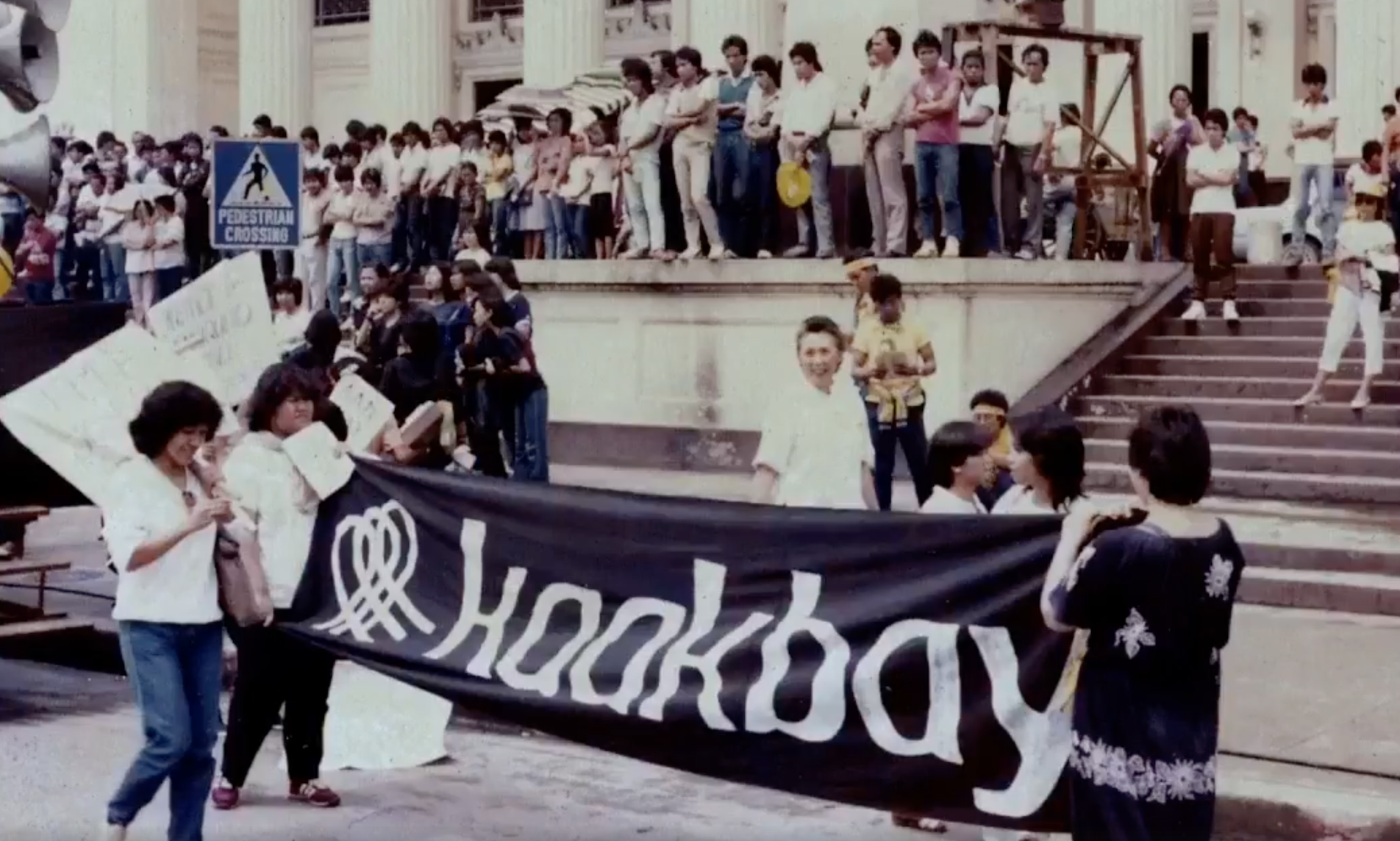|
Ecology Movement
The environmental movement (sometimes referred to as the ecology movement), also including conservation and green politics, is a diverse philosophical, social, and political movement for addressing environmental issues. Environmentalists advocate the just and sustainable management of resources and stewardship of the environment through changes in public policy and individual behaviour. In its recognition of humanity as a participant in (not enemy of) ecosystems, the movement is centered on ecology, health, and human rights. The environmental movement is an international movement, represented by a range of organizations, from enterprises to grassroots and varies from country to country. Due to its large membership, varying and strong beliefs, and occasionally speculative nature, the environmental movement is not always united in its goals. The movement also encompasses some other movements with a more specific focus, such as the climate movement. At its broadest, the movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion And Environmentalism
Religion and environmentalism is an emerging interdisciplinary subfield in the academic disciplines of religious studies, religious ethics, the sociology of religion, and theology amongst others, with environmentalism and ecological principles as a primary focus. Within the context of Christianity, in the encyclical "Laudato si'", Pope Francis called to fight climate change and ecological degradation as a whole. He claimed that humanity is facing a severe ecological crisis and blamed consumerism and irresponsible development. The encyclical is addressed to "every person living on this planet." Buddhism includes many principles linked to sustainability. The Dalai Lama has consistently called for strong climate action, reforestation, preserving ecosystems, a reduction in meat consumption. He declared that if he will ever join a political party it will be the green party and if Buddha returned to our world now: “Buddha would be green.” The leaders of Buddhism issued a special de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Acts
The Alkali Act 1863 (26 & 27 Vict c 124) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Under the Alkali Act 1863, an alkali inspector and four subinspectors were appointed to curb discharge into the air of muriatic acid gas (gaseous hydrochloric acid) from Leblanc alkali works. It was later extended to cover other industrial pollutants. Section 19 provided that the Alkali Act 1863 was to continue in force until 1 July 1868, and no longer. This section was repealed by section 1 of 31 & 32 Vict c 36, which enacted that the Alkali Act 1863 was "continued without any such limitation". Related legislation Alkali Act 1868 The Act 31 & 32 Vict c 36, sometimes called the Alkali Act 1868, the Alkali Act Perpetuation Act 1868, or the Alkali Act (1863) Perpetuation Act 1868, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It made perpetual the Alkali Act 1863. The Bill for this Act was originally called the Alkali Act Continuance Bill and was subsequently called the Alk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Pressure
Pressure politics generally refers to political action which relies heavily on the use of mass media and mass communications to persuade politicians that the public wants or demands a particular action. However, it can also refer to intimidation, threats, and other covert techniques as well. Temperance movement The use of pressure, intimidation and manipulation has existed for millennia. However, its origins are most commonly associated with the temperance movement in the late 19th century and first two decades of the 20th century. Discovering the power of utilizing the mass media to exert pressure on politicians is usually attributed to Wayne Wheeler, the ''de facto'' leader of the Anti-Saloon League. Under his mentorship, a number of skilled practitioners of pressure politics emerged within the league (Odegard, 1928). One of the most accomplished of these was William E. Johnson, better known as "Pussyfoot" Johnson. One leader of the league testified that prior to its passage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Coal Mining
The history of coal mining goes back thousands of years, with early mines documented in ancient China, the Roman Empire and other early historical economies. It became important in the Industrial Revolution of the 19th and 20th centuries, when it was primarily used to power steam engines, heat buildings and generate electricity. Coal mining continues as an important economic activity today, but has begun to decline due to the strong contribution coal plays in global warming and environmental issues, which result in decreasing demand and in some geographies, peak coal. Compared to wood fuels, coal yields a higher amount of energy per unit mass, specific energy or massic energy, and can often be obtained in areas where wood is not readily available. Though it was used historically as a domestic fuel, coal is now used mostly in industry, especially in smelting and alloy production, as well as electricity generation. Large-scale coal mining developed during the Industrial Revolution, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants. Although environmental pollution can be caused by natural events, the word pollution generally implies that the contaminants have an anthropogenic source – that is, a source created by human activities. Pollution is often classed as point source or nonpoint source pollution. In 2015, pollution killed nine million people worldwide (one in six deaths). This remained unchanged in 2019, with little real progress against pollution being identifiable. Air pollution accounted for of these earlier deaths. Major forms of pollution include air pollution, light pollution, litter, noise pollution, plastic pollution, soil contamination, radioactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires (including stoves, candles, internal combustion engines, oil lamps, and fireplaces), but may also be used for pest control ( fumigation), communication ( smoke signals), defensive and offensive capabilities in the military (smoke screen), cooking, or smoking (tobacco, cannabis, etc.). It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative. Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death in victims of indoor fires. The smoke kills by a combination of thermal damage, poisoning and pulmonary irritation caused by carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide and other combustion products. Smoke is an aerosol (or mist) of solid particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordsworth and other Lake Poets and also with Beatrix Potter and John Ruskin. The Lake District National Park was established in 1951 and covers an area of . It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2017. The Lake District is today completely within Cumbria, a county and administrative unit created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972. However, it was historically divided between three English counties ( Cumberland, Westmorland and Lancashire), sometimes referred to as the Lakes Counties. The three counties met at the Three Shire Stone on Wrynose Pass in the southern fells west of Ambleside. All the land in England higher than above sea level lies within the National Park, including Scafell Pike, the highest mountain in England. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |