|
Economy-wide Material Flow Accounts
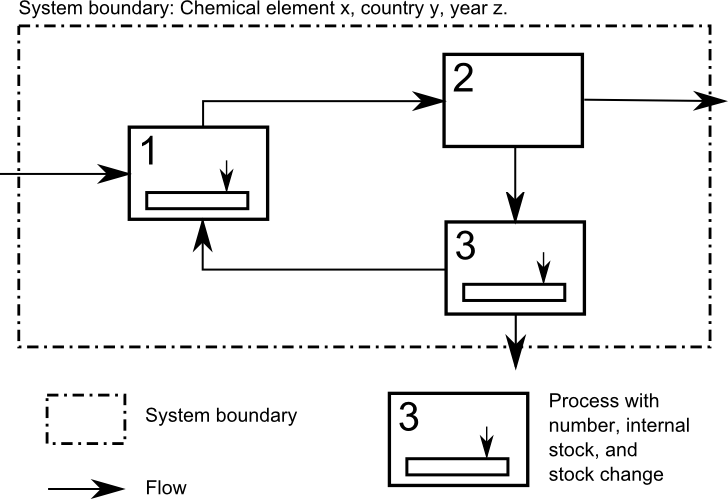
Economy-wide material flow accounts (EW-MFA) is a framework to compile statistics linking flows of materials from natural resources to a national economy. EW-MFA are descriptive statistics, in physical units such as tonnes per year. EW-MFA is consistent with the principles and system boundaries of the United Nations System of National Accounts (SNA) and follows the residence principle. This means that EW-MFA is also a part of the System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting (SEEA). Scope The underlying definition of economy-wide material flow accounts includes statistics on the overall material inputs into national economies, the changes of material stock within the economic system and the material outputs to other economies or to the environment. Statistics on EW-MFA cover all solid, gaseous, and liquid materials, except for water and air. However, water in products is included. EW-MFA includes statistics on material flows crossing the national (geographical) borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. On Earth, it includes sunlight, atmosphere, water, land, all minerals along with all vegetation, and wildlife. Natural resources is a part of humanity's natural heritage or protected in nature reserves. Particular areas (such as the rainforest in Fatu-Hiva) often feature biodiversity and geodiversity in their ecosystems. Natural resources may be classified in different ways. Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, air, as well as any living organism such as a fish, or it may be transformed by extracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Accounting
Environmental accounting is a subset of accounting proper, its target being to incorporate both economic and environmental information. It can be conducted at the corporate level or at the level of a national economy through the System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting, a satellite system to the National Accounts of Countries (among other things, the National Accounts produce the estimates of gross domestic product otherwise known as GDP). Environmental accounting is a field that identifies resource use, measures and communicates costs of a company's or national economic impact on the environment. Costs include costs to clean up or remediate contaminated sites, environmental fines, penalties and taxes, purchase of pollution prevention technologies and waste management costs. An environmental accounting system consists of environmentally differentiated conventional accounting and ecological accounting. Environmentally differentiated accounting measures effects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Statistics
Environment statistics is the application of statistical methods to environmental science. It covers procedures for dealing with questions concerning the natural environment in its undisturbed state, the interaction of humanity with the environment, and urban environments. The field of environmental statistics has seen rapid growth in the past few decades as a response to increasing concern over the environment in the public, organizational, and governmental sectors. The United Nations' Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) defines the scope of environment statistics as follows:http://unstats.un.org/unsd/environment/FDES/FDES-2015-supporting-tools/FDES.pdf United Nations Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics The scope of environment statistics covers biophysical aspects of the environment and those aspects of the socio-economic system that directly influence and interact with the environment. The scope of environment, social and economic st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Metabolism
Urban metabolism is a model to facilitate the description and analysis of the flows of the materials and energy within cities, such as undertaken in a material flow analysis of a city. It provides researchers with a metaphorical framework to study the interactions of natural and human systems in specific regions.Pincetl, S., Bunje, P., & Holmes, T. (2012). An expanded urban metabolism method: Toward a systems approach for assessing urban energy processes and causes. Landscape and Urban Planning, 193-202. From the beginning, researchers have tweaked and altered the parameters of the urban metabolism model. C. Kennedy and fellow researchers have produced a clear definition in the 2007 paper ''The Changing Metabolism of Cities'' claiming that urban metabolism is "the sum total of the technical and socio-economic process that occur in cities, resulting in growth, production of energy and elimination of waste."Kennedy, C., Cuddihy, J., & Engel-Yan, J. (2007). The changing metabolism of ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Metabolism
Social metabolism or socioeconomic metabolism is the set of flows of materials and energy that occur between nature and society, between different societies, and within societies. These human-controlled material and energy flows are a basic feature of all societies but their magnitude and diversity largely depend on specific cultures, or sociometabolic regimes. El metabolismo social: una nueva teoría socioecológica. Relaciones. 2013. Social or socioeconomic metabolism is also described as "the self-reproduction and evolution of the structures of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Flow Analysis
Material flow analysis (MFA), also referred to as substance flow analysis (SFA), is an analytical method to quantify flows and stocks of materials or substances in a well-defined system. MFA is an important tool to study the bio-physical aspects of human activity on different spatial and temporal scales. It is considered a core method of industrial ecology or anthropogenic, urban, social and industrial metabolism. MFA is used to study material, substance, or product flows across different industrial sectors or within ecosystems. MFA can also be applied to a single industrial installation, for example, for tracking nutrient flows through a waste water treatment plant. When combined with an assessment of the costs associated with material flows this business-oriented application of MFA is called material flow cost accounting. MFA is an important tool to study the circular economy and to devise material flow management. Since the 1990s, the number of publications related to materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Flow Accounting
Material flow accounting (MFA) is the study of material flows on a national or regional scale. It is therefore sometimes also referred to as regional, national or economy-wide material flow analysis. Introduction Material flow accounting provides economy-wide data on material use. Through international standardization, this data has become reliable and comparable across countries. Increasingly, the data are also being made available in medium- to long-term time series allowing for the analysis of past trends as well as potential future developments. Material flow accounts provide information on the material inputs into, the changes in material stock within, and the material outputs in the form of exports to other economies or discharges to the environment of an economy. Material flow accounting can be used in national planning, especially for scarce resources, and also allows for forecasting. The method can be used to assess environmental burdens associated with the economic activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Metabolism
Industrial metabolism is a concept to describe the material and energy turnover of industrial systems. It was proposed by Robert Ayres in analogy to the biological metabolism as "the whole integrated collection of physical processes that convert raw materials and energy, plus labour, into finished products and wastes..." In analogy to the biological concept of metabolism, which is used to describe the whole of chemical reactions in, for example, a cell to maintain its functions and reproduce itself, the concept of industrial metabolism describes the chemical reactions, transport processes, and manufacturing activities in industry. Industrial metabolism presupposes a connection between different industrial activities by seeing them as part of a larger system, such as a material cycle or the supply chain of a commodity. System scientists, for example in industrial ecology, use the concept as paradigm to study the flow of materials or energy through the industrial system in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Accounting
Green accounting is a type of accounting that attempts to factor environmental costs into the financial results of operations. It has been argued that gross domestic product ignores the environment and therefore policymakers need a revised model that incorporates green accounting. The major purpose of green accounting is to help businesses understand and manage the potential quid pro quo between traditional economics goals and environmental goals. It also increases the important information available for analyzing policy issues, especially when those vital pieces of information are often overlooked. Green accounting is said to only ensure weak sustainability, which should be considered as a step toward ultimately a strong sustainability. It is a controversial practice however, since depletion may be already factored into accounting for the extraction industries and the accounting for externalities may be arbitrary. It is obvious therefore that a standard practice would need to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropogenic Metabolism
Anthropogenic metabolism, also referred to as metabolism of the anthroposphere, is a term used in industrial ecology, material flow analysis, and waste management to describe the material and energy turnover of human society. It emerges from the application of systems thinking to the industrial and other man-made activities and it is a central concept of sustainable development. In modern societies, the bulk of anthropogenic (man-made) material flows is related to one of the following activities: sanitation, transportation, habitation, and communication, which were "of little metabolic significance in prehistoric times". Global man-made stocks of steel in buildings, infrastructure, and vehicles, for example, amount to about 25 Gigatonnes (more than three tonnes per person), a figure that is surpassed only by construction materials such as concrete. Sustainable development is closely linked to the design of a sustainable anthropogenic metabolism, which will entail substantial changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations System Of National Accounts
The System of National Accounts (often abbreviated as SNA; formerly the United Nations System of National Accounts or UNSNA) is an international standard system of national accounts, the first international standard being published in 1953. Handbooks have been released for the 1968 revision, the 1993 revision, and the 2008 revision. The System of National Accounts, in its various released versions, frequently with significant local adaptations, has been adopted by many nations. It continues to evolve and is maintained by the United Nations The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ..., the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and Eurostat. The aim of SNA is to provide an integrated, complete system of accounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts European legislation, following a proposal by the European Commission. The Parliament is composed of 705 members (MEPs). It represents the second-largest democratic electorate in the world (after the Parliament of India), with an electorate of 375 million eligible voters in 2009. Since 1979, the Parliament has been directly elected every five years by the citizens of the European Union through universal suffrage. Voter turnout in parliamentary elections decreased each time after 1979 until 2019, when voter turnout increased by eight percentage points, and rose above 50% for the first time since 1994. The voting age is 18 in all EU member states except for Malta and Austria, where it is 16, and Greece, where it is 17. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |