|
EKWB
EKWB (Edvard König Water Blocks), better known as EK Water Blocks, is a Slovenian company founded in 2003 that manufactures high-end computer water cooling, extreme cooling, and some air cooling components for CPUs, GPU, RAM and SSDs. Their target audience consists of custom PC building enthusiasts and professionals, and the company offers a complete range of water cooling products from radiators to tubing to water blocks. EKWB sells its products through a number of authorized distributors worldwide, but also maintains its own web store focused on direct to consumer sales. Its primary brand strategy makes use of influencer marketing to advertise products through sponsorships or review samples. History EKWB was founded in 2003 by Edvard König, who wanted a better thermal and acoustic performance for his personal computer. The company released new versions of its products, resulting in a 40% cooling performance increase from 2006 to 2011. As of 2011 EKWB was one of the three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komenda
Komenda (; german: Commenda''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, pp. 26–27.) is a village in the Upper Carniola region of Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Komenda. It includes the formerly independent settlement of Kaplja Vas ( sl, Kapla vas, german: Kaplawas). Name Komenda was first mentioned in written sources in 1147–54 as ''de sancto Petro'' (and as ''hospitale Sancti Petri'' in 1296, ''in der pharren von Sand Peter'' in 1322, and ''comendator ad S. Petrum'' in 1446). The name of the village is identical to the Slovene common noun ''komenda'' 'commandry', referring to a property and residence owned by the Knights Hospitaller from 1223 to 1872. The noun ''komenda'' is borrowed (probably via German ''Kommende'') from Medieval Latin ''commenda'' 'entrusted property'. In the past the German name was ''Commenda''. Mass grave Komenda is the site of a mass g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Block
A water block is the watercooling equivalent of a heatsink. It is a type of plate heat exchanger and can be used on many different computer components, including the central processing unit (CPU), GPU, PPU, and northbridge chipset on the motherboard. There are also Monoblocks on the market that are mounted on PC motherboards and cover the CPU and its power delivery VRM's (Voltage Regulator Module) that surround the CPU socket area. It consists of at least two main parts; the "base",which is the area that makes contact with the device being cooled and is usually manufactured from metals with high thermal conductivity such as aluminum or copper. The second part, the "top" ensures the water is contained safely inside the water block and has connections that allow hosing to connect it with the water cooling loop. The top can be made of the same metal as the base, transparent Perspex, Delrin, Nylon, or HDPE. Most newer high-end water blocks also contain mid-plates which serve to add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the computer case, case, central processing unit (CPU), Random-access memory, random access memory (RAM), Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, Computer speakers, speakers and motherboard. By contrast, software is the set of instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware is so-termed because it is "Hardness, hard" or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is "soft" because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or Instruction (computing), instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although Digital electronics, other systems exist with only hardware. Von Neumann architecture The template for all modern computers is the Von Neumann architecture, detailed in a First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, 1945 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Regulator Module
A voltage regulator module (VRM), sometimes called processor power module (PPM), is a buck converter that provides microprocessor and chipset the appropriate supply voltage, converting , or to lower voltages required by the devices, allowing devices with different supply voltages be mounted on the same motherboard. On personal computer (PC) systems, the VRM is typically made up of power MOSFET devices. Overview Most voltage regulator module implementations are soldered onto the motherboard. Some processors, such as Intel Haswell and Ice Lake CPUs, feature some voltage regulation components on the same CPU package, reduce the VRM design of the motherboard; such a design brings certain levels of simplification to complex voltage regulation involving numerous CPU supply voltages and dynamic powering up and down of various areas of a CPU. A voltage regulator integrated on-package or on-die is usually referred to as ''fully integrated voltage regulator'' (''FIVR'') or simply a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threadripper
Ryzen ( ) is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and marketed by AMD for desktop, mobile, server, and embedded platforms based on the Zen microarchitecture. It consists of central processing units (CPUs) marketed for mainstream, enthusiast, server, and workstation segments and accelerated processing units (APUs) marketed for mainstream and entry-level segments and embedded systems applications. AMD announced a new series of processors on December 13, 2016, named "Ryzen", and delivered them in Q1 2017, the first of several generations. The 1000 series featured up to eight cores and 16 threads, with a 52% instructions per cycle (IPC) increase over their prior CPU products. The second generation of Ryzen processors, the Ryzen 2000 series, released in April 2018, featured the Zen+ microarchitecture, a 12 nm process (GlobalFoundries); the aggregate performance increased 10% (of which approximately 3% was IPC, 6% was frequency); most importantly, Zen+ fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epyc
Epyc is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and sold by AMD, based on the company's Zen microarchitecture. Introduced in June 2017, they are specifically targeted for the server and embedded system markets. Epyc processors share the same microarchitecture as their regular desktop-grade counterparts, but have enterprise-grade features such as higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, and larger cache memory. They also support multi-chip and dual-socket system configurations by using the Infinity Fabric interconnect. History In March 2017, AMD announced plans to re-enter the server market with a platform based on the Zen microarchitecture, codenamed Naples, and officially revealed it under the brand name Epyc in May. That June, AMD officially launched Epyc 7001 series processors, offering up to 32 cores per socket, and enabling performance that allowed Epyc to be competitive with the competing Intel Xeon product line. Two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 2066
LGA 2066, also called ''Socket R4'', is a CPU socket by Intel that debuted with Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X processors in June 2017. It replaces Intel's LGA 2011-3 (R3) in the performance, high-end desktop and Workstation platforms (based on the X299 "Basin Falls" and C422 chipsets), while LGA 3647 (Socket P) replaces LGA 2011-3 (R3) in the server platforms based on Skylake-SP (Xeon "Purley"). Compatible processors High-End Desktop (HEDT) All of these CPUs require the Intel X299 chipset to work. So, the C422 chipset is strictly limited to work with workstation processors only. Kaby Lake-X Kaby Lake-X processors were discontinued in May 2018. Starting October 2019, BIOS In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ... updates for most of the X299-based motherboards removed supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
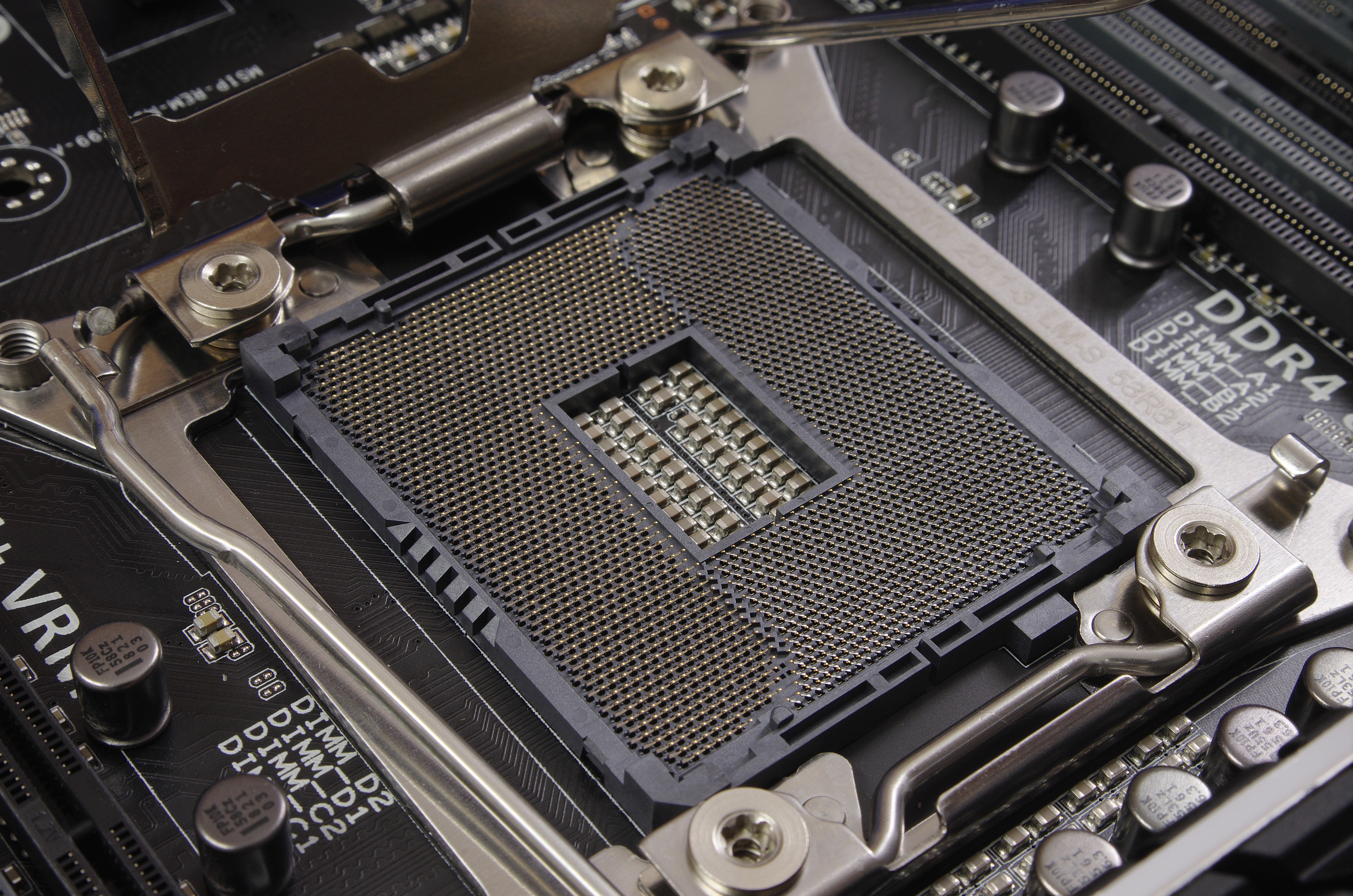
LGA 2011
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor. The LGA 2011 socket uses QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM memory channels with up to three unbuffered or registered DIMMs per channel, as well as up to 40 PCI Express 2.0 or 3.0 lanes. LGA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than having separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
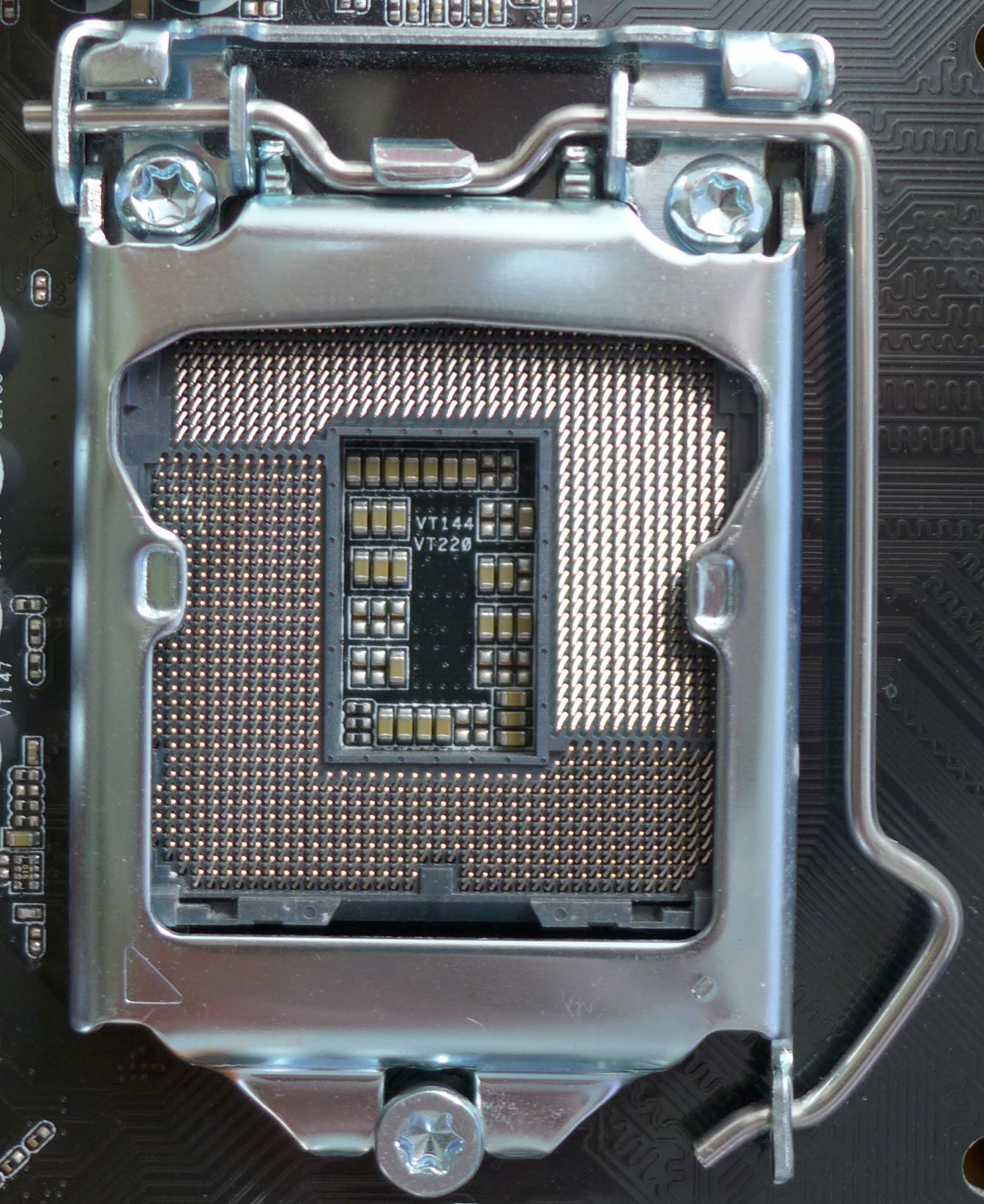
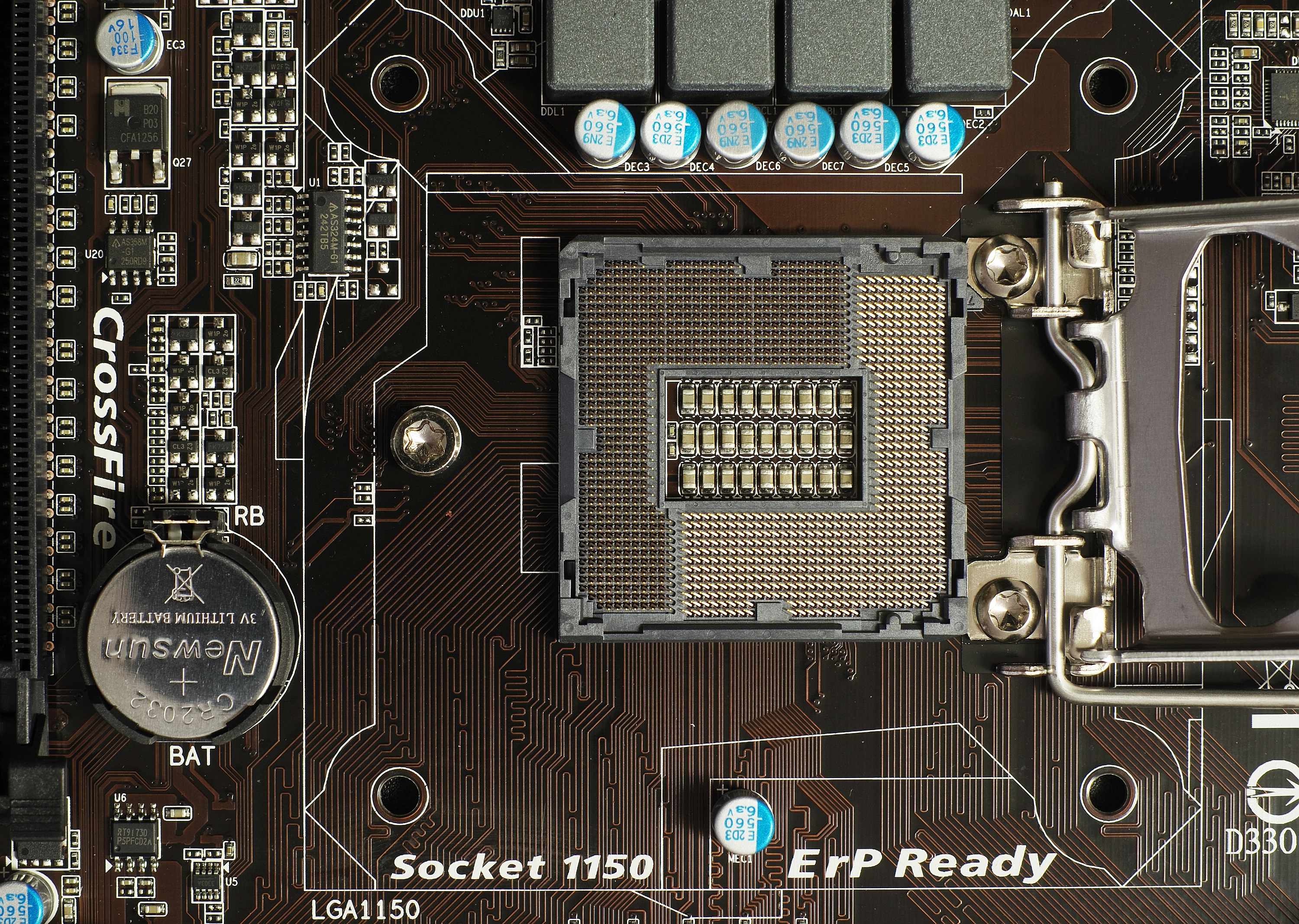
LGA 1150
LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for CPUs built on the Haswell microarchitecture. This socket is also used by the Haswell's successor, Broadwell microarchitecture. It is the successor of LGA 1155 and was itself succeeded by LGA 1151 in 2015. Most motherboards with the LGA 1150 socket support varying video outputs (VGA, DVI or HDMI depending on the model) and Intel Clear Video Technology. Full support of Windows on LGA 1150 platform starts on Windows 7 - official Windows XP support is limited to selected CPUs, chipsets and only for embedded and industrial systems. Intel's Platform Controller Hub (PCH) for the LGA 1150 CPUs is codenamed Lynx Point. Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150 use the Intel C222, C224, and C226 chipsets. Heatsink The 4 holes for fastening the heatsink to the motherboard are placed in a square with a lateral length of 75&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge (2nd Gen) and Ivy Bridge (3rd Gen) microarchitectures. It is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as ''Socket H'') and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013. Along with selected variations of LGA 2011 socket, it was the last Intel socket to fully support Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008. LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compatible with each other since they have different socket notches. LGA 1155 al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1156
LGA 1156 (land grid array 1156), also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155. The last processors supporting it ceased production in 2011. LGA 1156, along with LGA 1366, were designed to replace LGA 775. Whereas LGA 775 processors connect to a northbridge using the Front Side Bus, LGA 1156 processors integrate the features traditionally located on a northbridge within the processor itself. The LGA 1156 socket allows the following connections to be made from the processor to the rest of the system: * PCI-Express 2.0 ×16 for communication with a graphics card. Some processors allow this connection to be divided into two ×8 lanes to connect two graphics cards. Some motherboard manufacturers use Nvidia's NF200 chip to allow even more graphics cards to be used. * DMI for communication with the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). This consists of a PCI-Express 2.0 ×4 connection. * FDI for communication with the PCH. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |