|
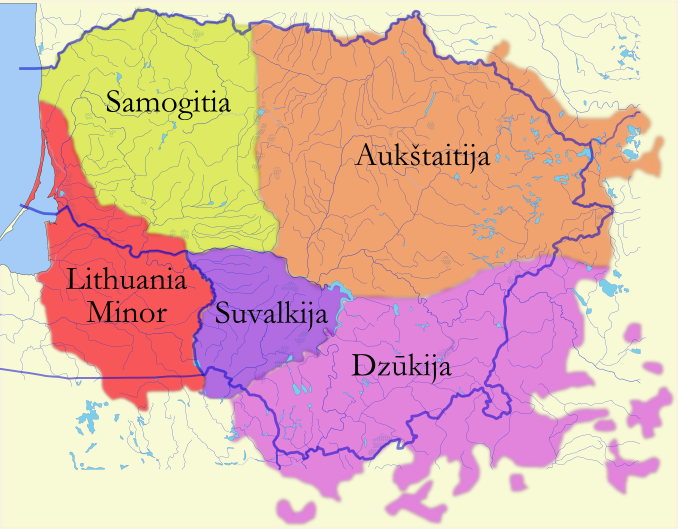
Dzūkian Dialect
Dzūkian dialect ( lt, dzūkų tarmė), known in academic works as Southern Aukštaitian dialect ( lt, pietų aukštaičių patarmė), is one of the three main sub-dialects of the Aukštaitian dialect of Lithuanian language. Dzūkian dialect is spoken in Dzūkija, southern Lithuania. Its most distinctive feature is replacing ''t'', ''d'' before ''i'', ''į'', ''y'', ''ie'' and ''č'', ''dž'' with ''c'' and ''dz'' () instead of ( – just, ( instead of – size, instead of – to braid, instead of – guests). Since the region borders Slavic lands, the dialect has many Slavic loanwords and barbarism Barbarism, barbarity, or barbarous may refer to: * Barbarism (linguistics), a non-standard word, expression, or pronunciation ** Hybrid words, formerly called "barbarisms" * Any society construed as barbarian ** Barbarian invasions, a period of m ...s. References * Lithuanian dialects {{Ie-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Dialects Of Lithuanian Language
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aukštaitian Dialect
Aukštaitian ( lt, Aukštaičių tarmė) is one of the dialects of the Lithuanian language, spoken in the ethnographic regions of Aukštaitija, Dzūkija and Suvalkija. It became the basis for the standard Lithuanian language. Classification Revised classification of the dialects, proposed in 1965 by linguists Zigmas Zinkevičius and Aleksas Girdenis, divides the Aukštaitian dialect into three sub-dialects based on pronunciation of the mixed diphthongs ''an'', ''am'', ''en'', ''em'' and the ogonek vowels ''ą'' and ''ę'': Western Aukštaitianmost similar to standard Lithuanianpreserves both the diphthongs and the vowels. It is further subdivided into two sub-dialects: * The Kaunas sub-dialect is spoken mostly in Suvalkija. This sub-dialect separates long and short vowels pretty well and properly stresses word endings. * The Šiauliai sub-dialect is spoken in a strip between Samogitia and Aukštaitija. This sub-dialect almost always shortens unaccented long vowels (''dum� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 speakers elsewhere. Lithuanian is closely related to the neighbouring Latvian language. It is written in a Latin script. It is said to be the most conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languages, Lithuanian is conservative in some aspects of its grammar and phonology, retaining archaic features otherwise found only in ancient languages such as Sanskrit (particularly its early form, Vedic Sanskrit) or Ancient Greek. For this reason, it is an important source for the reconstruction of the Proto-Indo-Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzūkija
Dzūkija or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population (mostly rural farmers) and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit. Traditionally, Alytus is regarded as the capital of the region, although it is not the largest city in Dzūkija, this title corresponding to the Lithuanian capital, Vilnius. The region has a significant Polish minority of 180 thousand people or around 20% of the region's total population. Geography Dzūkija is situated in southeastern Lithuania, and consists of Alytus County and southern Vilnius County. Historically, it extended into what is now northeastern Poland (Podlaskie Voivodeship) and northwestern Belarus (Grodno Region). Large parts of Dzūkija have light sandy soil, unsuited for agriculture. Therefore, the region is densely covered with pine forests, one of which is Dainava Forest, the largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania shares land borders with Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and Russia to the southwest. It has a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west on the Baltic Sea. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.8 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities are Kaunas and Klaipėda. Lithuanians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, one of only a few living Baltic languages. For millennia the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united by Mindaugas, Monarchy of Lithuania, becoming king and founding the Kingdom of Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between them � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because they share an etymological origin, and calques, which involve translation. Loanwords from languages with different scripts are usually transliterated (between scripts), but they are not translated. Additionally, loanwords may be adapted to phonology, phonotactics, orthography, and morphology of the target language. When a loanword is fully adapted to the rules of the target language, it is distinguished from native words of the target language only by its origin. However, often the adaptation is incomplete, so loanwords may conserve specific features distinguishing them from native words of the target language: loaned phonemes and sound combinations, partial or total conserving of the original spelling, foreign plural or case forms or indecli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarism (linguistics)
A barbarism is a nonstandard word, expression or pronunciation in a language, particularly one regarded as an error in morphology, while a ''solecism'' is an error in syntax. The label was originally applied to mixing Ancient Greek or Latin with other languages, but expanded to indicate any inappropriate words or expressions in classical studies and eventually to any language considered unpolished or rude. The term is used mainly for the written language. With no accepted technical meaning in modern linguistics, the term is little used by contemporary descriptive scientists. Classical The word ''barbarism'' (Greek: βαρβαρισμός) was originally used by the Greeks for foreign terms used in their language and is related to the word "barbarian". The first Latin grammarian to use the word ''barbarolexis'' was Marius Plotius Sacerdos in the 3rd century AD. Cominianus provides a definition. Charisius, in the 4th century, clearly excluded Greek words from being considered ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |