|
EF-Ts
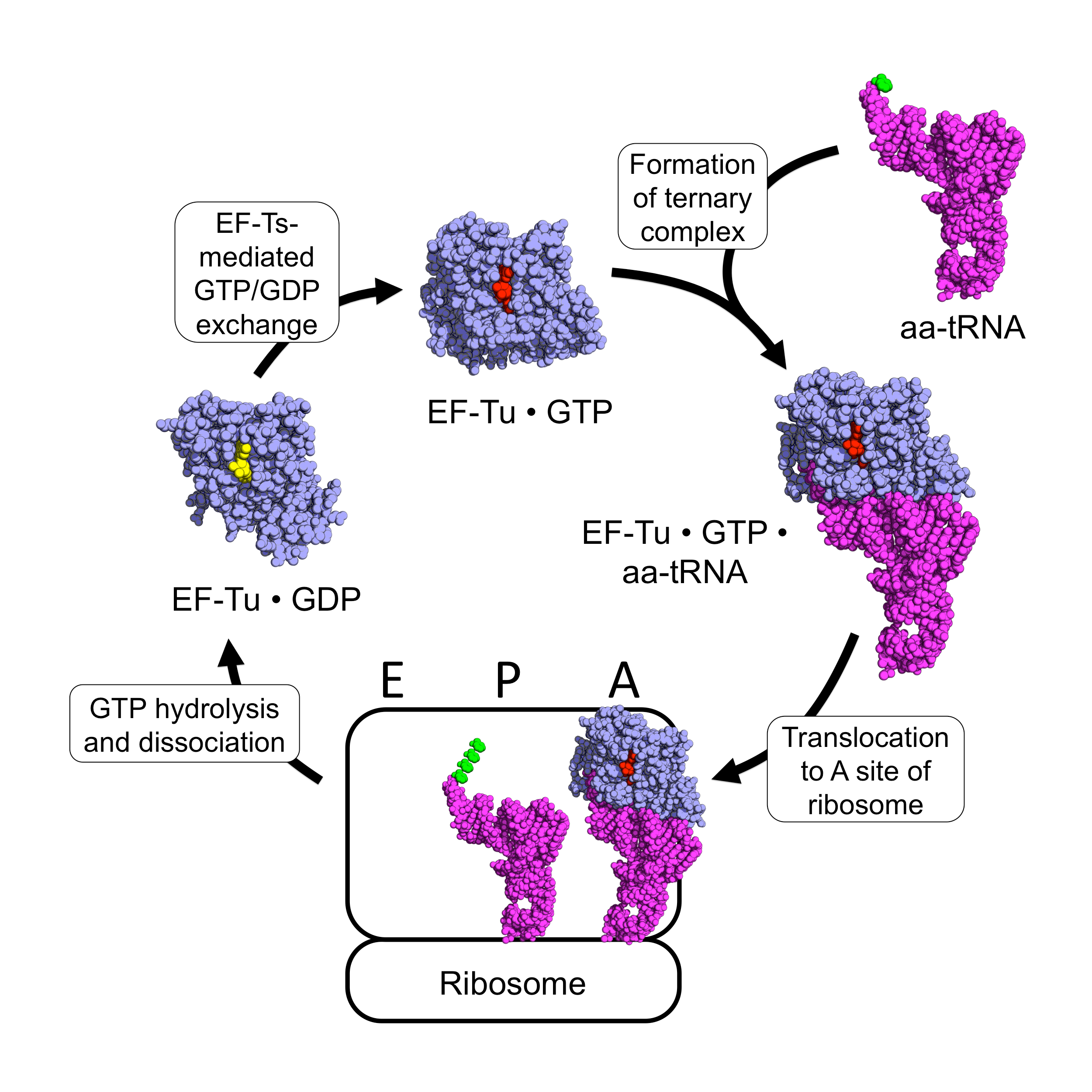
EF-Ts (elongation factor thermo stable) is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochrondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B. EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable), catalyzing the release of guanosine diphosphate from EF-Tu. This enables EF-Tu to bind to a new guanosine triphosphate molecule, release EF-Ts, and go on to catalyze another aminoacyl tRNA addition. Structure The protein Qβ-Replicase is a tetrameric protein, meaning it contains four subunits. These subunits are the two elongation factors, EF-Tu & EF-Ts, the ribosomal protein subunit S1, and the RNA dependent RNA polymerase β-subunit. The two elongation factors form a heterodimer structure known as The Elongation factor complex, which is necessary for the polymerization activity of the RDRP β-Subunit. Its secondary structural components consists of α-helices, β-sheets and β-barrels. EF-Ts comprises the maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
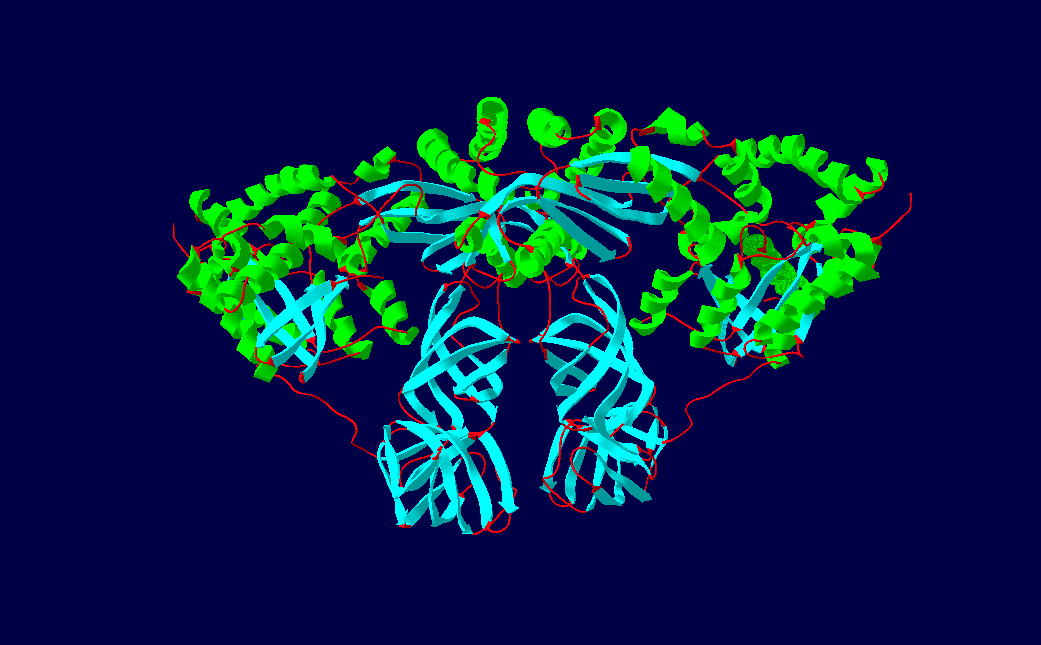
EF-Ts Dimer Structure
EF-Ts (elongation factor thermo stable) is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochrondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B. EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable), catalyzing the release of guanosine diphosphate from EF-Tu. This enables EF-Tu to bind to a new guanosine triphosphate molecule, release EF-Ts, and go on to catalyze another aminoacyl tRNA addition. Structure The protein Qβ-Replicase is a tetrameric protein, meaning it contains four subunits. These subunits are the two elongation factors, EF-Tu & EF-Ts, the ribosomal protein subunit S1, and the RNA dependent RNA polymerase β-subunit. The two elongation factors form a heterodimer structure known as The Elongation factor complex, which is necessary for the polymerization activity of the RDRP β-Subunit. Its secondary structural components consists of α-helices, β-sheets and β-barrels. EF-Ts comprises the maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF-Tu
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM. As a family of elongation factors, EF-Tu also includes its eukaryotic and archaeal homolog, the alpha subunit of eEF-1 (EF-1A). Background Elongation factors are part of the mechanism that synthesizes new proteins through translation in the ribosome. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) carry the individual amino acids that become integrated into a protein sequence, and have an anticodon for the specific amino acid that they are charged with. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information that encodes the primary structure of a protein, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Elongation Factors
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function at the ribosome, during protein synthesis, to facilitate translational elongation from the formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. Most common elongation factors in prokaryotes are EF-Tu, EF-Ts, EF-G. Bacteria and eukaryotes use elongation factors that are largely homologous to each other, but with distinct structures and different research nomenclatures. Elongation is the most rapid step in translation. In bacteria, it proceeds at a rate of 15 to 20 amino acids added per second (about 45-60 nucleotides per second). In eukaryotes the rate is about two amino acids per second (about 6 nucleotides read per second). Elongation factors play a role in orchestrating the events of this process, and in ensuring the high accuracy translation at these speeds. Nomenclature of homologous EFs In addition to their cytoplasmic machinery, eukaryotic mitochondria and plastids have their own translation ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Elongation Factors
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function at the ribosome, during protein synthesis, to facilitate translational elongation from the formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. Most common elongation factors in prokaryotes are EF-Tu, EF-Ts, EF-G. Bacteria and eukaryotes use elongation factors that are largely homologous to each other, but with distinct structures and different research nomenclatures. Elongation is the most rapid step in translation. In bacteria, it proceeds at a rate of 15 to 20 amino acids added per second (about 45-60 nucleotides per second). In eukaryotes the rate is about two amino acids per second (about 6 nucleotides read per second). Elongation factors play a role in orchestrating the events of this process, and in ensuring the high accuracy translation at these speeds. Nomenclature of homologous EFs In addition to their cytoplasmic machinery, eukaryotic mitochondria and plastids have their own translation ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elongation Factor P
EF-P (elongation factor P) is an essential protein that in bacteria stimulates the formation of the first peptide bonds in protein synthesis. Studies show that EF-P prevents ribosomes from stalling during the synthesis of proteins containing consecutive prolines. EF-P binds to a site located between the binding site for the peptidyl tRNA ( P site) and the exiting tRNA ( E site). It spans both ribosomal subunits with its amino-terminal domain positioned adjacent to the aminoacyl acceptor stem and its carboxyl-terminal domain positioned next to the anticodon stem-loop of the P site-bound initiator tRNA. The EF-P protein shape and size is very similar to a tRNA and interacts with the ribosome via the exit “E” site on the 30S subunit and the peptidyl-transferase center (PTC) of the 50S subunit. EF-P is a translation aspect of an unknown function, therefore It probably functions indirectly by altering the affinity of the ribosome for aminoacyl-tRNA, thus increasing their reactivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSFM
Elongation factor Ts, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSFM'' gene. It is an EF-Ts EF-Ts (elongation factor thermo stable) is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochrondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B. EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu (elongatio ... homolog. References Further reading * * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEF-1
eEF-1 are two eukaryotic elongation factors. It forms two complexes, the EF-Tu homolog EF-1A and the EF-Ts homolog EF-1B, the former's guanide exchange factor. Both are also found in archaea. Structure The nomenclature for the eEF-1 subunits have somewhat shifted around circa 2001, as it was recognized that the EF-1A and EF-1B complexes are to some extent independent of each other. Components as currently recognized and named include: The precise manner eEF1B subunit attaches onto eEF1A varies by organ and species. eEF1A also binds actin. Other species Various species of green algae, red algae, chromalveolates, and fungi lack the EF-1α gene but instead possess a related gene called EFL (elongation factor-like). Although its function has not been studied in depth, it appears to be similar to EF-1α. , only two organisms are known to have both EF-1α and EFL: the fungus '' Basidiobolus'' and the diatom ''Thalassiosira''. The evolutionary history of EFL is unclear. It may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF-G
EF-G (elongation factor G, historically known as translocase) is a prokaryotic elongation factor involved in protein translation. As a GTPase, EF-G catalyzes the movement (translocation) of transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) through the ribosome. Structure Encoded by the ''fusA'' gene on the ''str'' operon, EF-G is made up of 704 amino acids that form 5 domains, labeled Domain I through Domain V. Domain I may be referred to as the G-domain or as Domain I(G), since it binds to and hydrolyzes guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Domain I also helps EF-G bind to the ribosome, and contains the N-terminal of the polypeptide chain. Domain IV is important for translocation, as it undergoes a significant conformational change and enters the A site on the 30S ribosomal subunit, pushing the mRNA and tRNA molecules from the A site to the P site. The five domains may be also separated into two super-domains. Super-domain I consists of Domains I and II, and super-domain II consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. This unsaturated arrangement means the bicyclic molecule is planar. Properties Guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA, and uracil only in RNA. Guanine has two tautomeric forms, the major keto form (see figures) and rare enol form. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. In cytosine, the amino group acts as the hydrogen bond donor and the C-2 carbonyl and the N-3 amine as the hydrogen-bond acceptors. Guanine has the C-6 carbonyl group that acts as the hydrogen bond acceptor, while a group at N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs) are proteins that stimulate the exchange (replacement) of nucleoside diphosphates for nucleoside triphosphates bound to other proteins. Function Many cellular proteins cleave (hydrolyze) nucleoside triphosphates–adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or guanosine triphosphate (GTP)–to their diphosphate forms ( ADP and GDP) as a source of energy and to drive conformational changes. These changes in turn affect the structural, enzymatic, or signalling properties of the protein. Nucleotide exchange factors actively assist in the exchange of depleted nucleoside diphosphates for fresh nucleoside triphosphates. NEFs are specific for the nucleotides they exchange (ADP or GDP, but not both) and are often specific to a single protein or class of proteins with which they interact. See also * Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase * Guanine nucleotide exchange factor Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine. GDP is the product of GTP dephosphorylation by GTPases, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction. GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate. See also * DNA *Guanosine triphosphate *Nucleoside *Nucleotide *Oligonucleotide *RNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanosine phosphate2 Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purines Pyrophosphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)