|
Early Indian Treaty Territories In North Dakota
Native Americans from various tribes lived in North Dakota before the arrival of settlers. With time, a number of treaties and agreements were signed between the Indians and the newcomers. Many of the treaties defined the domain of a specific group of Indians. The three maps below show the treaty territories of different Indians living in North Dakota and how the territories changed and diminished over time in the 19th century. (The Dakota Territory became a reality on March 2, 1861. Most treaties and agreements antedate the final division of the territory into the Dakotas. For sake of convenience, "North Dakota" is used in the text instead of "present-day North Dakota". The narrow tracks of Indian territories in the southernmost part of North Dakota is not discussed here, since they were segments of considerable areas in South Dakota.) Map 1 Area 445 (map 1) Area 445 was the land of the Red Lake and Pembina bands of the Chippewa. It extended eastward into Minnesota. The I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Indian Treaty Territories, North Dakota - An Overview Map
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * Early (Scritti Politti album), ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * Early (A Certain Ratio album), ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
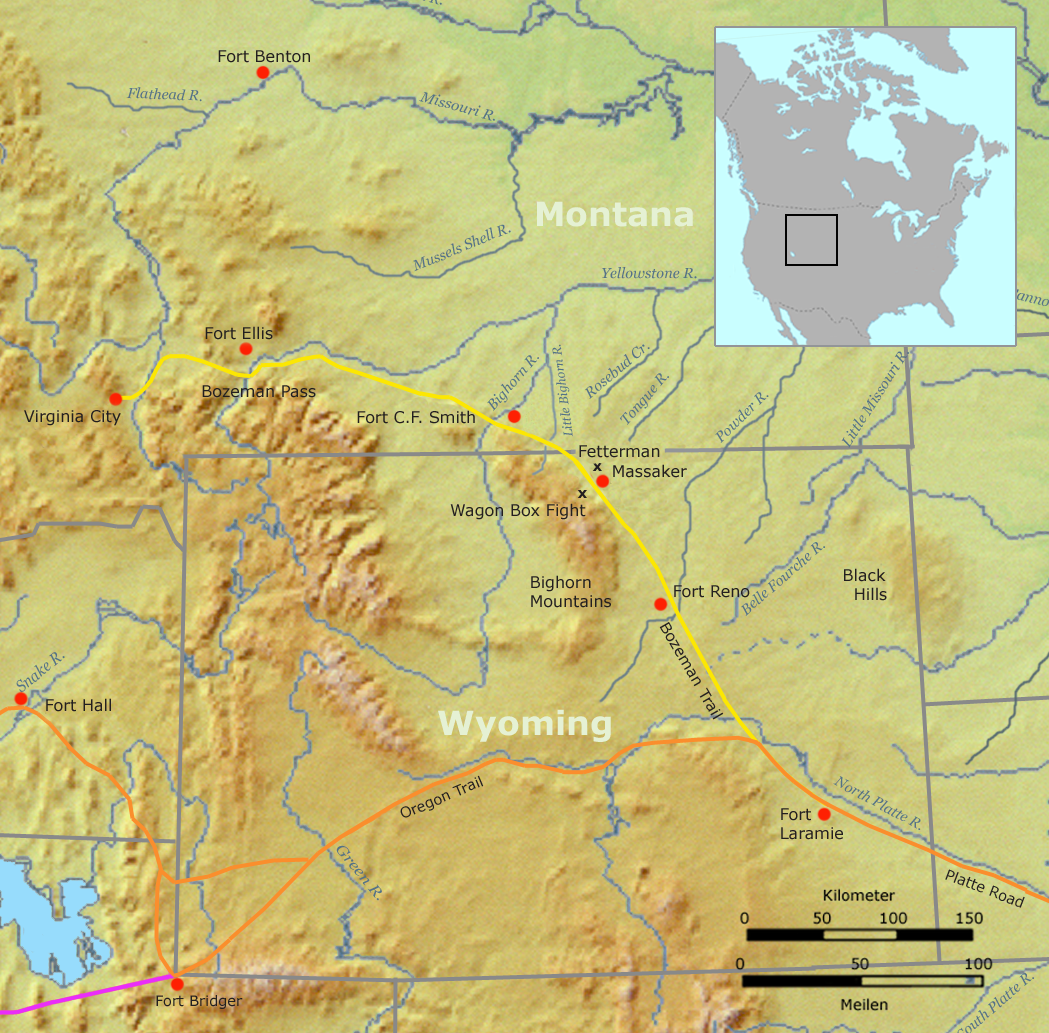
Red Cloud's War
Red Cloud's War (also referred to as the Bozeman War or the Powder River War) was an armed conflict between an alliance of the Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, and Northern Arapaho peoples against the United States that took place in the Wyoming and Montana territories from 1866 to 1868. The war was fought over control of the western Powder River Country in present north-central Wyoming. In 1863, European Americans had blazed the Bozeman Trail through the heart of the traditional territory of the Cheyenne, Arapaho, and Lakota. It was the shortest and easiest route from Fort Laramie and the Oregon Trail to the Montana gold fields. From 1864 to 1866, the trail was traversed by about 3,500 miners, emigrant settlers and others, who competed with the Indians for the diminishing resources near the trail.Fort Phil Kearney/Bozeman Trail As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle Mountain Chippewa Reserve, 1882 And 1884
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Like-a-Fishhook Village
Like-a-Fishhook Village was a Native American settlement next to Fort Berthold in North Dakota, United States, established by dissident bands of the Three Affiliated Tribes, the Mandan, Arikara and Hidatsa. Formed in 1845, it was also eventually inhabited by non-Indian traders, and became important in the trade between Natives and non-Natives in the region. The village was founded eight years after a disastrous epidemic of smallpox in 1837. The numbers of the dissident Mandan in the region had been reduced to approximately 125; the population of the Hidatsa was also affected, though not as severely. These Mandan and Hidatsa bands were later joined by the Arikara 18 years after the village was constructed. The village, consisting of earthen lodges and log cabins, was abandoned in the mid-1880s. The site of Like-a-Fishhook Village was lost when the construction of Garrison Dam flooded the area to create Lake Sakakawea in 1954. The decision to move "Enemies gave our tribes much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Berthold Reservation
The Fort Berthold Indian Reservation is a U.S. Indian reservation in western North Dakota that is home for the federally recognized Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation, also known as the Three Affiliated Tribes. The reservation includes lands on both sides of the Missouri River. Created in 1870, the reservation is a small part of the lands originally reserved to the tribes by the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851, which allocated nearly 12 million acres (49,000 km²) in North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, Nebraska and Wyoming. Location The reservation is located on the Missouri River in (in descending order of reservation land) McLean, Mountrail, Dunn, McKenzie, Mercer and Ward counties. The reservation consists of 988,000 acres (4,000 km²), of which 457,837 acres (1,853 km²) are owned by Native Americans, either as individual allotments or communally by the tribe. The McLean National Wildlife Refuge lies within its boundaries. The Four Bears Bridge, which ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the south. With a population of 576,851 in the 2020 United States census, Wyoming is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, least populous state despite being the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 10th largest by area, with the List of U.S. states by population density, second-lowest population density after Alaska. The state capital and List of municipalities in Wyoming, most populous city is Cheyenne, Wyoming, Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018. Wyoming's western half is covered mostly by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie called the High Plains (United States), High Plains. It is drier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the fourth-largest state by area, the eighth-least populous state, and the third-least densely populated state. Its state capital is Helena. The western half of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges found throughout the state. Montana has no official nickname but several unofficial ones, most notably "Big Sky Country", "The Treasure State", "Land of the Shining Mountains", and " The Last Best Place". The economy is primarily based on agriculture, including ranching and cereal grain farming. Other significant economic resources include oil, gas, coal, mining, and lumber. The health ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still reside in the area of the reservation; the rest reside around the United States and in Canada. The Mandan historically lived along both banks of the Upper Missouri River and two of its tributaries—the Heart and Knife rivers— in present-day North and South Dakota. Speakers of Mandan, a Siouan language, they developed a settled, agrarian culture. They established permanent villages featuring large, round, earth lodges, some in diameter, surrounding a central plaza. Matrilineal families lived in the lodges. The Mandan were a great trading nation, trading especially their large corn surpluses with other tribes in exchange for bison meat and fat. Food was the primary item, but they also traded for horses, guns, and other trade goods. Popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidatsa
The Hidatsa are a Siouan people. They are enrolled in the federally recognized Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. Their language is related to that of the Crow, and they are sometimes considered a parent tribe to the modern Crow in Montana. Name The Hidatsa's autonym is Hiraacá. According to the tribal tradition, the word ''hiraacá'' derives from the word "willow"; however, the etymology is not transparent and the similarity to ''mirahací'' ‘willows’ inconclusive. The present name ''Hidatsa'' was formerly borne by one of the three tribal villages. When the villages consolidated, the name was adopted for the tribe as a whole. They are called the ''Mį́nįtaree'' (″to cross the water″) by their allies, the Mandan; in Assiniboine the Assiniboine (called Hidusidi by the Hidatsa) know them as: ''wakmúhaza yúde, ȟewáktųkta'' Occasionally they have also been confused with the Gros Ventres in present-day Montana and Prairie Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011) Arikaree, Ree, or Hundi, are a tribe of Native Americans in . Today, they are enrolled with the and the as the |
Battle Of The Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and also commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes and the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army. The battle, which resulted in the defeat of U.S. forces, was the most significant action of the Great Sioux War of 1876. It took place on June 25–26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River in the Crow Indian Reservation in southeastern Montana Territory. Most battles in the Great Sioux War, including the Battle of the Little Bighorn (14 on the map to the right), "were on lands those Indians had taken from other tribes since 1851". The Lakotas were there without consent from the local Crow tribe, which had treaty on the area. Already in 1873, Crow chief Blackfoot had called for U.S. military actions against the Indian intruders. The steady Lakota i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yankton Indian Reservation
The Yankton Indian Reservation is the homeland of the Yankton Sioux Tribe of the Dakota tribe. The reservation occupies the easternmost 60 percent of Charles Mix County in southeastern South Dakota, United States and abuts the Missouri River along its southwest border. It has a land area of 665.712 sq mi (1,724.186 km²) and a total area (land and water) of 684.406 sq mi (1,772.604 km²), and a resident population of 6,500 persons as of the 2000 census. The population as of the 2010 census was 6,465 inhabitants. After the Osage Indian Reservation, it is the second-largest Indian reservation that is located entirely within one county. The largest community on the reservation is the city of Wagner, which is the location of the tribal headquarters. The blues-rock group Indigenous is originally from this community, as is early 20th-century author and activist Zitkala-Sa. Tribal information * Reservation: Diminished Yankton Reservation; part of Charles Mix County * Divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)


.jpg)
