|
Edfou
Edfu ( egy, bḥdt, ar, إدفو , ; also spelt Idfu, or in modern French as Edfou) is an Egyptian city, located on the west bank of the Nile River between Esna and Aswan, with a population of approximately sixty thousand people. Edfu is the site of the Ptolemaic Temple of Horus and an ancient settlement, Tell Edfu. About south of Edfu are remains of ancient pyramids. Ancient history Ancient Tell Edfu The remains of the ancient settlement of Edfu are situated about 50 m to the west of the Ptolemaic temple – to the left of the older temple pylon. This settlement is known as ''Wetjeset-hor'' and the Greek name was ''Apollinopolis Magna'' ( Ancient Greek: ''Apollinòpolis'', ''Απολλινόπολις''). According to ''Notitia Dignitatum'', part of Legio II ''Traiana Fortis'' was camped in ''Apollo superior'', which was the Roman name for the town. Although unassuming and unglamorous to the visiting tourists, Tell Edfu is a monument that contains evidence of more E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
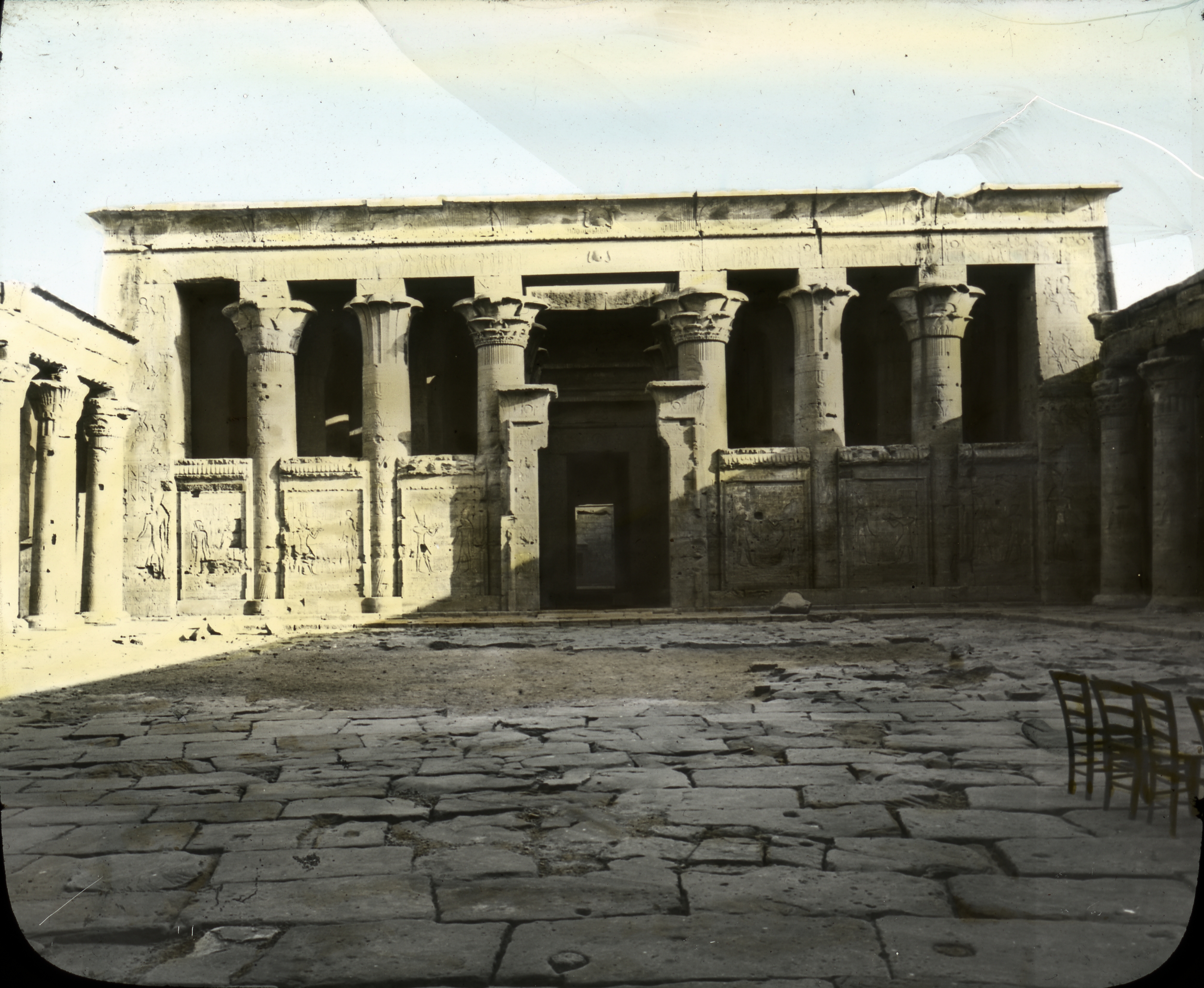
Temple Of Edfu
The Temple of Edfu is an Egyptian temple located on the west bank of the Nile in Edfu, Upper Egypt. The city was known in the Hellenistic period in grc-koi, Ἀπόλλωνος πόλις and in Latin as ''Apollonopolis Magna'', after the chief god Horus, who was identified as Apollo under the ''interpretatio graeca''. It is one of the best preserved shrines in Egypt. The temple was built in the Ptolemaic Kingdom between 237 and 57 BC. The inscriptions on its walls provide important information on language, myth and religion during the Hellenistic period in Egypt. In particular, the Temple's inscribed building texts "provide details othof its construction, and also preserve information about the mythical interpretation of this and all other temples as the Island of Creation." There are also "important scenes and inscriptions of the Sacred Drama which related the age-old conflict between Horus and Seth." They are translated by the Edfu-Project. History Edfu was one of several t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierz Michałowski
Kazimierz Józef Marian Michałowski (born December 14, 1901 in Tarnopol – January 1, 1981 in Warsaw) was a Polish archaeologist and Egyptologist, art historian, member of the Polish Academy of Sciences, professor ordinarius of the University of Warsaw as well as the founder of the Polish school of Mediterranean archaeology and a precursor of Nubiology. Biography Early life and the beginning of scientific career Kazimierz Michałowski graduated from a gymnasium in Tarnopol and then studied classical archaeology and art history at the Philosophy Department of the Jan Kazimierz University in Lwów; he also attended philosophy lectures by Professor Kazimierz Twardowski. He broadened his knowledge at universities in Berlin, Heidelberg, Paris, Rome and Athens. As a young scientist he took part in excavations managed by École Française d`Athènes in Delphi, Thasos and Delos. In 1926 he defended his doctoral thesis devoted to Niobids in Greek art, which he prepared at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebakh
Sebakh ( ar, سباخ, sabākh, less commonly transliterated as ''sebbakh'') is an Arabic word that translates to "fertilizer". In English, the term is primarily used to describe decomposed mudbricks from archaeological sites, which is an organic material that can be employed both as an agricultural fertilizer and as a fuel for fires. Composition Most sebakh consists of ancient, deteriorated mudbrick, a primary building material in ancient Egypt. This material is composed of ancient mud mixed with the nitrous compost of the hay and stubble that the bricks were originally formulated with to give added strength before being baked in the sun. Affecting archaeology A common practice in Egypt, in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, was for farmers to obtain government permits to remove this material from ancient mounds; such farmers were known as ''sebakhin''. Mounds indicating the location of ancient cities are also known as a '' tell'', or ''tel''. An archaeological s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Egypt
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis. Overview After the turbulent last years of the Second Dynasty, which might have included civil war, Egypt came under the rule of Djoser, marking the beginning of the Third Dynasty.Dodson, Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 Both the Turin King List and the Abydos King List record five kings,Toby A.H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge, 2001 while the Saqqara Tablet only records four, and Manetho records nine,Aidan Dodson: ''The Layer Pyramid of Zawiyet el-Aryan: Its Layout and Context.'' In: ''Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt (JARCE)'', No. 37 (2000). American Research Center (Hg.), Eisenbrauns, Winona Lake/Bristol 2000, , pp. 81–90. many of whom did not exist or are simply the same king unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
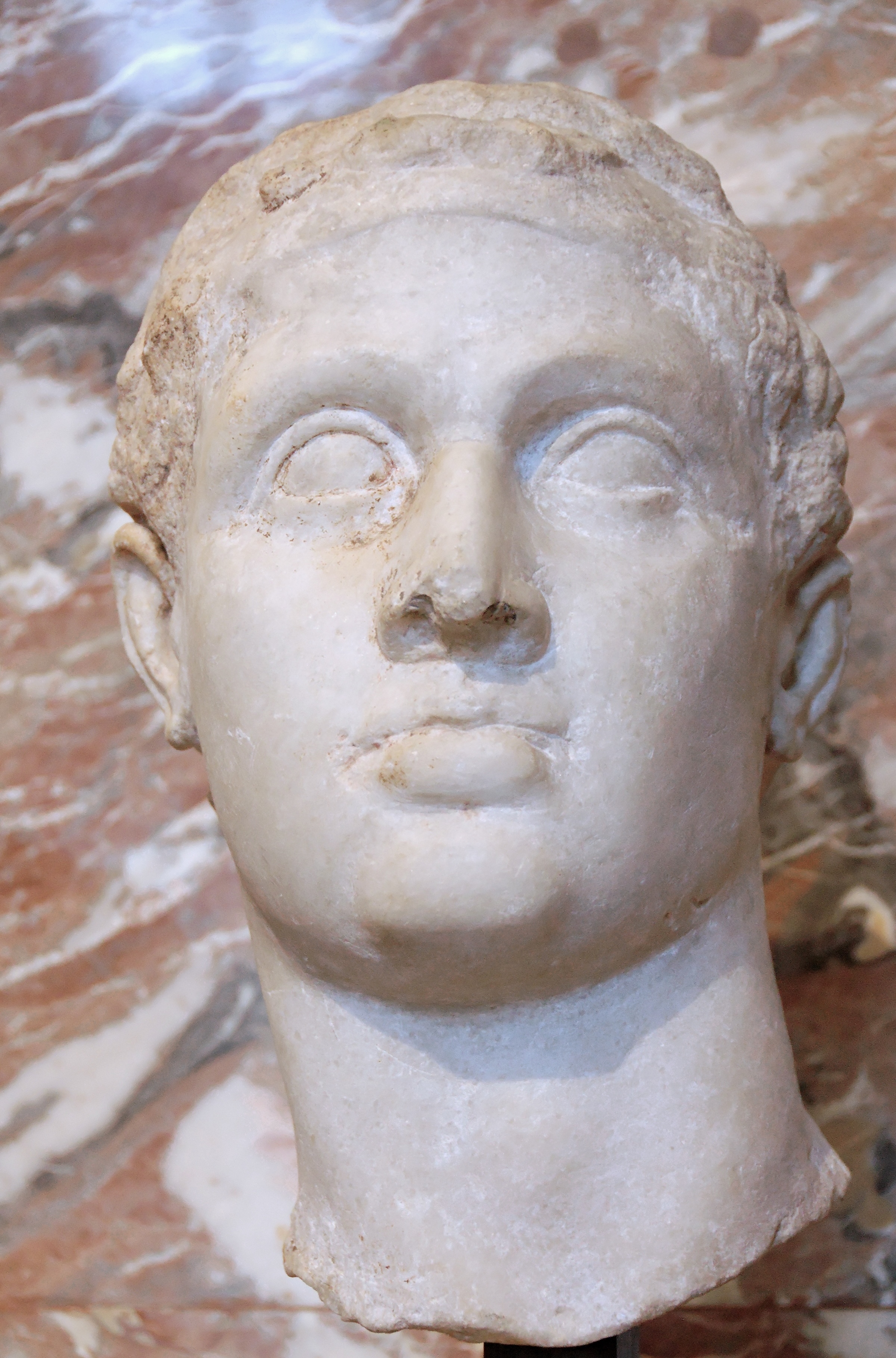
Huni
Huni (original reading unknown) was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC. Huni's chronological position as the last king of the third dynasty is seen as fairly certain, but there is still some uncertainty on the succession order of rulers at the end of the 3rd dynasty. It is also unclear under which Hellenized name the ancient historian Manetho could have listed him in his historical writing ''Aegyptiacae''. Most possibly he is to be identified with the Hellenized name Aches, as Winfried Barta proposes. Many Egyptologists believe that Huni was the father and direct predecessor of king Sneferu, but this is questioned by other scholars. Huni is seen by scholars as a confusing figure in Egyptian history, because he was long remembered in Egyptian traditions, but very few documents, objects or monuments f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from '' Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation) * Northeast Wrestling, a professional wrestling promotion in the northeastern United States Transport * New Orleans Lakefront Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horus
Horus or Heru, Hor, Har in Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as god of kingship and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Roman Egypt. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history, and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists."The Oxford Guide: Essential Guide to Egyptian Mythology", Edited by Donald B. Redford, Horus: by Edmund S. Meltzer, pp. 164–168, Berkley, 2003, . These various forms may be different manifestations of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality. He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner falcon or peregrine falcon, or as a man with a falcon head. The earliest recorded form of Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a diplomat, naval commander, linguist, and medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the fourth century BC. The Ptolemies were not of Egyptian extraction, but stemmed from Ptolemy Soter, a Macedonian Greek in the entourage of Alexander the Great."For additional sources that describe the Ptolemaic dynasty as " Macedonian Greek", please see , , , and . Alternatively, describes them as a "Macedonian, Greek-speaking" dynasty. Other sources such as and describe the Ptolemies as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemaic Dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. Their rule lasted for 275 years, from 305 to 30 BC. The Ptolemaic was the last dynasty of ancient Egypt. Ptolemy, one of the seven somatophylakes (bodyguard companions), a general and possible half-brother of Alexander the Great, was appointed satrap of Egypt after Alexander's death in 323 BC. In 305 BC, he declared himself Pharaoh Ptolemy I, later known as ''Sōter'' "Saviour". The Egyptians soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the pharaohs of independent Egypt. Ptolemy's family ruled Egypt until the Roman conquest of 30 BC. Like the earlier dynasties of ancient Egypt, the Ptolemaic dynasty practiced inbreeding including sibling marriage, but this did not start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba
A mastaba (, or ), also mastabah, mastabat or pr- djt (meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity" or "eternal house" in Ancient Egyptian), is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks. These edifices marked the burial sites of many eminent Egyptians during Egypt's Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. In the Old Kingdom epoch, local kings began to be buried in pyramids instead of in mastabas, although non-royal use of mastabas continued for over a thousand years. Egyptologists call these tombs ''mastaba'', from the Arabic word (maṣṭaba) "stone bench". History The afterlife was important in the religion of ancient Egyptians. Their architecture reflects this, most prominently by the enormous amounts of time and labour involved in building tombs. Ancient Egyptians believed the soul could live only if the body was fed and preserved from corruption and depredation. Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village D’Edfou, Vue Prise Du Pylone Du Temple
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |