|
Eastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English Rail transport, railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Great Yarmouth, Yarmouth. Construction began in 1837 on the first nine miles at the London end. Construction was beset by engineering and other problems, leading to severe financial difficulties. As a result, the project was truncated at Colchester in 1843 but through a series of acquisitions (including the Eastern Union Railway who completed the link between Colchester and Norwich) and opening of other lines, the ECR became the largest of the East Anglian railways. In 1862 ECR was merged with a number of other companies to form the Great Eastern Railway. Opening In 1835 a surveyor called Henry Sayer presented a plan for a new railway from London to York via Cambridge to London solicitors Dimes & Boyman. Together with John Clinton Robertson who was to become the first secretary of the ECR and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Eastern Railway
The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923. Formed in 1862 after the amalgamation of the Eastern Counties Railway and several other smaller railway companies the GER served Cambridge, Chelmsford, Colchester, Great Yarmouth, Ipswich, King's Lynn, Lowestoft, Norwich, Southend-on-Sea (opened by the GER in 1889), and East Anglian seaside resorts such as Hunstanton (whose prosperity was largely a result of the GER's line being built) and Cromer. It also served a suburban area, including Enfield, Chingford, Loughton and Ilford. This suburban network was, in the early 20th century, the busiest steam-hauled commuter system in the world. The majority of the Great Eastern's locomotives and rolling stock were built at Stratford Works, part of which was on the site of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopsgate Railway Station
Bishopsgate was a railway station located on the eastern side of Shoreditch High Street in the parish of Bethnal Green (now within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets) on the western edge of the East End of London and just outside the City of London. It was in use from 1840 to 1875 as a passenger station and then as a freight terminal until it was destroyed by fire in 1964. Substantial remains lay derelict until they were demolished in the early 2000s to make way for Shoreditch High Street railway station which now stands on the site. History of the site up to 1840 In connection with the extension of the East London Line, some archaeological excavations were undertaken on the site c 2007-2010 by the Museum of London Archaeology Service. To the west of the site the discovery of Mesolithic struck flint suggested occupation of the banks of the River Walpole. Bishopsgate follows the line of the Roman road and burial plots were found on both sides of the road. The site remained as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Parker Bidder
George Parker Bidder (13 June 1806 – 20 September 1878) was an English engineer and calculating prodigy.W. W. Rouse Ball (1960) ''Calculating Prodigies'', in Mathematical Recreations and Essays, Macmillan, New York, chapter 13. Early life Born in the town of Moretonhampstead, Devon, England, he displayed a natural skill at calculation from an early age. In childhood, his father, William Bidder, a stonemason, exhibited him as a "calculating boy", first in local fairs up to the age of six, and later around the country. In this way his talent was turned to profitable account, but his general education was in danger of being completely neglected. Still, many of those who saw him developed an interest in his education, a notable example being Sir John Herschel. His interest led him to arrange it so George could be sent to school in Camberwell. There he did not remain long, being removed by his father, who wished to exhibit him again, but he was saved from this misfortune and enabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Park And Bow Railway Station
Victoria Park & Bow was a short-lived railway station in Bow, east London. It was located close to the present-day Bow Junction on what is now the Great Eastern Main Line between and . Built by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR), it opened on 2 April 1849, seemingly for the main purpose of providing an interchange between the London and Blackwall Extension Railway's (LBER) branch and the ECR's main line between and Stratford. The LBER had hoped to run through to Stratford but its relationship with the ECR was poor and a junction allowing connection from the LBER's line to the ECR's was not constructed. It appears Victoria Park & Bow station was little-used, as the ECR stopped few trains there. Study of Bradshaw's Railway Guide for March 1850 reveals the only ECR services out of the Bishopsgate terminus which called at the station were the 6:07 a.m. to on weekdays and the 1:37 p.m. to Norwich on Sundays. In the London-bound direction there were no weekday services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limehouse Railway Station
Limehouse is a National Rail and connected Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station in Limehouse, London, England. It is served by regional services operated by c2c to and from Fenchurch Street railway station, Fenchurch Street, and by light metro services provided by the DLR to and from Tower Gateway DLR station, Tower Gateway or Bank-Monument station, Bank. On the main line, Limehouse is located from Fenchurch Street and the following station is West Ham station, West Ham; on the DLR it is between Shadwell DLR station, Shadwell and Westferry DLR station, Westferry in Travelcard Zone 2. The station was opened by the London and Blackwall Railway, Commercial Railway (later the London and Blackwall Railway) in 1840 with the name Stepney. At that time, the Commercial Railway had a Limehouse railway station (1840-1926), separate station named Limehouse one stop to the east. Stepney was renamed Stepney East in 1923, and in 1926 the other Limehouse station was closed. Stepney East adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London & Blackwall Extension Railway
Originally called the Commercial Railway, the London and Blackwall Railway (L&BR) in east London, England, ran from Minories to Blackwall via Stepney, with a branch line to the Isle of Dogs, connecting central London to many of London's docks. It was operational from 1840 until 1926 (for passengers) and 1968 (for goods), closing after the decline of inner London's docks. Much of its infrastructure was reused as part of the Docklands Light Railway. The L&BR was leased by the Great Eastern Railway in 1866, but remained independent until absorbed into the London and North Eastern Railway at the 1923 Grouping. Another branch was opened in 1871, the Millwall Extension Railway. History It was authorised by an Act of Parliament entitled ''An Act for making a Railway from the Minories to Blackwall, with Branches, to be called "The Commercial Railway"'' dated 28 July 1836 in the reign of William IV. The length of the railway was to be . The engineer of the line was intended to be Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
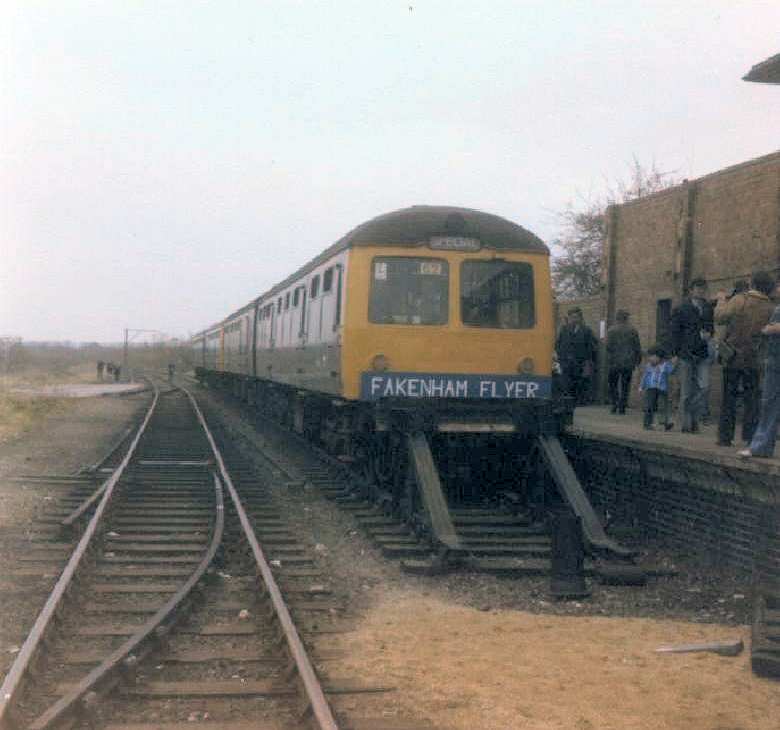
Fakenham East Railway Station
Fakenham East railway station was a railway station in the market town of Fakenham in the English county of Norfolk. The station was opened by the Norfolk Railway on 20 March 1849 and was originally named ''Fakenham''. Following nationalisation, it was renamed ''Fakenham East'' by British Railways on 27 September 1948; it was closed on 5 October 1964. This station is one of the possible sites protected in local plans, if needed as part of the Norfolk Orbital Railway's long-term plans to return trains to Fakenham. Any replacement station would be built on the throat of the original site, as sheltered housing has been built on the main station site. Other developments north of the former station make further extension impractical; instead the 'Norfolk Orbital' scheme proposes reopening towards the North Norfolk line at Holt and the Mid-Norfolk line at County School. The railway formation south of the station, as far as the three-arch viaduct over the River Wensum, is now owned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfield Town Branch Line
The Enfield Town branch is a suburban branch line in the England. In 2014 it is in fact the combination of the original Enfield branch which was built in 1849 by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) and a later line built by the Great Eastern Railway (GER) from to Edmonton in 1872. The line is currently a double-tracked suburban railway with services running between Liverpool Street station and Enfield Town as well as some other services running from Liverpool Street to . Part of the original branch is closed and little visible remains today. Early history (1849–1862) Enfield had been missed by the Northern and Eastern Railway line which had opened between Stratford and Broxbourne on 15 September 1840 and had to make do with Ponders End station some two miles away. Local pressure led to the deposit of a bill before parliament in 1844 which failed. Two years later the Enfield and Edmonton Railway Bill was passed with arrangements for the Eastern Counties Railway to take over man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Anglian Railway
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or "dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisbech East Railway Station
Wisbech East was a railway station in Wisbech, Cambridgeshire. It was opened in 1848 and became part of the Great Eastern Railway network, providing connections to March, Watlington and St Ives, as well as Upwell via the Wisbech and Upwell Tramway. The station closed in 1968 and no trace of it remains today. A freight-only line remains extant as far as a factory based in the station's former goods yard, and a heritage railway based in March is aiming to reinstate services to Wisbech and construct a new station as near as possible to Newbridge Lane crossing. In June 2009 the Association of Train Operating Companies published a report indicating that the reopening of the line to Wisbech and construction of a new station could be viable, in that the ratio of business, economic and social benefits to costs would be just over £1m. History Opening It was the Eastern Counties Railway which first reached Wisbech from the south in May 1847 with the opening of a line from St I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
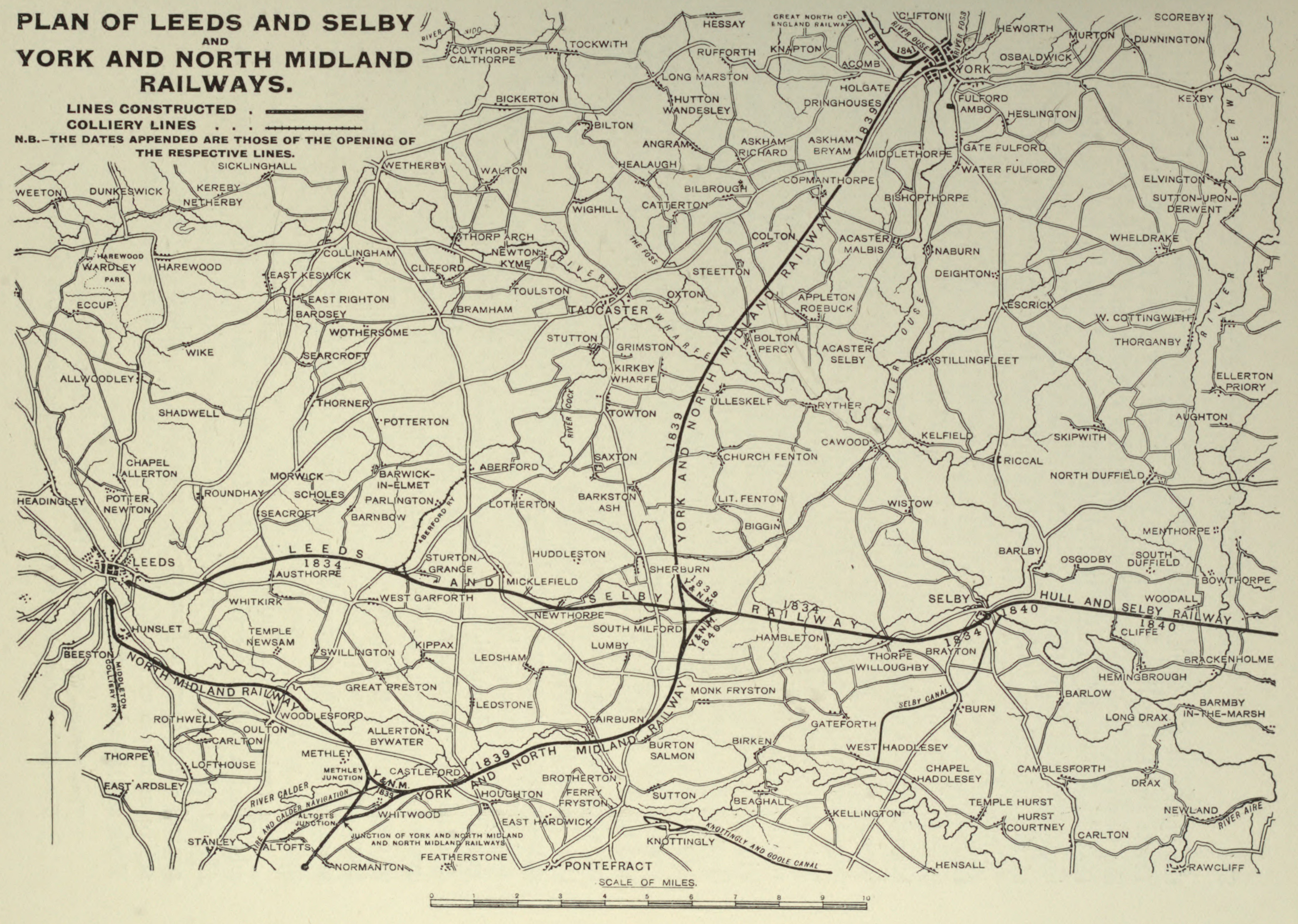
North Midland Railway
The North Midland Railway was a British railway company, which opened its line from Derby to Rotherham (Masbrough) and Leeds in 1840. At Derby, it connected with the Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway and the Midland Counties Railway at what became known as the Tri-Junct Station. In 1844, the three companies merged to form the Midland Railway. Origin The East Midlands had for some years been at the centre of plans to link the major cities throughout the country. In Yorkshire, George Hudson was the Chairman of the York and North Midland Railway, a proposed line from York towards the industrial markets of Manchester and Liverpool. The new line would connect it, and the Manchester and Leeds Railway as part of a trunk route from the South and London to Yorkshire and the North East of England. Meanwhile, financiers in Birmingham, were looking to expand their system northwards. George Carr Glyn was the first Chairman of the new company, with George Stephenson appointed as engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hudson
George Hudson (probably 10 March 1800 – 14 December 1871) was an English railway financier and politician who, because he controlled a significant part of the railway network in the 1840s, became known as "The Railway King"—a title conferred on him by Sydney Smith in 1844. Hudson played a significant role in linking London to Edinburgh by rail, carrying out the first major merging of railway companies (the Midland Railway) and developing his home city of York into a major railway junction. He also represented Sunderland in the House of Commons. Hudson's success was built on dubious financial practices and he frequently paid shareholders out of capital rather than money the company had earned. Eventually in 1849, a series of enquiries, launched by the railways he was chairman of, exposed his methods, although many leading the enquiries had benefited from and approved of Hudson's methods when it suited them. Hudson fell a long way, becoming bankrupt, and after losing his Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_p13_-_Our_Starting_Train.jpg)
_p74_-_Platform_(back_cover).jpg)