commercially is often enhanced by dyeing or heating. The name ''chalcedony'' comes from the Latin ''chalcedonius'' (alternatively spelled ''calchedonius'') and is probably derived from the town of Chalcedon in Turkey. The name appears in Pliny the Elder's ''Naturalis Historia'' as a term for a translucent kind of jaspis. Another reference to a gem by the name of ''khalkedon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosesite
Mosesite is a very rare mineral found in few locations. It is a mercury mineral found as an accessory in deposits of mercury, often in conjunction with limestone. It is known to be found in the U.S. states of Texas and Nevada, and the Mexican states of Guerrero and Querétaro. It was named after Professor Alfred J. Moses (1859–1920) for his contributions to the field of mineralogy in discovering several minerals found alongside mosesite. The mineral itself is various shades of yellow and a high occurrence of spinel twinning. It becomes isotropic when heated to . Composition Mosesite contains 16 Hg, 3 Cl, SO4, CO3, MoO4, 16 H, and 8 N with a volume of 8.4777x10−1 nm3 and calculated density of 7.53 g/cm3. Its chemical formula is . Geologic occurrence Discovered in a mercury mine in Terlingua, Texas, mosesite has also been seen in Nevada and Mexico. Mosesite is a secondary mineral formed at low temperature in hydrothermal mercury deposits. The mercury ore at the mine in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |