|
EMDT
2-Ethyl-5-methoxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (EMDT) is a tryptamine derivative which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective 5-HT6 receptor agonist, with a Ki of 16 nM, and was one of the first selective agonists developed for this receptor. EMDT inhibits both short- and long-term memory formation in animal studies, and this effect can be reversed by the selective 5-HT6 antagonist SB-399,885. Additionally, it is active in the tail suspension test The tail suspension test (TST) is an experimental method used in scientific research to measure stress in rodents. It is based on the observation that if a mouse is subjected to short term inescapable stress then the mouse will become immobile ..., suggesting that it could be an effective antidepressant. See also * EMD-386,088 * ST-1936 References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethyl-5-methoxy-N, N-dimethyltryptamine 5-HT6 agonists Tryptamines Phenol ethers Dimethylamino compounds Methoxy compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
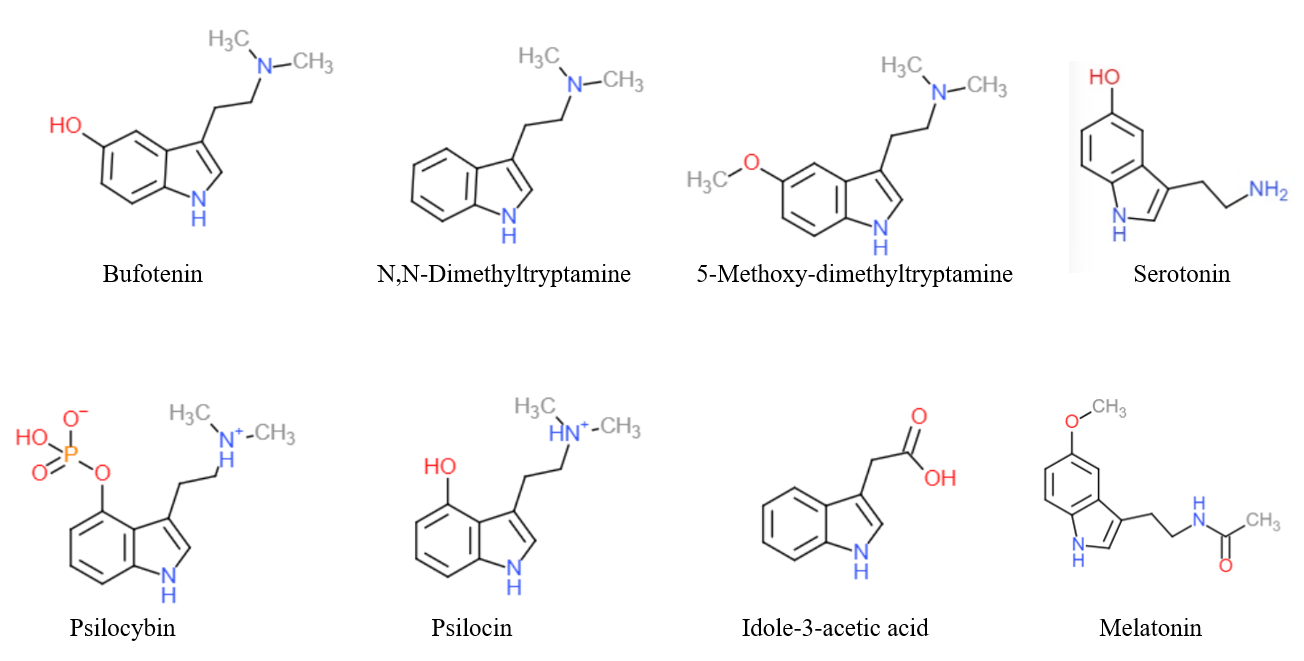
Tryptamines
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained from numerous plant sources, like chacruna, and it is often used in ayahuasca brews. Many synthetic tryptamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD-386,088
EMD-386088 is an indole derivative which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent 5-HT6 receptor partial agonist, with a Ki of 1 nM, a significantly higher affinity than older 5-HT6 agonists such as EMDT, although it possesses moderate affinity for the 5-HT3 receptor as well. Subsequent research has determined that EMD-386088 is also a dopamine reuptake inhibitor and that this action is involved in the antidepressant-like effects of the drug in rodents. See also * EMDT 2-Ethyl-5-methoxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (EMDT) is a tryptamine derivative which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective 5-HT6 receptor agonist, with a Ki of 16 nM, and was one of the first selective agonists developed ... * ST-1936 References 5-HT6 agonists Dopamine reuptake inhibitors Indoles Tetrahydropyridines Chloroarenes {{Nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT6 Receptor
The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR6'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor. Distribution The 5HT6 receptor is expressed almost exclusively in the brain. It is distributed in various areas including, but not limited to, the olfactory tubercle, cerebral cortex (frontal and entorhinal regions), nucleus accumbens, striatum, caudate nucleus, hippocampus, and the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Based on its abundance in extrapyramidal, limbic, and cortical regions it can be suggested that the 5HT6 receptor plays a role in functions like motor control, emotionality, cognition, and memory. Function Blockade of central 5HT6 receptors has been shown to increase glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain areas, whereas activation enhances GA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT6 Agonists
The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR6'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor. Distribution The 5HT6 receptor is expressed almost exclusively in the brain. It is distributed in various areas including, but not limited to, the olfactory tubercle, cerebral cortex (frontal and entorhinal regions), nucleus accumbens, striatum, caudate nucleus, hippocampus, and the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Based on its abundance in extrapyramidal, limbic, and cortical regions it can be suggested that the 5HT6 receptor plays a role in functions like motor control, emotionality, cognition, and memory. Function Blockade of central 5HT6 receptors has been shown to increase glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain areas, whereas activation enhanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ST-1936
ST-1936 (2-methyl-5-chloro-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective 5-HT6 receptor agonist, with a Ki of 13 nM, and much weaker action at 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 subtypes. In animal studies it has been found to increase dopamine and noradrenaline mediated signalling but decreases glutamatergic transmission, and has antidepressant effects. See also * EMD-386,088 * EMDT * 5-Bromo-DMT 5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges '' Smenospongia aurea'' and '' Smenospongia echina'', as well as in '' Verongula rigida'' (0.00142% dry weight) alongside 5,6-D ... * 5-Chloro-AMT References {{Tryptamines 5-HT6 agonists Tryptamines Chloroarenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common Side effect, side-effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is a slight increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, Discontinuation syndrome may occur after stopping any antidepressant which resembles recurrent depression. Some research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults has found benefits, whilst other research has not. Evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear. The twenty-one most commonly prescribed antidepressant medications are more effective than placebo for the short-term (acute) treatments of adults with major depressive disorder. There is debate in the medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Neuroscience
''The Journal of Neuroscience'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Society for Neuroscience. It covers empirical research on all aspects of neuroscience. Its editor-in-chief is Marina Picciotto (Yale University). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 6.167. History The journal was established in 1981 and issues appeared monthly; as its popularity grew it switched to a biweekly schedule in 1996 and then to a weekly in July 2003. Themes Main themes Articles appear within one of the following five sections of the journal: * Cellular/Molecular * Development/Plasticity/Repair * Systems/Circuits * Behavioral/Cognitive * Neurobiology of Disease The journal has revised its sections over the years. In 2004, it added the Neurobiology of Disease section due to the growing number of papers on this subject. In January 2013, the journal split the section Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive into two sections, Systems/Circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Suspension Test
The tail suspension test (TST) is an experimental method used in scientific research to measure stress in rodents. It is based on the observation that if a mouse is subjected to short term inescapable stress then the mouse will become immobile. It is used to measure the effectiveness of antidepressant-like agents but there is significant controversy over its interpretation and usefulness. History The TST was introduced in 1985 due to the popularity of a similar test called the forced swim test (FST). However this test only recently became popular in the 2000s where data has shown that animals do show a change in behavior when injected with antidepressants. TST is more reliable when done in conjunction with other depression models such as FST, learned helplessness, anhedonia models and olfactory bulbectomy. Modeling depression Depression is a complex multi-faceted disorder with symptoms that can have multiple causes such as psychological, behavioral, and genetics. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific method for additional detail.) It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, given that cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the observation. It involves formulating hypotheses, via induction, based on such observations; the testability of hypotheses, experimental and the measurement-based statistical testing of deductions drawn from the hypotheses; and refinement (or elimination) of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings. These are ''principles'' of the scientific method, as distinguished from a definitive series of steps applicable to all scientific enterprises. Although procedures vary from one field of inquiry to another, the underlying process is frequently the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SB-399,885
SB-399885 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 9.0nM. SB-399885 and other 5-HT6 antagonists show nootropic effects in animal studies, as well as antidepressant and anxiolytic effects which are comparable to and synergistic with drugs such as imipramine and diazepam, and have been proposed as potential novel treatments for cognitive disorders such as schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit ... and Alzheimer's disease. References 5-HT6 antagonists N-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazines Sulfonamides Chlorobenzenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |